In this note we will consider the anatomy of the penis.
The penis is an organ of the male reproductive system, which serves to excrete urine and deliver seminal fluid to the genital tract of a woman.
Due to the significant blood supply and innervation, this organ has a high sensitivity and the ability to increase in volume, passing into an erect state.
The penis consists of several parts:
1. The root (radix penis), which is the posterior part that attaches to the pubic bones
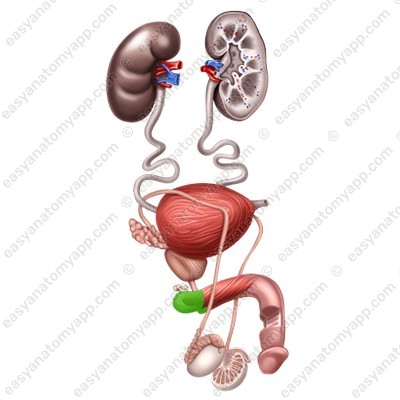
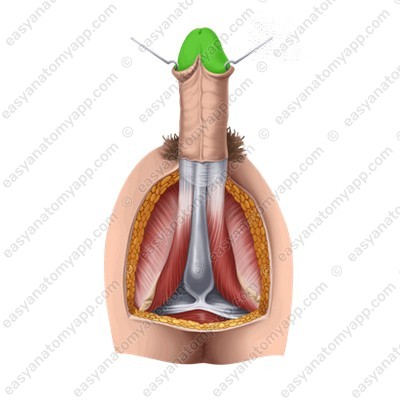
2. The glans (glans penis), which is the anterior part of the penis
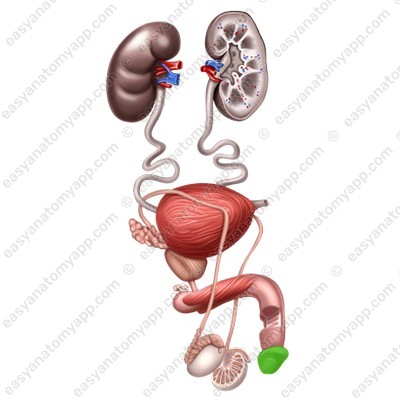
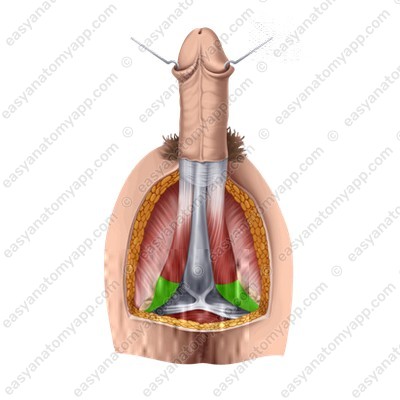
3. The body (corpus penis), which is located between the root and the glans
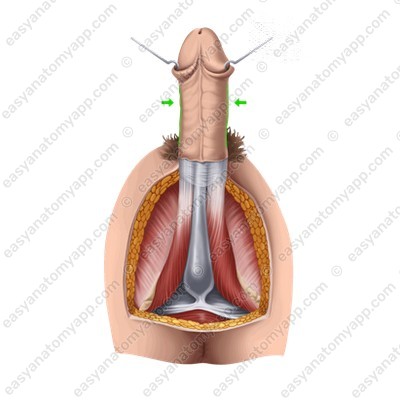
4. The dorsum (dorsum penis), which is the superior surface of the body
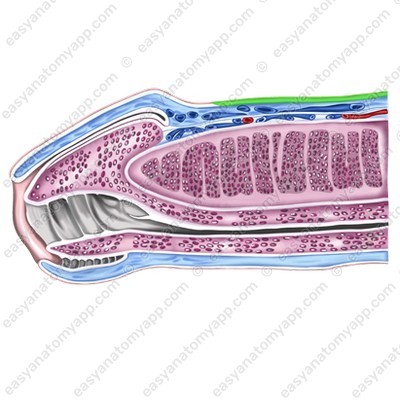
The glans has an expanded part on the flanks and in the dorsum area, it is called the crown (corona glandis).

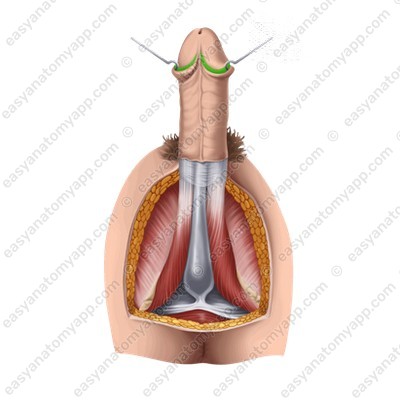
Behind the crown, the head narrows and forms the neck (collum glandis).
