For a comprehensive understanding of the anatomy of the pelvic girdle, we must examine the bony pelvis.
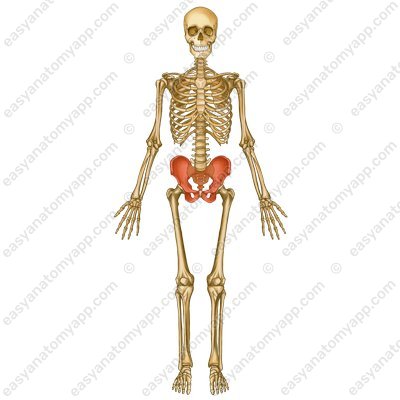
Its consists of:
hip bone (os coxae), 2x
sacrum (os sacrum)
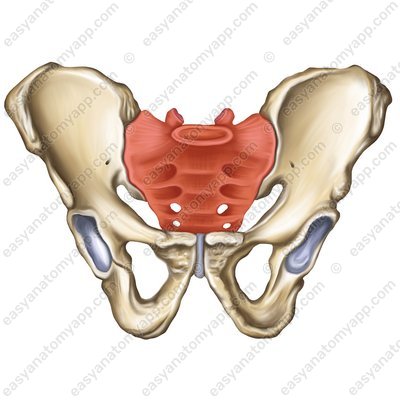
Sacrum (os sacrum) coccyx (os coccygis)
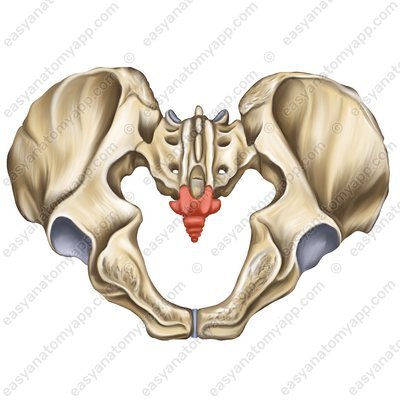
Coccyx (os coccygis) There are the greater pelvis (pelvis major)
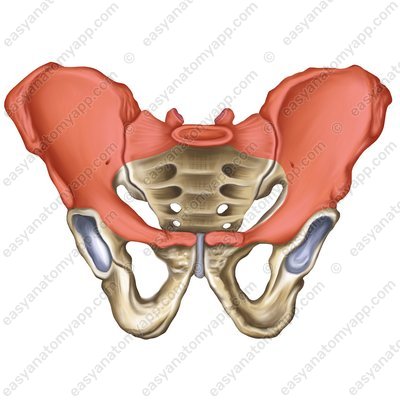
Greater pelvis (pelvis major) 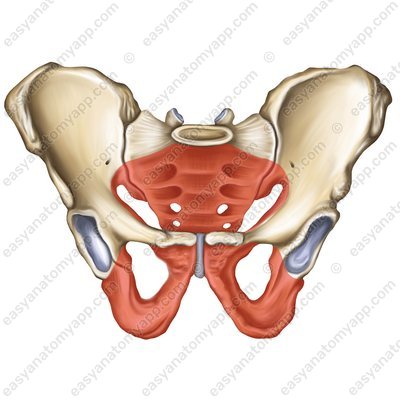
Lesser pelvis (pelvis minor) and the lesser pelvis (pelvis minor).
