Let’s learn about the structure of the knee joint (articulatio genus).
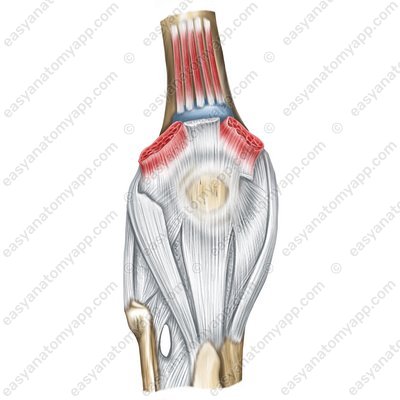
It connects three bones: the femur (femur), tibia (tibia) and patella (patella).
This joint includes two separate joints.
The first is the tibiofemoral joint, which is formed between the articular surfaces on the condyles of the femur (facies articularis condyli femoris) and the superior articular surface of the tibia (facies articularis superior tibiae).
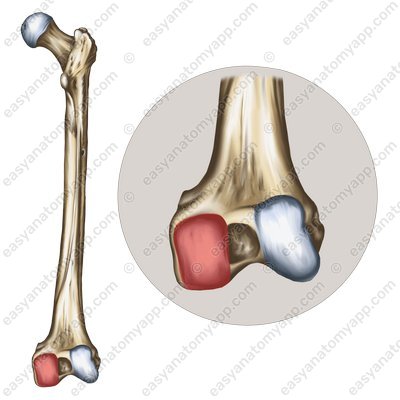
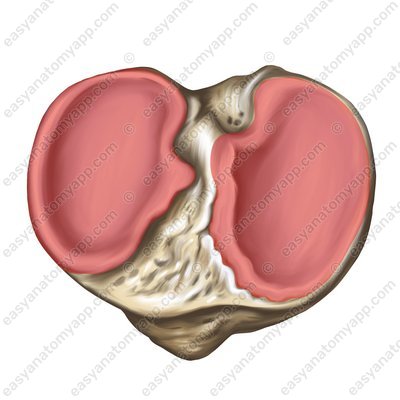
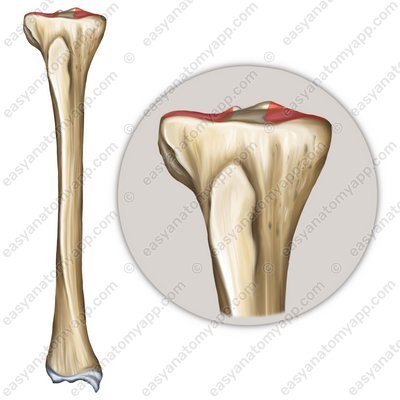
The second is the patellofemoral joint, which is formed between the patellar surface of the femur (facies patellaris) and the articular surface of the patella (facies articularis patellae).
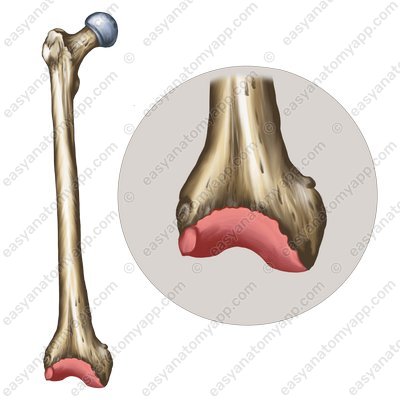
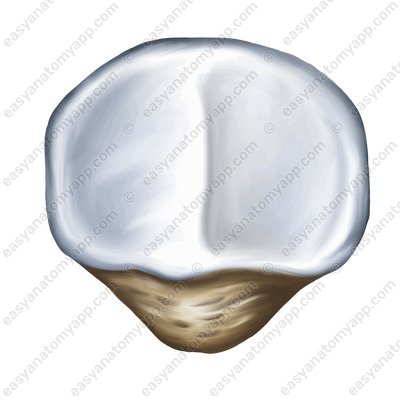
The articular capsule of the knee joint is thin and elastic, it is attached to the femur anteriorly slightly above the patellar surface, and laterally along the epicondyles, leaving them outside the joint cavity. On the tibia and patella it is attached along the margin of the articular surfaces.
.jpg)
According to the classification, the joint is bicondylar, biaxial, complex, and not combined.