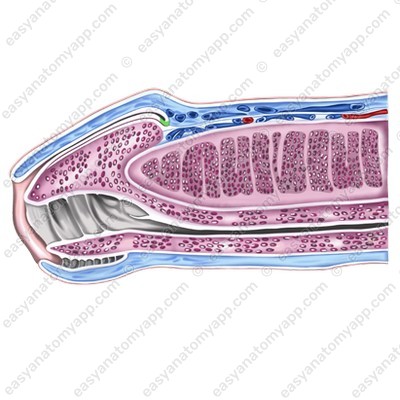
The external urethral orifice (ostium urethrae externum) is located on the superior part of the glans of the penis.
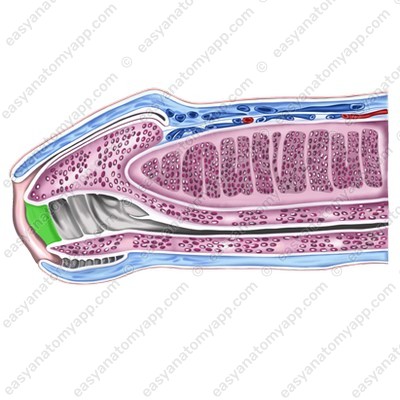
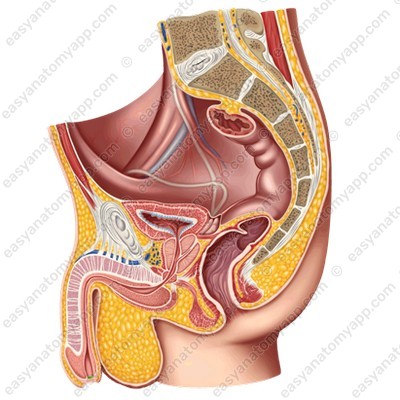
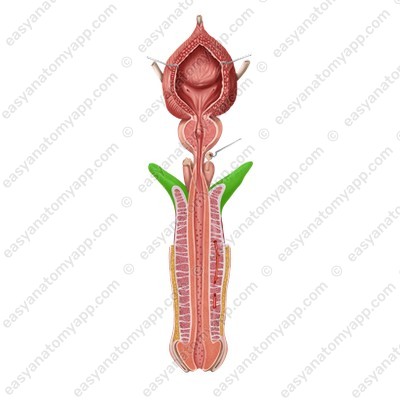
The penis is covered with skin. It is very thin and has no hair. The skin of the penis may fold and easily stretch during an erection. In the area of the base of the glans, the fold is more expressed, it is called the foreskin (preputium).
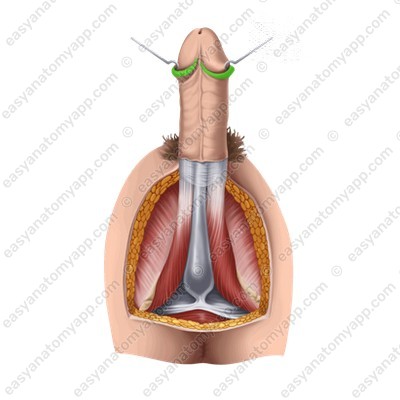
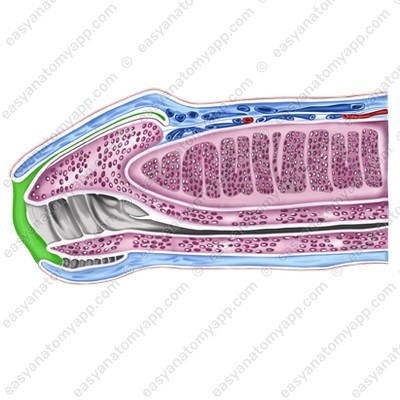
Inferiorly, the foreskin is connected to the skin of the frenulum (frenulum preputii),

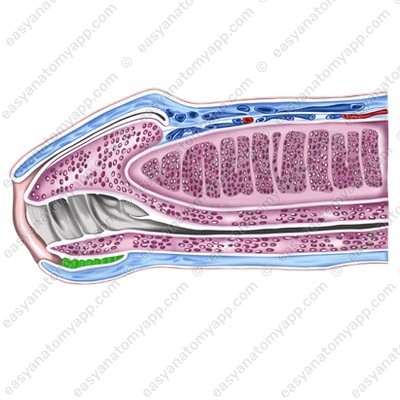
from which the raphe (raphe) goes down.

