The bones of the leg are connected to the bones of the foot with the ankle joint (articulatio talocruralis).
.jpg)
.jpg)
_1.jpg)
.jpg)
The bones forming the joint are fibula (fibula), tibia (tibia), and talus (talus).
This joint is formed between the articular surface of the medial malleolus (facies articularis malleoli medialis), the articular surface of the lateral malleolus (facies articularis malleoli lateralis), the inferior articular surface of the tibia (facies articularis inferior), the trochlea of the talus (trochlea tali), the medial malleolar facet (facies malleolaris medialis) and the lateral malleolar facet (facies malleolaris lateralis) of the talus.
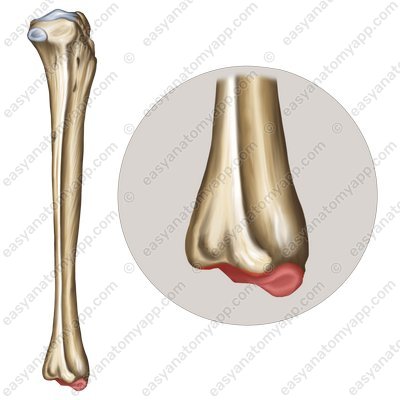
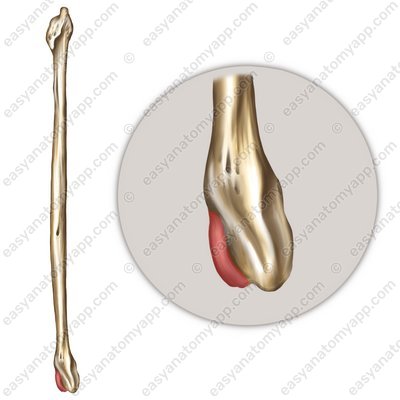
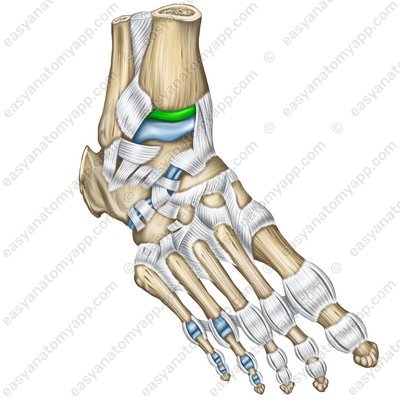
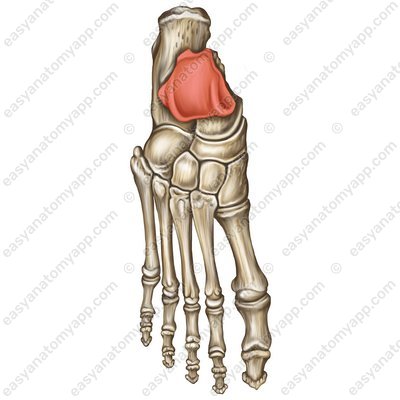

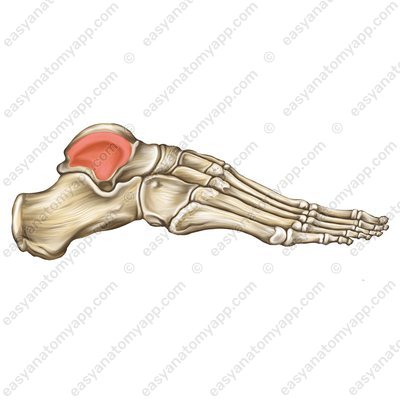
The articular capsule on the anterior surface of the leg bones and on the talus bone inserts near the articular cartilage, and on the posterior and lateral ones — along the line of articular cartilage.
According to the classification, the joint is complex, hinge, uniaxial, combined (with the subtalar joint (articulatio subtalaris) and with the talocalcaneonavicular joint (articulatio talocalcaneonavicularis).
