Vertebral column (columna vertebralis) is formed by vertebrae lying on top of each other, which are interconnected with various structures: intervertebral discs and symphyses, joints and ligaments.
In any typical vertebra, there are the body, arch and various processes. According to these parts of vertebra, there are joints of bodies, joints of arches, and joints of processes.
Let’s learn about the joints of vertebral bodies.
These joints are the so-called intervertebral discs (discus intervertebralis).
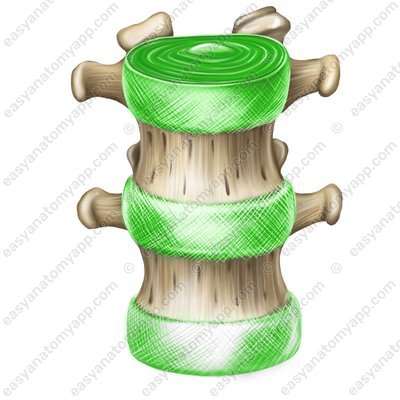
The discs consist of a nucleus pulposus (nucleus pulposus) located in the center, surrounded by a anulus fibrosus (anulus fibrosus) formed by fibrous cartilage.
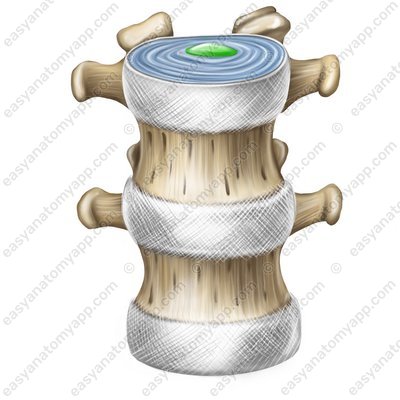
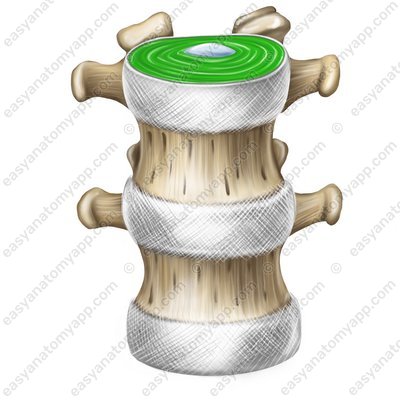
There is often a horizontal fissure inside the nucleus pulposus, which makes it possible to call such joints semijoints or intervertebral joints.
The discs are additionally reinforced with the following ligaments:
Anterior longitudinal ligament (ligamentum longitudinale anterius) passes along the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies, and fuses firmly with the intervertebral discs starting from the pharyngeal tubercle of the occipital bone and the anterior tubercle of the anterior arch of the atlas to the second-third transverse lines of the pelvic surface of the sacrum.
Anterior longitudinal ligament (lig. longitudinale anterius) 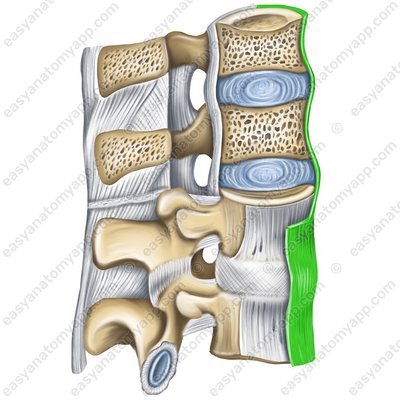
Posterior longitudinal ligament (ligamentum longitudinale posterius) is located along the posterior surface of the vertebral bodies in the spinal canal. From the lower edge of the clivus of the occipital bone, it passes through the joints of cervical vertebrae 1 and 2 and further down to the coccygeal vertebra 1.