It goes to the scrotum and perineum.
The foreskin contains a large number of small preputial glands (glandulae preputiales), which secrete a preputial lubricant called smegma (smegma preputii). This secretion is collected in the space between the glans and the foreskin.
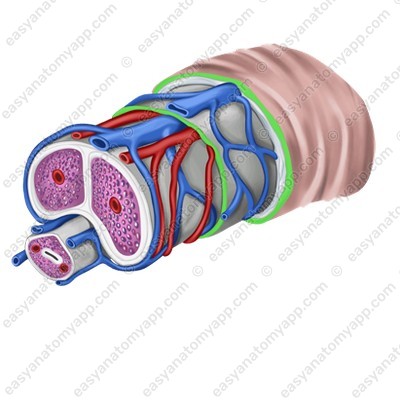
The penis is formed by erectile structures, that is, structures capable of erection. They include:
1. Two corpora cavernosa (corpora cavernosa penis)
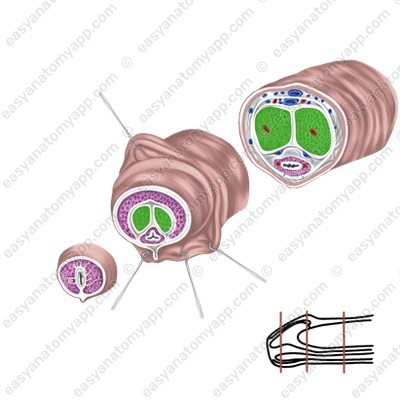
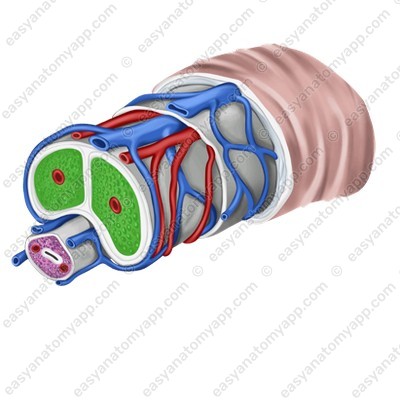
2. One corpus spongiosum (corpus spongiosum penis)

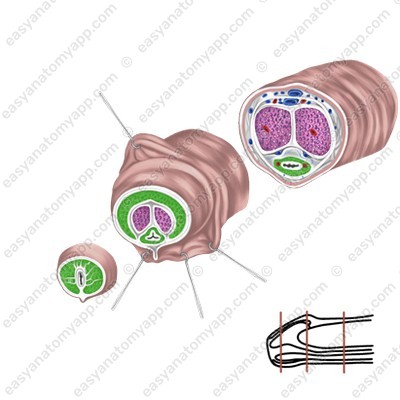

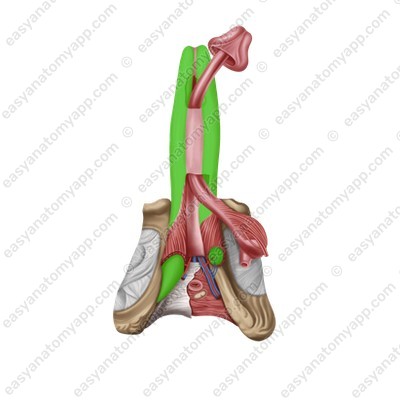
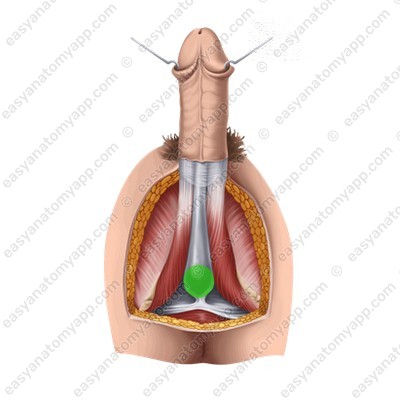
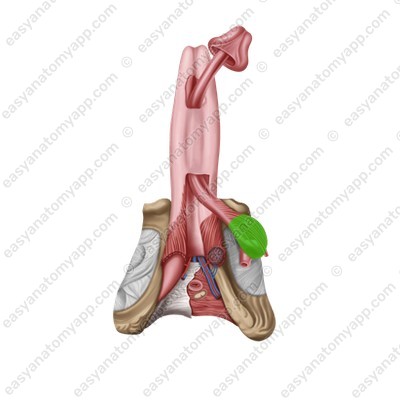
Corpora cavernosa are cellular structures that consist of capillaries. The posterior ends of the corpora cavernosa form crura (crura penis), which attach to the inferior branches of the pubic bones, and the anterior ends are fused with the glans of the organ.

