In this note, we will consider the anatomy of the vagina (vagina).

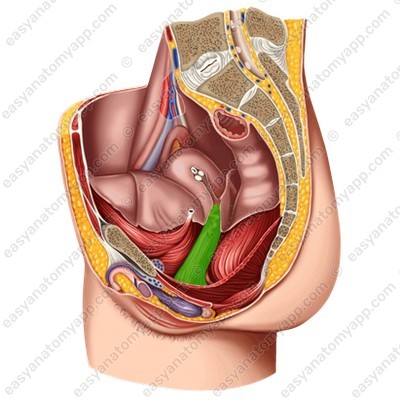
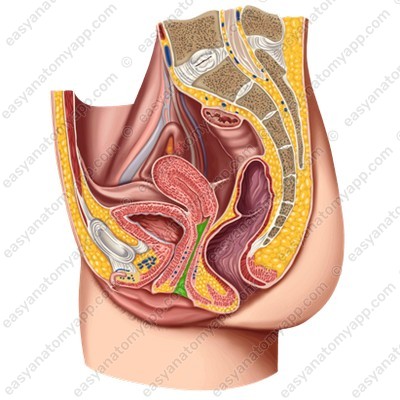
It is an organ of the female reproductive system.
The vagina connects the uterus with the external genitals; it serves for sexual intercourse, menstrual blood excretion, and fetal birth.
Holotopy
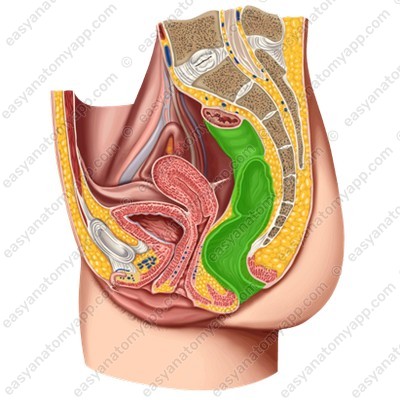
This organ is located in the pelvic cavity.
Skeletotopy
The vagina is located at the level between the third sacral and first coccygeal vertebrae (S3-Co1).
Syntopy
Let’s consider which anatomical structures and organs adhere to the vagina.
- The rectum is located posteriorly.
- Anteriorly to the vagina, there is the urethra and the fundus of the bladder.

- The venous vaginal plexus and the pelvic part of the ureter are located laterally from the vagina in the cellular tissue.
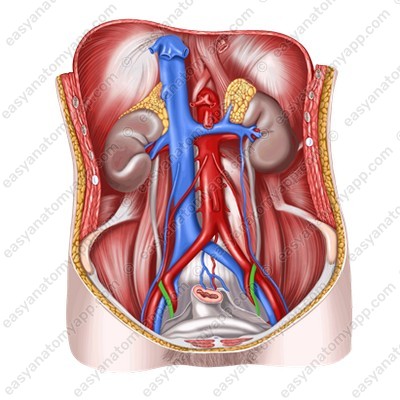
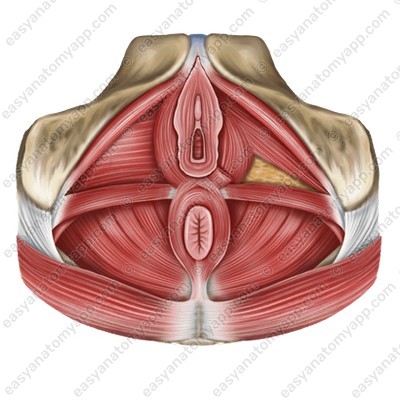
Inferiorly, the vagina passes through the perineum.