Posterior longitudinal ligament (lig. longitudinale posterius) 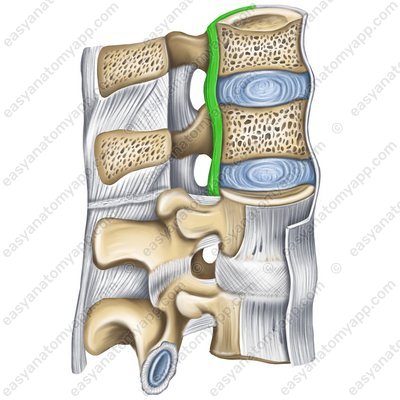
Next, let’s learn about the connections of the vertebral arches
They are represented by the ligamenta flava (ligamenta flava), which are located in the spaces between the arches of the vertebrae. These ligaments counteract excessive anterior flexion of the spinal column.
Ligamenta flava (ligg. flava) 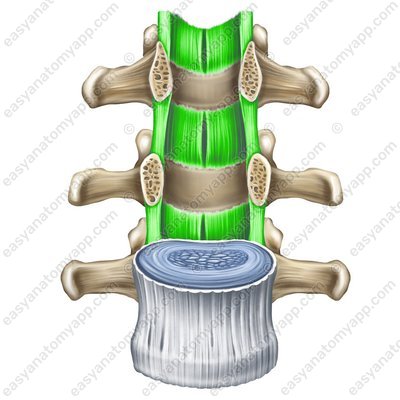
Let’s move on to the vertebral processes’ joints.
The spinous processes are connected with several ligaments.
These are the interspinous ligaments (ligamenta interspinalia), which fill the spaces between the spinous processes of neighboring vertebrae.
Interspinous ligaments (ligg. interspinalia) 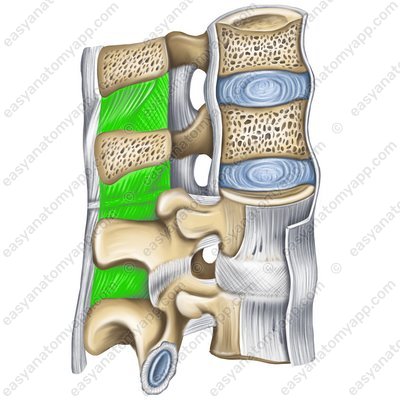
Supraspinous ligament (ligamentum supraspinale) attaches to the apices of the spinous processes of all vertebrae.
Supraspinous ligament (lig. supraspinale) 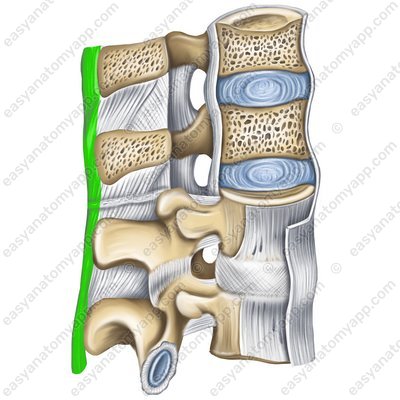
And the nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae), which is the superior part of the supraspinous ligament and is stretched between the external crest of the occipital bone and the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Nuchal ligament (lig. nuchae) 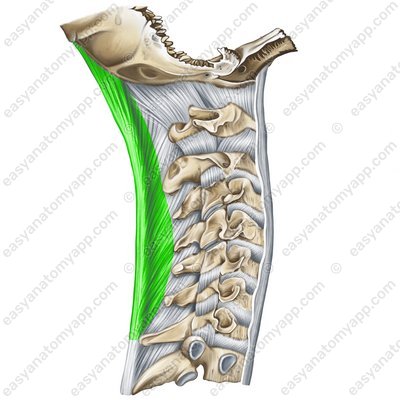
The transverse processes are connected with interstitial ligaments (ligamenta intertransversaria). They are stretched between the apices of the transverse processes of neighboring vertebrae.
Interstitial ligaments (ligg. intertransversaria) 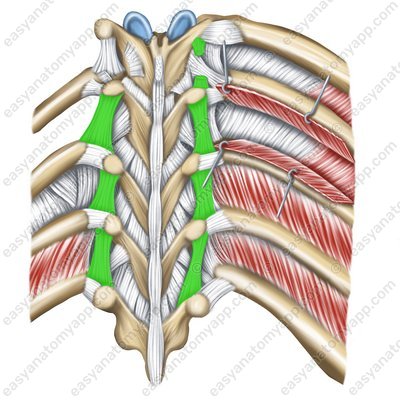
Articular processes are connected to each other with the help of more complex formations, which are called zygapophysial joints (articulationes zygapophysiales).