anterior wall is formed by the muscles of the anterior wall of the abdomen
posterior wall is formed by the fifth lumbar vertebra, the base of the sacrum, the iliolumbar ligament
anterior wall is formed by the pubic bones and pubic symphysis
posterior wall is formed by the sacrum and the coccyx
lateral walls are formed by the ischia, the obturator membrane, the sacrotuberous and the sacrospinous ligaments
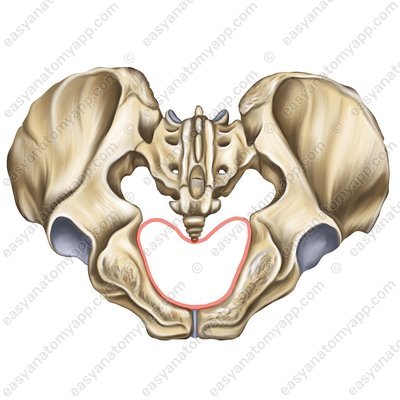
pelvic inlet (apertura pelvis superior), which is bounded by the linea terminalis (linea terminalis). In turn, the linea terminalis extends through the following formations: pubic symphysis → pecten pubis → arcuate line → promontory
pelvic outlet (apertura pelvis inferior) is bounded by the following formations: pubic symphysis → inferior pubic ligament → inferior pubic ramus → ramus of ischium → ischial tuberosity → sacrotuberous ligament → coccyx
Male pelvis is narrower, taller, the wings of the ilia are upright, the pelvic inlet is rounded, and the pubic bones form a pubic angle
Female pelvis is wider, the wings of the ilia are horizontal, the pelvic inlet is heart-shaped, and the pubic bones form the pubic arch
- pelvis
- pelvis
- hip bone
- os coxae
- sacrum
- os sacrum
- coccyx
- os coccygis
- greater pelvis
- pelvis major
- lesser pelvis
- pelvis minor
- pelvin inlet
- apertura pelvis superior
- pelvin outlet
- apertura pelvis inferior
- distantia spinarum
- distantia spinarum
- distantia cristarum
- distantia cristarum
- distantia trochanterica
- distantia trochanterica
- external conjugate
- conjugata externa
- anatomical conjugate
- diameter recta/conjugata anatomica
- true conjugate
- diameter vera/conjugata gynecologica
- diagonal conjugate
- conjugata diagonalis
- transverse diameter
- diameter transversa
- oblique diameter
- diameter obliqua
The walls of the greater pelvis are formed by the following structures:
lateral walls are formed by the wings of the ilia
The walls of the lesser pelvis are formed by the following structures:
The pelvis also has two apertures (inlet/outlet):
.jpg)
One must also understand the differences between the sexes in the pelvis:
In obstetrics, the study of the pelvis is critical because the structure and size of the pelvis are crucial to the course and outcome of the birth. The presence of a normal pelvis is one of the main conditions for the correct course of childbirth. In this regard, it is essential to know the measurements of the female pelvis.

The following dimensions of the pelvis are distinguished:
| Greater pelvis (false pelvis) diameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Distantia spinarum (distantia spinarum) |
Distance between the superior anterior iliac spines | 25-26 cm |
| Distantia cristarum (distantia cristarum) |
Distance between the most distant points of the iliac crests | 28-29 cm |
| Distantia trochanterica (distantia trochanterica) |
Distance between the greater trochanters of the femurs | 31-32 cm |
| External conjugate (conjugata externa) |
Distance between the spinous process of the 5th lumbar vertebra and the most prominent point of the external surface of the pubic symphysis | 20-21 cm |
| Pelvic inlet diameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Anatomical conjugate (diameter recta / conjugata anatomica) |
Distance between the superior border of the pubic symphysis and the most prominent point of the sacral promontory | 11.5 cm |
| True conjugate (diameter vera / conjugata gynecologica) |
Distance between the most prominent point of the posterior surface of the pubic symphysis to the most prominent point of the sacral promontory | 10.5-11.0 cm |
| Diagonal conjugate (conjugata diagonalis) |
Distance between the bottom of the pubic symphysis and the most prominent point of the sacral promontory | 12.5-13.0 cm |
| Transverse diameter (diameter transversa) |
Distance between the distant points of the arcuate line | 13.5 cm |
| Oblique diameter (diameter obliqua) |
Distance between the iliopubic eminence on one side and the sacroiliac joint on the other side | 12-12.5 cm |
| Pelvic cavity (true pelvis) diameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Anteroposterior diameter (diameter recta) |
Distance between the middle of the pubic symphysis and the place of articulation of II and III sacral vertebrae | 12.5 cm |
| Transverse diameter (diameter transversa) |
Distance between the centers of the acetabula | 12.5 cm |
| Pelvic outlet diameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Anteroposterior diameter (diameter recta) |
Distance between the apex of the coccyx and the inferior border of the pubic symphysis | In women, it is 9 cm, and due to the mobility of the coccyx during childbirth it increases to 11 cm. |
| Transverse diameter (diameter transversa) |
Distance between the tubercles of the ischia | 11 cm |
The line connecting the centers of all anatomical conjugates of the pelvis is called the pelvic axis. It is along this line that the fetus passes through the birth canal.


