The first cervical vertebra (C1) is called the atlas. It is an atypical cervical vertebra that has its own distinctive characteristics.
._Вид_Сверху.jpg)
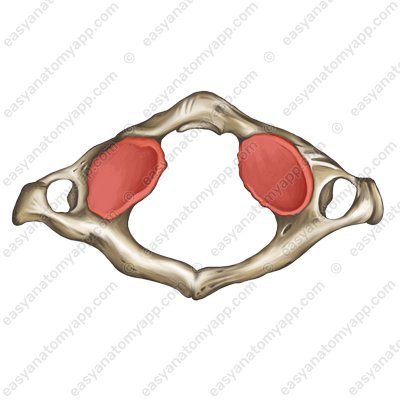
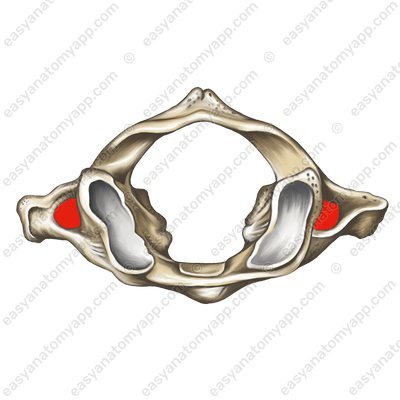
It does not have a body; during the embryonic period, it transformed into a dens of the 2nd cervical vertebra (C2). The role of the body is performed by two lateral masses (massa lateralis).
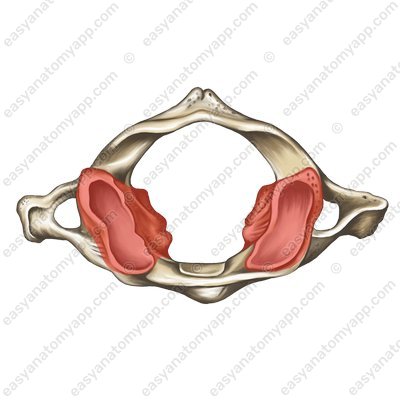
At the top and bottom of each lateral mass there are superior and inferior articular surfaces (facies articulares superior et inferior). It is necessary to clarify that there are no articular processes, only surfaces.
The superior articular surfaces are connected to the occipital bone and the inferior articular surfaces are connected to the 2nd cervical vertebra (C2).
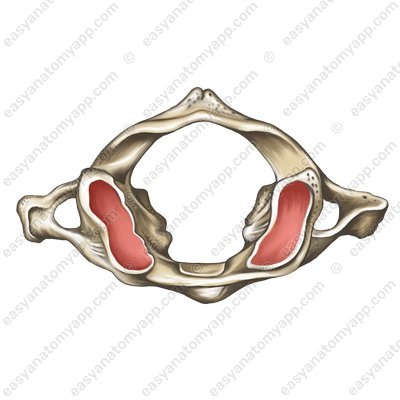
The two lateral masses are connected by the anterior arch of the atlas (arcus anterior atlantis);
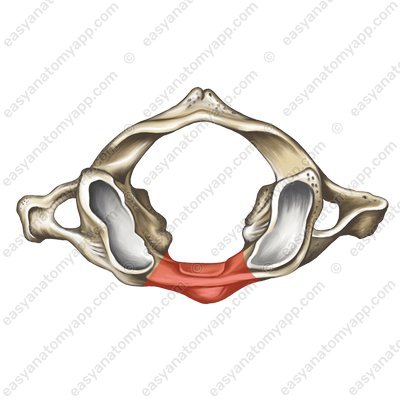
and the posterior arch of the atlas (arcus posterior atlantis)
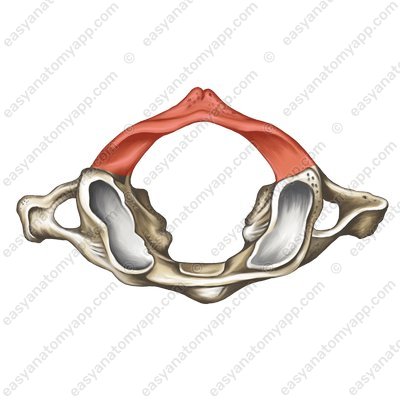
There is an anterior tubercle (tuberculum anterius) on the anterior arch, and a posterior tubercle (tuberculum posterius) on the posterior arch. The latter plays the role of the spinous process, which the atlas does not have.