In the joint, dorsal and plantar flexion around the frontal axis may take place.
Minor lateral motions may also occur with plantar flexion.
The ligamentous apparatus of the joint consists of several ligaments.
These include the medial collateral or deltoid ligament (ligamentum collaterale mediale or deltoideum), which arises from the medial calcaneus, descends and inserts into the navicular bone, talus and calcaneus bones.
Medial collateral ligament (lig. mediale) _2.jpg)
Medial collateral ligament (lig. mediale) .jpg)
Medial collateral ligament (lig. mediale) _1.jpg)
The ligament consists of four parts:
the tibionavicular (pars tibionavicularis),
Tibionavicular (pars tibionavicularis) .jpg)
tibiocalcaneal (pars tibiocalcanea),
Tibiocalcaneal (pars tibiocalcanea) .jpg)
anterior tibiotalar (pars tibiotalaris anterior)
Anterior tibiotalar (pars tibiotalaris anterior) .jpg)
and posterior tibiotalar parts (pars tibiotalaris posterior).
Posterior tibiotalar parts (pars tibiotalaris posterior) .jpg)
The anterior talofibular ligament (ligamentum talofibulare anterius) connects the external surface of the lateral malleolus with the neck of the talus.
Anterior talofibular ligament (lig. talofibulare anterius) 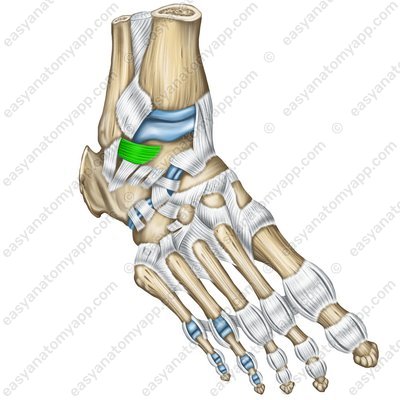
Anterior talofibular ligament (lig. talofibulare anterius) 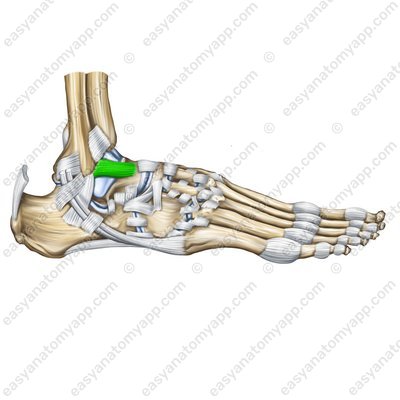
The posterior talofibular ligament (ligamentum tabofibulare posterius) arises from the lateral malleolus, passes posteriorly and inserts into the posterior process of the talus.
Posterior talofibular ligament (lig. talofibulare posterius) 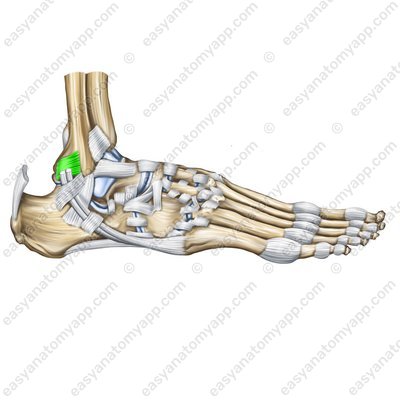
Posterior talofibular ligament (lig. talofibulare posterius) 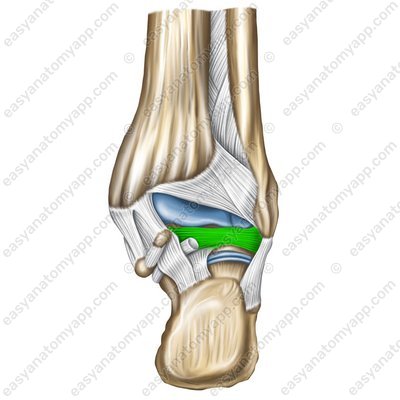
Posterior talofibular ligament (lig. talofibulare posterius) 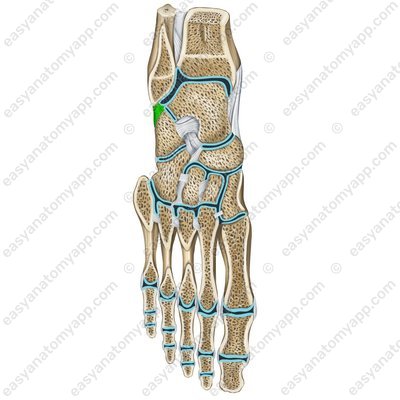
The calcaneofibular ligament (ligamentum calcaneofibulare) arises from on the lateral malleolus, passes inferiorly and inserts into the external surface of the calcaneus.