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
around the frontal axis: flexion and extension
around the vertical axis: rotation, but provided that the lower limb is flexed
The fixing apparatus of the joint is represented by several ligaments:
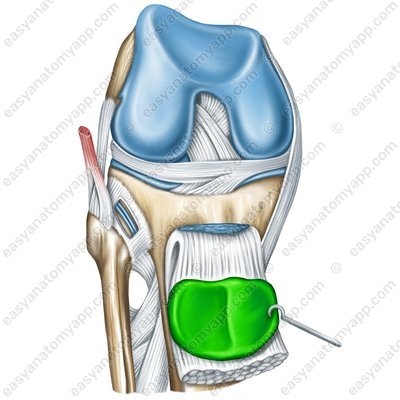
These include the fibular collateral ligament (ligamentum collaterale fibulare), which arises from the lateral epicondyle of the femur and inserts into the lateral surface of the head of the fibula.
Fibular collateral ligament (lig. collaterale fibulare) 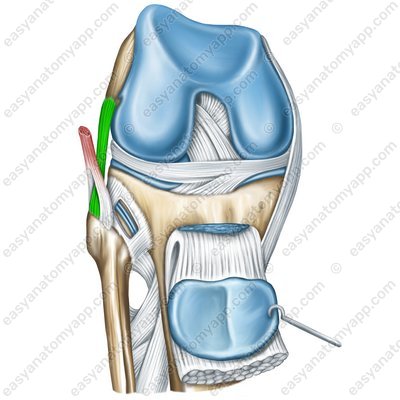
Fibular collateral ligament (lig. collaterale fibulare) 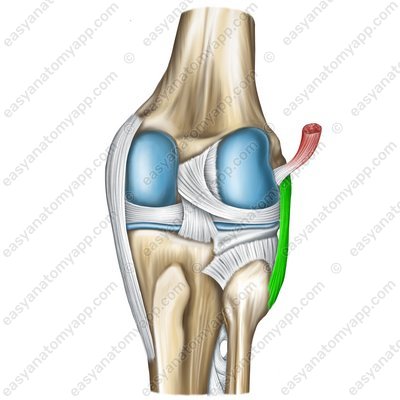
Fibular collateral ligament (lig. collaterale fibulare) 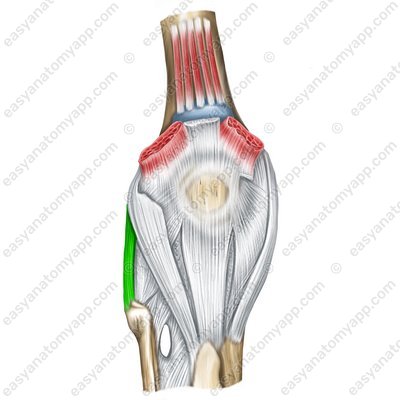
The tibial collateral ligament (ligamentum collaterale tibiale), which arises from the medial epicondyle of the femur and inserts into the medial margin of the tibia.
Tibial collateral ligament (lig. collaterale tibiale) 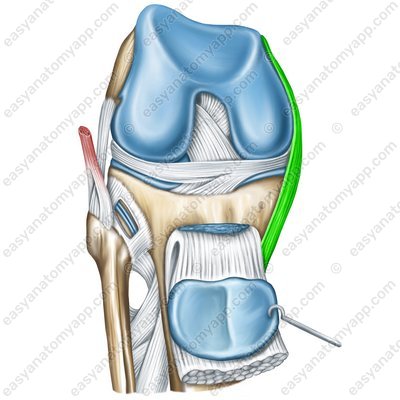
Tibial collateral ligament (lig. collaterale tibiale) 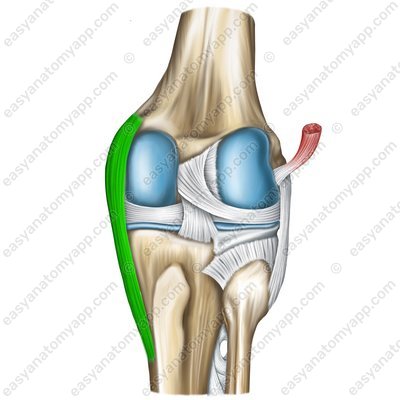
Tibial collateral ligament (lig. collaterale tibiale) 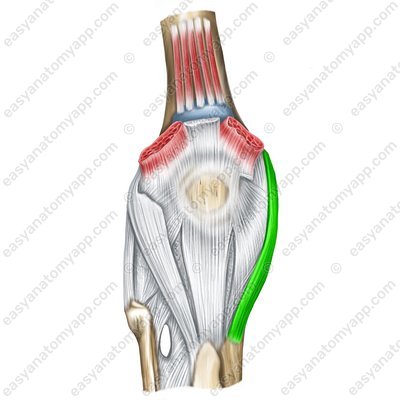
The patellar ligament (ligamentum patellae) is located between the patella and the tibial tuberosity, which is part of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris.