The corpus spongiosum lies in the groove between the corpora cavernosa. It has a similar structure, but a smaller diameter and expanded ends, which form the bulb of the penis (bulbus penis), posteriorly, and the glans anteriorly.
The urethra passes through the thickness of the corpus spongiosum.
Erectile structures (except the glans) are covered with the tunica albuginea (tunica albuginea).
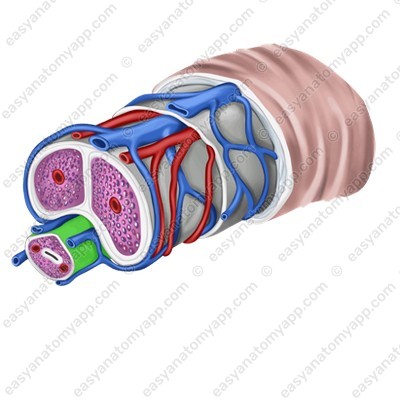
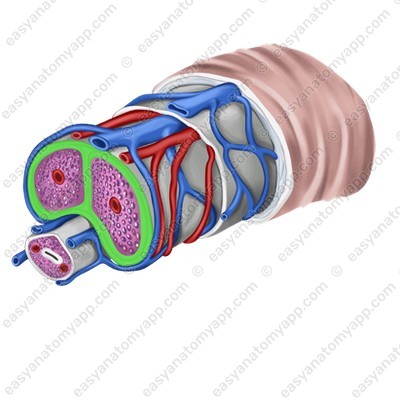
Connective tissue septa, which divide the tissue into cells, arise from it into the thickness of the organ.
These cells are lined with endothelium, and a helicine artery (a. helicina) opens into each of the cells.
During arousal, this artery straightens, the vessel fills with blood, and the penis goes into an erect state.
The erectile structures are also covered with the deep fascia (fascia penis profunda), which in turn is covered with the superficial fascia and a thin layer of adipose tissue.
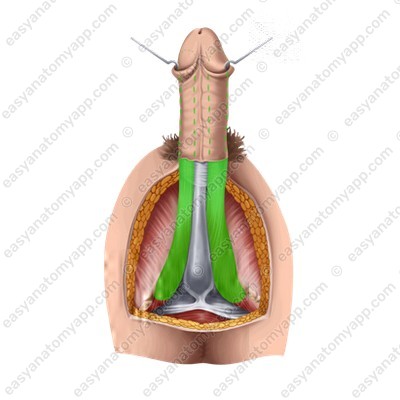
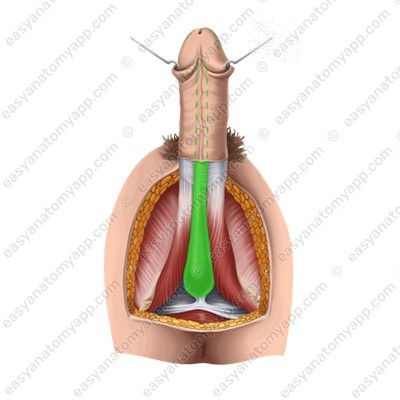
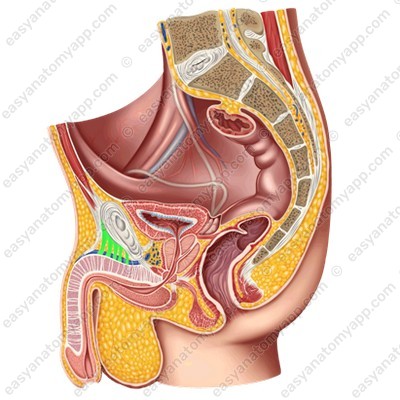
The supporting structures of the penis are represented by two ligaments.
The suspensory ligament of the penis (lig. suspensorium penis), which is the continuation of the superficial abdominal fascia.
