Human bones are connected to each other with various formations that differ in their structure and functionality. All joints can be divided into two large groups:
The synovial joints contain a cavity between the bones
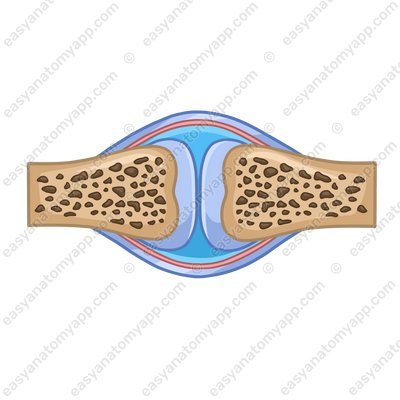
Synovial joints And the synarthroses contain no cavity, and the bones are held together by connective tissue.

Let’s start with synarthroses. Depending on what type of connective tissue the bones are held together by, the following types of synarthroses are distinguished.
These are fibrous joints formed by dense fibrous connective tissue
Cartilaginous joints formed by cartilage tissue
Bony joints formed from the cartilaginous joints, in which the cartilage tissue densified and was replaced by the bone tissue
There are several varieties of the fibrous joints.
These include sutures
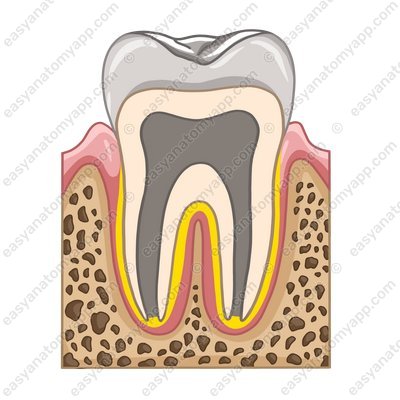
Dento-alveolar syndesmoses or gomphoses
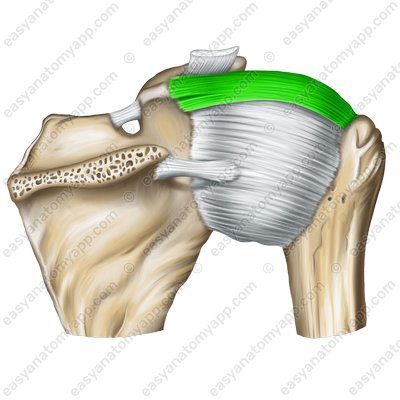
And syndesmoses
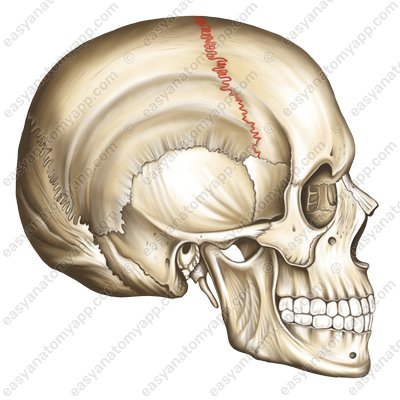
Sutures (in Latin suturae, singular sutura) connect some bones of the skull. Depending on the shape of the edges, the sutures can be serrate (sut. serrata), plane (sut. plana) and squamous (sut. squamosa).
Dento-alveolar syndesmoses are also called gomphoses (articulatio dentoalveolaris or gomphosis). They connect the root of the tooth and the dental alveolus.
The syndesmosis (syndesmosis) is the bony joint combined with additional structures, such as various ligaments, membranes and other fibrous formations. The main and most common are ligaments (ligamenta, sing. ligamentum).
Cartilaginous joints include synchondrosis and symphysis.
The synchondrosis (synchondrosis) is a fibrous cartilage tissue joint. In most synchondroses, the cartilage layer between the bones persists only until a certain age, after which the cartilage is replaced by bone tissue and synchondrosis turns into synostosis. At the same time, some cartilage joints persist over time, for example, the rib cartilage.
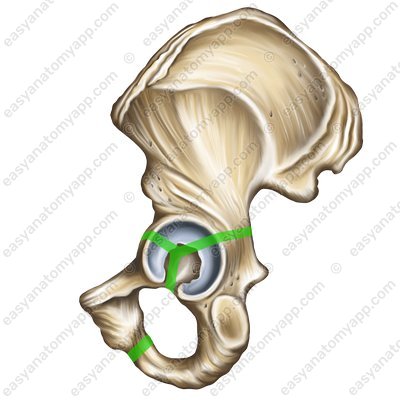
The symphysis (symphysis) is also a cartilaginous joint, however, in this cartilage, unlike synchondrosis, there is a small cavity. As was mentioned previously, the cavity is the main difference between a synarthrosis and a synovial joint. Therefore, symphyses are sometimes listed in another class of joints called semi-joints.
Synovial joints, or simply joints have numerous structural features, as well as their own separate classification, which we will consider in a separate video.
Joints and Ligaments
- serrate suture
- sutura serrata
- plane suture
- sutura plana
- squamous suture
- sutura squamosa
- dento-alveolar syndesmosis; gomphosis
- gomphosis/ articulatio dentoalveolaris
- syndesmosis
- syndesmosis
- ligament (ligaments)
- ligamentum (ligamenta)
- synchondrosis
- synchondrosis
- symphysis
- symphysis