Patellar ligament (lig. patellae) 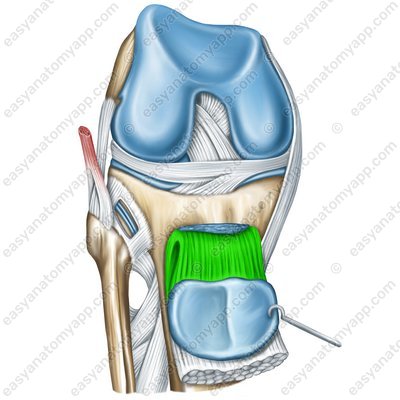
Patellar ligament (lig. patellae) 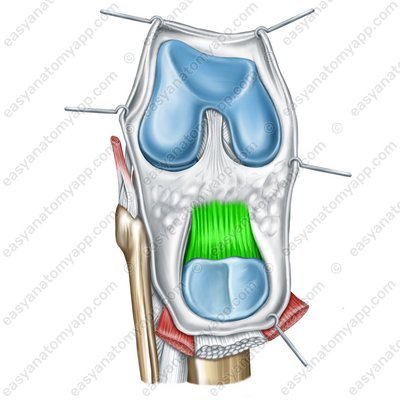
Patellar ligament (lig. patellae) 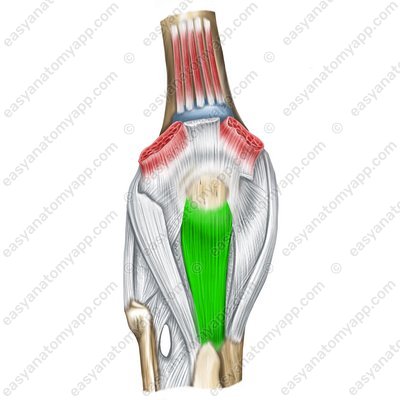
The oblique popliteal ligament (ligamentum popliteum obliquum) is located on the posterior side of the articular capsule, arises from the medial condyle of the tibia, weaves into the articular capsule and inserts into the posterior surface of the femur above its lateral condyle.
Oblique popliteal ligament (lig.popliteum obliquum) 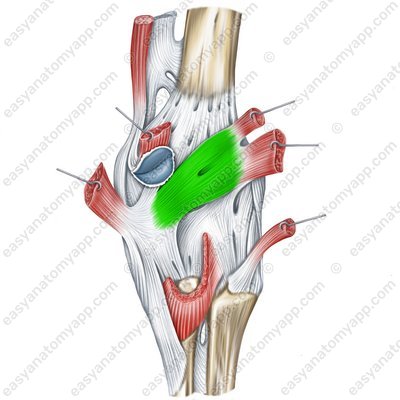
The arcuate popliteal ligament (ligamentum popliteum arcuatum) is located on the posterior surface of the joint, arises from the posterior side of the head of the fibula and the lateral epicondyle of the femur, arches in the medial side and inserts into the posterior surface of the tibia.
Arcuate popliteal ligament (lig. popliteum arcuatum) 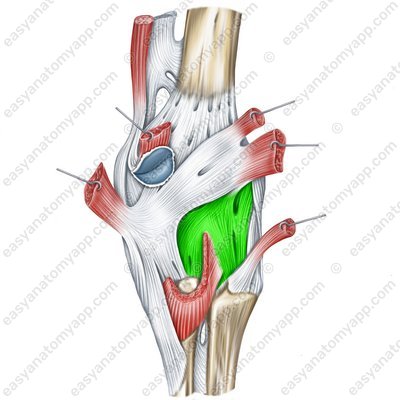
The composition of the additional structures of the knee joint is quite extensive. They include several formations.