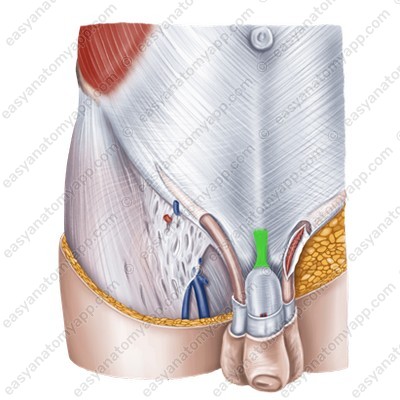
The deep (or fundiform) ligament (lig. fundiforme penis), which arises from the pubic symphysis and is woven into the tunica albuginea of the corpora cavernosa.
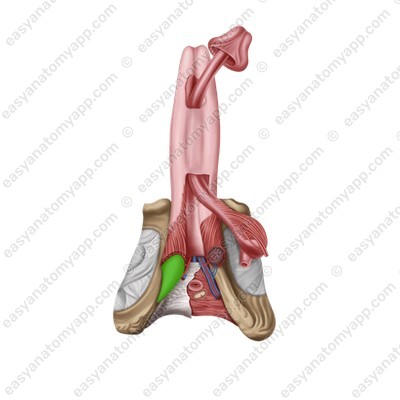
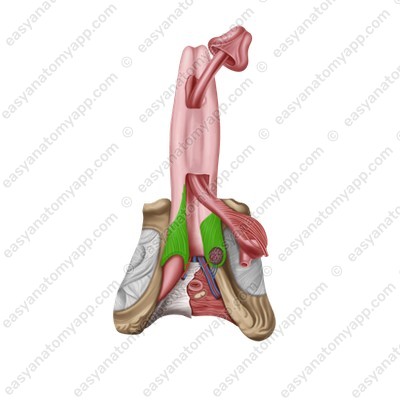
There are two muscles located in the penis area.
The paired bulbospongiosus muscle (m. bulbospongiosus), which restricts the drainage of venous blood from the corpora cavernosa during erection and squeezes sperm out of the urethra during ejaculation.
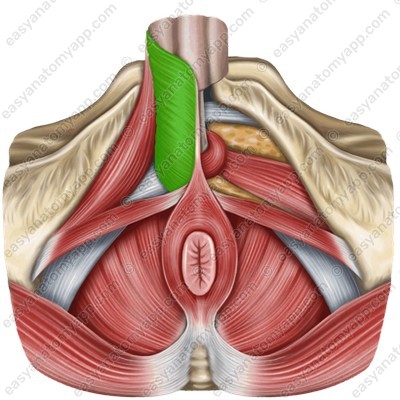

The paired ischiocavernosus muscle (m. ischiocavernosus), which straightens the penis.

(m. ischiocavernosus)
Blood supply
Arterial blood enters the skin of the penis from the anterior scrotal branches (from the external pudendal artery) and dorsal arteries of the penis (from the internal pudendal artery).
The corpus spongiosum is supplied with blood by the bulbo-urethral artery (from the internal pudendal artery), and the corpora cavernosa are supplied with blood by the deep and dorsal arteries of the penis (from the internal pudendal artery).
Venous drainage
Venous blood drains through the dorsal veins of the penis into the vesical venous plexus and the internal pudendal vein.
Innervation
Innervation is carried out by the dorsal nerve of the penis (somatic), the inferior hypogastric plexus (sympathetic), and the pelvic splanchnic nerves (parasympathetic).
Anatomy of the penis
- Penis
- penis
- Root of the penis
- radix penis
- Glans penis
- glans penis
- Body of the penis
- corpus penis
- Dorsum of the penis
- dorsum penis
- Crown of the glans
- corona glandis
- Neck of the glans
- collum glandis
- External urethral orifice
- ostium urethrae externum
- Corpora cavernosa
- corpora cavernosa penis
- Corpus spongiosum
- corpus spongiosum penis
- Crura of the penis
- crura penis
- Common tunica albuginea
- tunica albuginea corporu mcavernosorum penis
- Septum penis
- sepum penis
- Bulb of the penis
- bulbus penis
- Tunica albuginea
- tunica albuginea corporum spongiosum penis
- Deep fascia
- fascia penis profunda
- Foreskin
- preputium
- Frenulum
- frenulum preputii
- Raphe
- raphe
- Sebaceous glands
- glandulae preputiales
- Smegma
- smegma preputii
- Deep artery of the penis
- aa. profundae penis
- Dorsal artery of the penis
- aa. dorsalis penis
- Cavernous veins
- vv. cavernosae
- Deep vein of the penis
- vv. profundae penis
- Dorsal vein of the penis
- vv. dorsalis penis
- Pudendal nerve
- n. pudendus