Zygapophysial joints (articulationes zygapophysiales) .jpg)
The articular surfaces of this joint are located on the superior articular processes (processus articulares superior)
Superior articular processes (processus articularis superior) 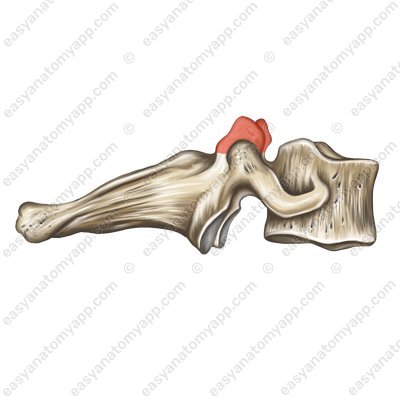
and inferior articular processes (processus articulares inferior)
Inferior articular processes (processus articularis inferior) 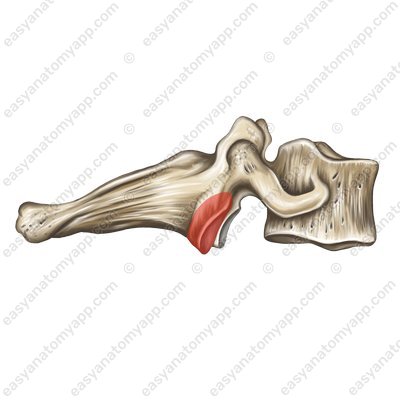
The joint capsule is attached along the edge of the articular surfaces.
Joint capsule (capsula articularis) .jpg)
According to the classification, the joint is simple, plane, multiaxial and combined with the joint of the same name on the opposite side.
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
Around the frontal axis: the torso tilts back and forth.
Around the sagittal axis: the torso tilts to the sides.
Around the vertical axis: the torso twists.
When shifting from the frontal axis to the sagittal, circumduction is performed.
There are no ligamentous apparatus and additional structures for this joint.
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the joint.
Arteries
Muscular branches of the vertebral artery (rami musculares a. vertebralis) in the cervical segment
Posterior intercostal arteries (aa. intercostales posteriors) in the thoracic segment.
Lumbar arteries (aa. lumbales) in the lumbar region.
Lateral sacral arteries (aa. sacrales laterals) in the sacral segment.
Median sacral artery (a. sacralis mediana) in the sacral segment.
Veins
The outflow of blood occurs in the internal and external vertebral venous plexuses (plexus venosi vertebrales externi et interni) and further:
From the cervical vertebrae to the vertebral vein (v. vertebralis)
From the thoracic vertebrae to the intercostal veins (vv. intercostales)
From the lumbar vertebrae to the lumbar veins (vv. lumbales)
From the sacrum and coccyx to the lateral sacral veins (vv. sacrales laterales)
Nerves
Dorsal branches of spinal nerves (rr. dorsalis nn. spinales)
Joints and ligaments of the vertebral column
- Vertebral column
- columna vertebralis
- Intervertebral disc
- discus intervertebralis
- Nucleus pulposus
- nucleus pulposus
- Anulus fibrosus
- anulus fibrosus
- Anterior longitudinal ligament
- lig. longitudinale anterius
- Posterior longitudinal ligament
- lig. longitudinale posterius
- Ligamenta flava
- ligg. flava
- Interspinous ligaments
- ligg. interspinalia
- Supraspinous ligament
- lig. supraspinale
- Nuchal ligament
- lig. nuchae
- Intertransverse ligaments
- ligg. intertransversaria
- Zygapophysial joint
- art. zygapophysialis
- Superior articular process
- processus articulares superior
- Inferior articular process
- processus articulares inferior