Macroscopic structure
The vagina has two walls:
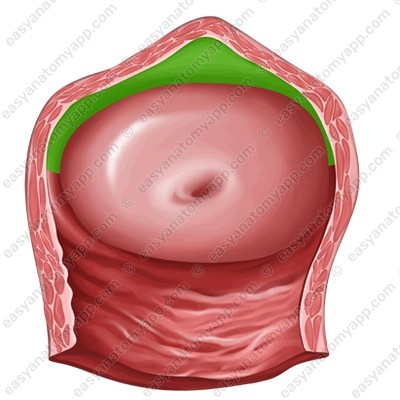
- The anterior wall (paries anterior)
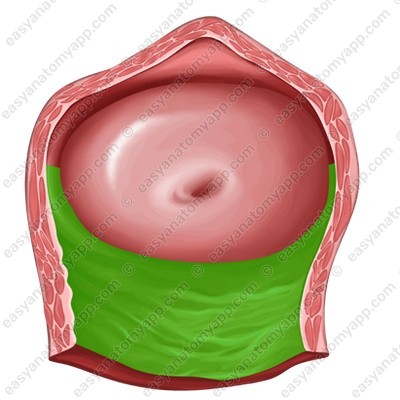
- The posterior wall (paries posterior)
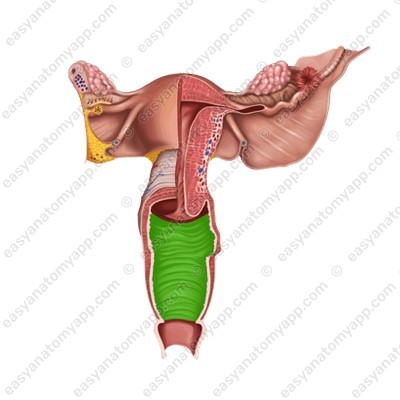
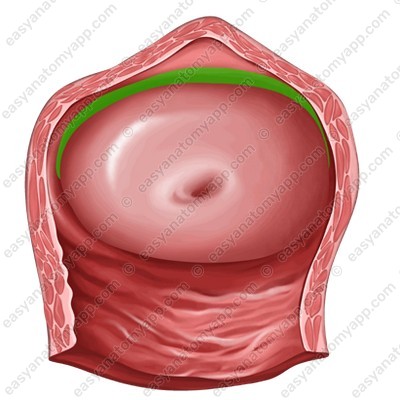
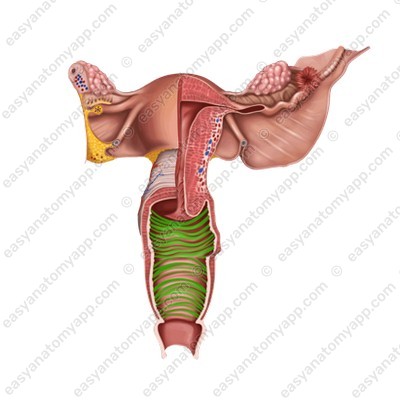
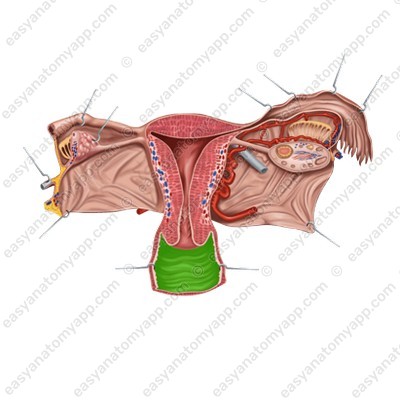
The vaginal fornix (fornix vaginae) is the space between the cervix of the uterus and the walls of the vagina. The fornix has 4 parts:
1. The anterior part (pars anterior)

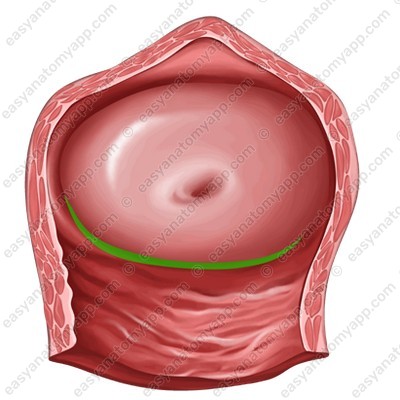
2. The posterior part (pars posterior), which is the deepest
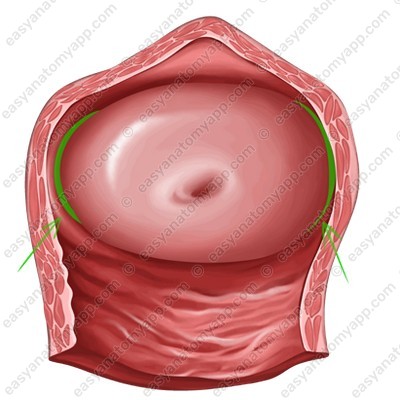
3. Lateral parts (partes laterales)
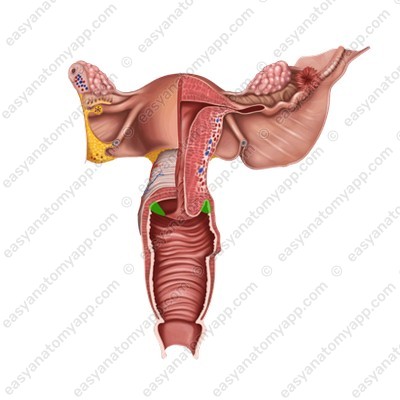
The vaginal orifice (ostium vaginae) opens into the vestibule of the vagina.