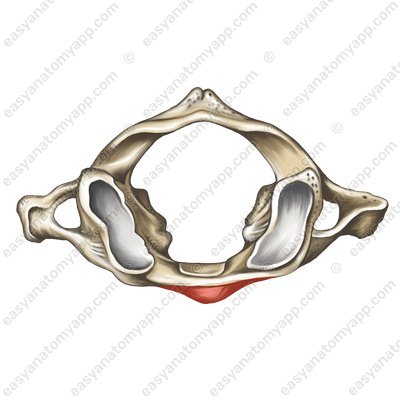

On the internal surface of the anterior arch, the facet for the dens (fovea dentis) can be seen, which serves to connect to the dens of the 2nd cervical vertebra.
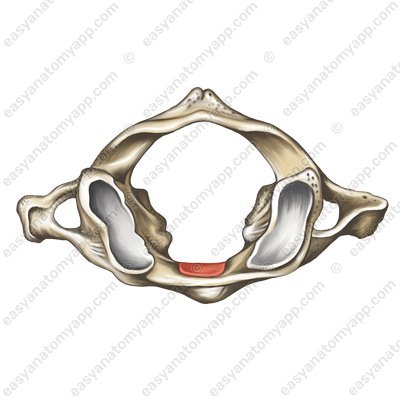
On the posterior arch, there is a small impression — the groove for the vertebral artery (sulcus arteriae vertebralis).

To the side of each lateral mass extends a transverse process (processus transversus).
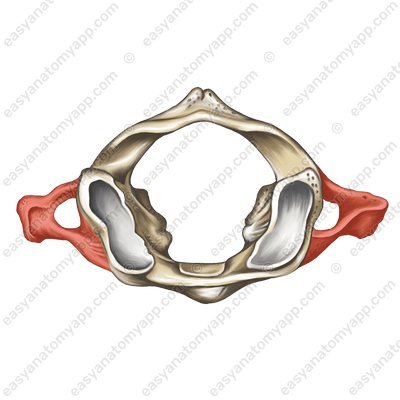
As with the other cervical vertebrae, there is a foramen transversarium, through which passes the vertebral artery, involved in the blood supply to the brain.
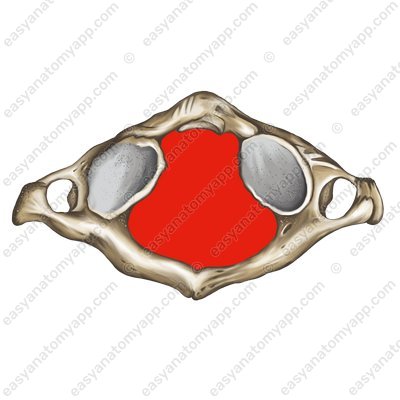
In the very center of the atlas is the vertebral foramen (foramen vertebrale).
Atlas (C1)
- atlas
- atlas
- massa lateralis
- lateral mass
- facies articularis superior
- superior articular surface
- facies articularis inferior
- inferior articular surface
- arcus anterior atlantis
- anterior arch
- arcus posterior atlantis
- posterior arch
- tuberculum anterius
- anterior tubercle
- tuberculum posterius
- posterior tubercle
- fovea dentis
- facet for dens
- sulcus arteriae vertebralis
- groove for vertebral artery
- processus transversus
- transverse process
- foramen transversarium
- foramen transversarium
- foramen vertebrale
- vertebral foramen