Calcaneofibular ligament (ligamentum calcaneofibulare) 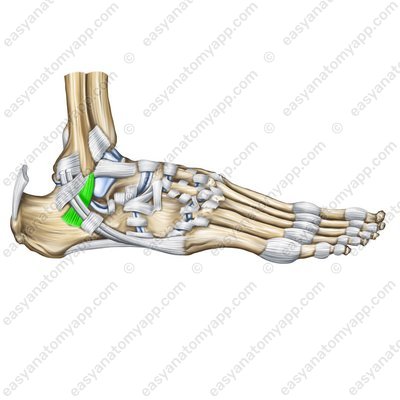
Calcaneofibular ligament (ligamentum calcaneofibulare) 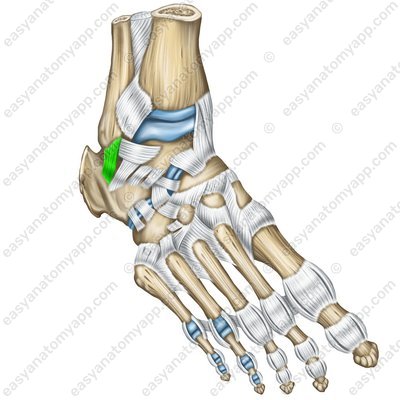
Calcaneofibular ligament (ligamentum calcaneofibulare) 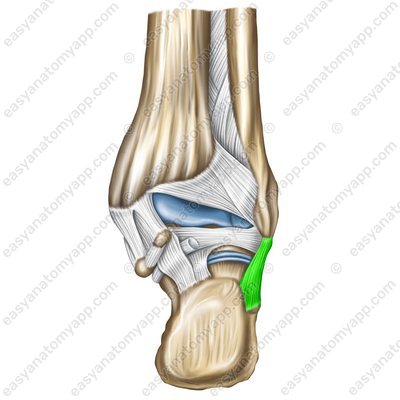
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the joint.
Arteries: anterior tibial artery (a. tibialis anterior), posterior tibial artery (a. tibialis posterior)
Veins: the blood outflows to the veins with the same name
Nerves: sciatic nerve (n. ischiadicus)
Ankle joint
- Ankle joint
- articulatio talocruralis
- Fibula
- fibula
- Tibia
- tibia
- Talus
- talus
- Articular surface of the medial malleolus
- facies articularis malleoli medialis
- Articular surface of the lateral malleolus
- facies articularis malleoli lateralis
- Trochlea of the talus
- trochlea tali
- Medial malleolar facet
- facies malleolaris medialis
- Lateral malleolar facet
- facies malleolaris lateralis
- Medial ligament
- ligamentum mediale
- Tibionavicular part
- pars tibionavicularis
- Tibiocalcaneal part
- pars tibiocalcanea
- Anterior tibiotalar part
- pars tibiotalaris anterior
- Posterior tibiotalar part
- pars tibiotalaris anterior
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- ligamentum talofibulare anterius
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- ligamentum talofibulare posterior
- Calcaneofibular ligament
- ligamentum calcaneofibulare