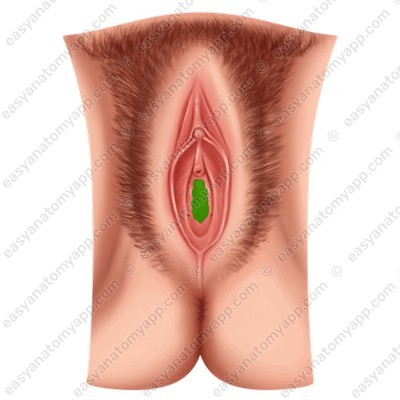

(vestibulum vaginae)
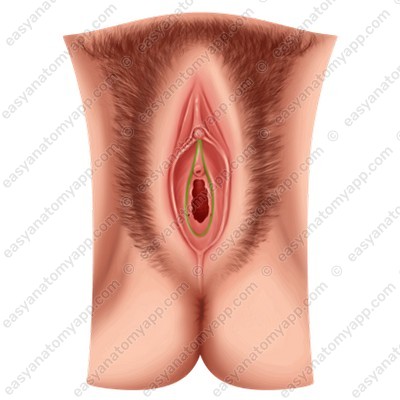
In virgins, it is covered by a fold of the mucous membrane called the hymen (hymen).
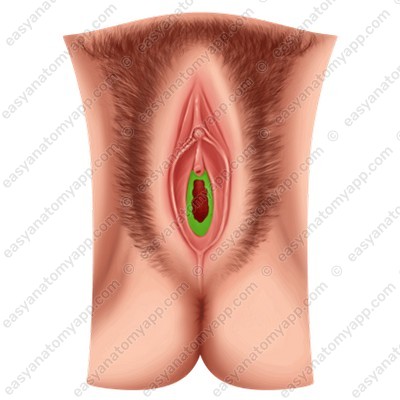
The vaginal wall consists of several layers.
The mucous membrane (tunica mucosa).
It is lined with a non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and does not contain glands. This membrane forms a number of rugae.
- Transverse vaginal rugae (rugae vaginales).
- Closer to the median line, the transverse vaginal rugae become higher and form longitudinally oriented columns of rugae (columnae rugarum).
- The anterior column of the rugae (columna rugarum anterior), which is more pronounced.
Inferiorly, it forms a longitudinally oriented protrusion called the urethral carina of the vagina (carina urethralis vaginae), which corresponds to the urethra adhering to the vagina.
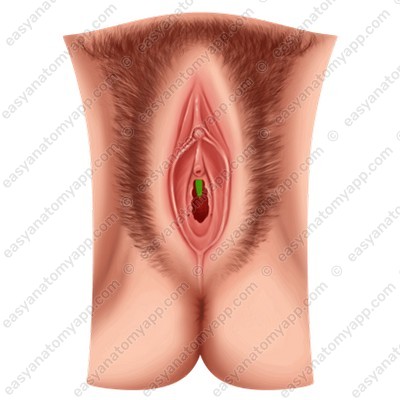
- The anterior and posterior columns are located on different sides of the median plane.
The muscular coat / layer (tunica muscularis)
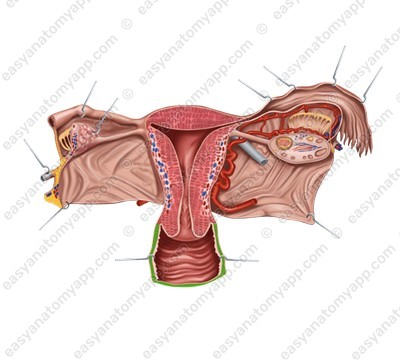
It consists of two layers of smooth muscles:
- Circular layer (stratum circulare), which is an internal layer
- Longitudinal layer (stratum longitudinale), which is an external layer
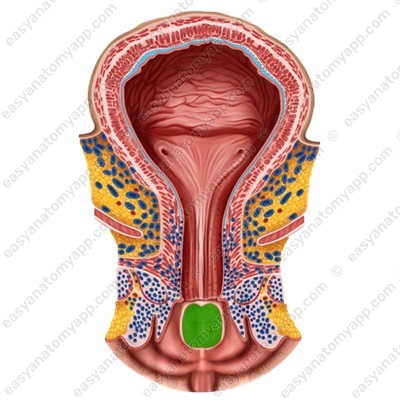
In the area of the vaginal orifice, there is a cluster of striated circular fibers of the perineal muscles.
