The radius and ulna are connected to each other by the proximal radioulnar joint (articulatio radioulnaris proximalis) and the distal radioulnar joint (articulatio radioulnaris distalis).
The first is part of a larger elbow joint, which is considered in greater detail in the corresponding pdf-note.
Let’s learn about the structure of the distal radioulnar joint.
_1.jpg)
.jpg)
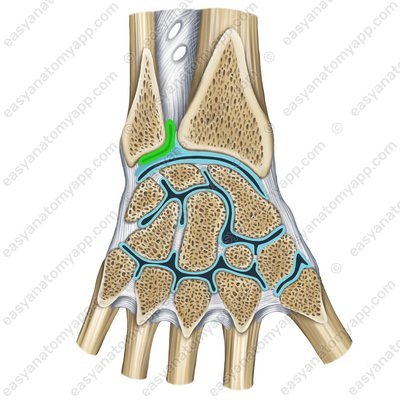
It is formed between the articular surfaces on the articular circumference of the ulna (circumferentia articularis ulnae) and the ulnar notch of the radius (incisura ulnaris radii).

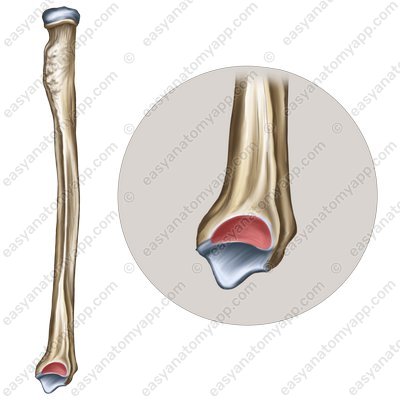
The joint capsule is attached along the edge of the articular surfaces.
.jpg)
There is a slight protrusion of the articular capsule between the distal parts of the forearm bones, called the sacciform recess (recessus sacciformis).
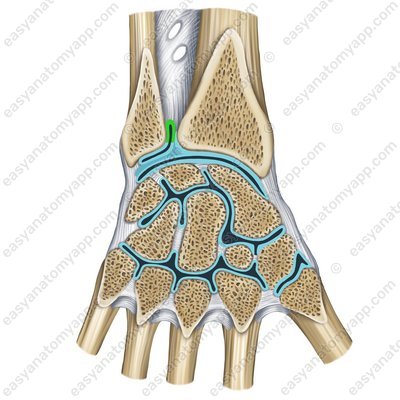
According to the classification, the joint is simple, cylindrical, uniaxial, combined, and complex.
When motion in the joint takes place, the proximal epiphysis of the radius rotates in place, and the distal epiphysis slides along the articular circumference of the ulna along an arc around the head of the ulna, which remains immobile.
In addition, when the radius rotates, the hand also rotates with it.
The auxiliary apparatus of the joint includes the articular disc (discus articularis).
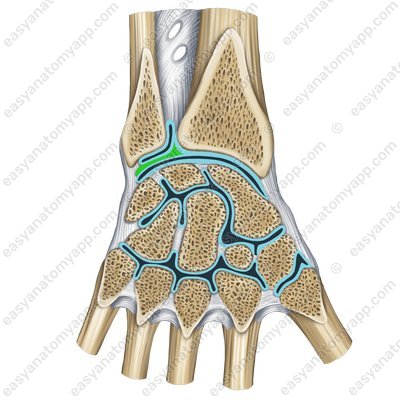
It is located between the ulnar notch of the radius and the styloid process of the ulna in the form of a triangular fibrous-cartilaginous lamina. The disc separates the distal radioulnar joint from the wrist joint and represents a kind of articular fossa for the head of the ulna.
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the elbow joint.
Arteries: radial artery (a. radialis), ulnar artery (a. ulnaris)
Veins: the blood outflows through the veins with the same name.
Nerves: median nerve (n. medianus), ulnar nerve (n. ulnaris), radial nerve (n. radialis)
Distal radioulnar joint
- distal radioulnar joint
- articulatio radioulnaris distalis
- radius
- radius
- ulna
- ulna
- articular circumference of head of ulna
- circumferentia articularis ulnae
- ulnar notch of radius
- incisura ulnaris radii
- sacciform recess
- recessus sacciformis
- articular disc
- discus articularis