This is the vaginal sphincter (m. sphincter vaginae).
The outer sheath consists of the peritoneum and adventitia.
In relation to the peritoneum, the organ lies extraperitoneally, it is covered with the peritoneum only within the recto-uterine pouch.
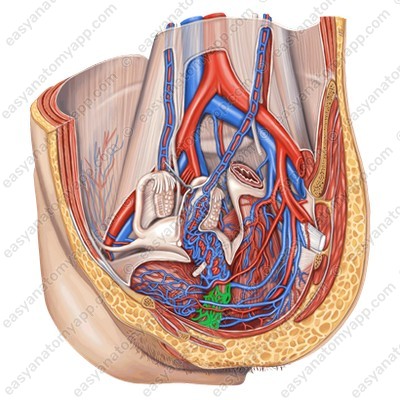
Blood supply
Arterial blood flows through the branches of the internal iliac artery (a. iliaca interna):
- The uterine artery (a. uterina);
- The inferior vesical artery (a. vesicalis inferior);
- The middle rectal artery (a. rectalis media);
- The internal pudendal artery (a. pudenda interna).
Venous drainage
Venous blood drains through the eponymous veins to:
- The vaginal venous plexus (plexus venosus vaginalis);
- The vesical venous plexus (plexus venosus vesicalis);
- The uterine venous plexus (plexus venosus uterinus);
- The rectal venous plexus (plexus venosus rectalis).
Lymph drainage
Lymph drains mainly into:
- The internal iliac lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici iliaci interni);
- The deep inguinal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici inguinales profundi);
- The superficial inguinal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici inguinales superficiales);
- The pelvic lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici sacrales).
Innervation
Along the course of the organ, nerve fibers form the so-called vaginal plexus (plexus vaginalis), which is part of the uterovaginal plexus (plexus uterovaginalis).
- Afferent innervation is provided by the sensitive fibers of the sacral spinal nerves.
- Parasympathetic innervation is provided by the fibers of the pelvic splanchnic nerve.
- Sympathetic innervation is provided by the fibers of the hypogastric plexus.
Anatomy of the vagina
- Female genitalia
- organa genitalia feminina
- Ovaries
- ovarium
- Uterus
- uterus
- Uterine tubes
- tuba uterina
- Vagina
- vagina
- Mons pubis
- mons pubis
- Labia majora
- labia majora pudendi
- Labia minora
- labia minora pudendi
- Greater vestibular glands
- glandulae vestibulares majores
- Lesser vestibular glands
- glandulae vestibulares minores
- Bulb of the vestibule
- bulbus vestibuli
- Clitoris
- clitoris
- Hymen
- hymen
- Mammary gland
- mamma
- Anterior wall
- paries anterior
- Posterior wall
- paries posterior
- Fornix of the vagina
- fornix vaginae
- Anterior part
- pars anterior
- Posterior part
- pars posterior
- Lateral parts
- partes laterales
- Vaginal orifice
- ostium vaginae
- Transverse vaginal rugae
- rugae vaginales
- Vaginal columns
- columnae rugarum
- Anterior vaginal column
- columna rugarum anterior
- Urethral carina of the vagina
- carina urethralis vaginae
- Mucous membrane
- tunica mucosa
- Muscular layer
- tunica muscularis
- Circular layer
- stratum circulare
- Longitudinal layer
- stratum longitudinale
- Sphincter muscle of the vagina
- m. sphincter vaginae
- Uterine artery
- a. uterina
- Inferior vesical artery
- a. vesicalis inferior
- Middle rectal artery
- a. rectalis media
- Internal pudendal artery
- a. pudenda interna
- Vaginal venous plexus
- plexus venosus vaginalis
- Vesical venous plexus
- plexus venosus vesicalis
- Uterine venous plexus
- plexus venosus uterinus
- Rectal venous plexus
- plexus venosus rectalis
- Internal iliac lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici iliaci interni
- Deep inguinal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici inguinales profundi
- Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici inguinales superficiales
- Pelvic lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici sacrales
- Vaginal plexus
- plexus vaginalis
- Uterovaginal plexus
- plexus uterovaginalis