First of all, these are intra-articular cartilages, or the socalled menisci:
The lateral meniscus (meniscus lateralis)
Lateral meniscus (meniscus lateralis) 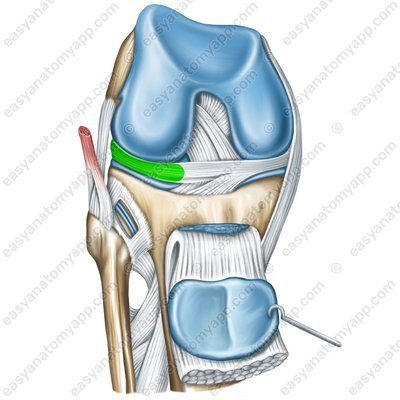
Lateral meniscus (meniscus lateralis) 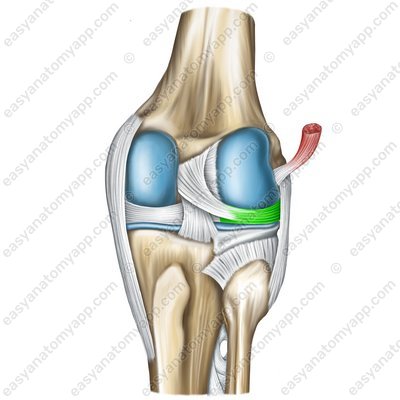
Lateral meniscus (meniscus lateralis) 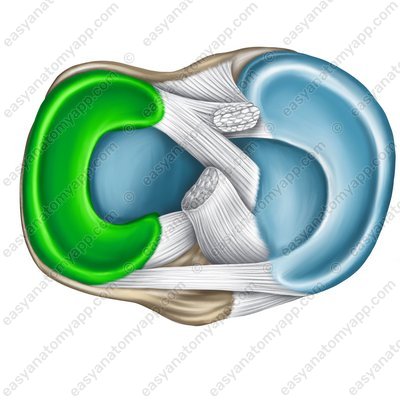
The medial meniscus (meniscus medialis)
Medial meniscus (meniscus medialis) 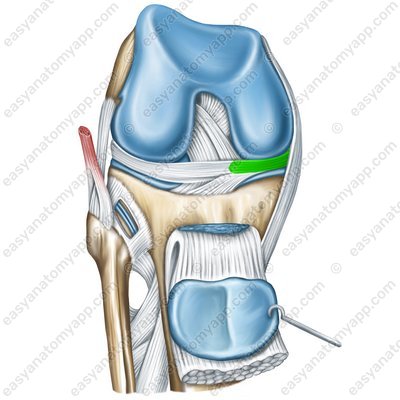
Medial meniscus (meniscus medialis) 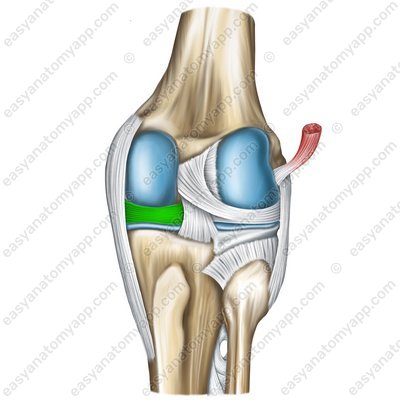
Medial meniscus (meniscus medialis) 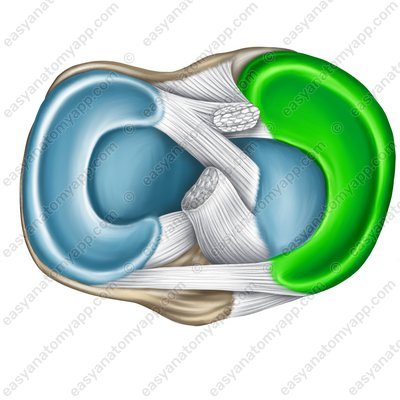
The external thick margin of each meniscus is fused to the capsule, and the thin margin faces inside the joint. The menisci are attached to the intercondylar eminence of the tibia, and the anterior borders of the menisci are connected by the transverse ligament of the knee (ligamentum transversum genus).
Transverse ligament of the knee (lig. transversum genus) 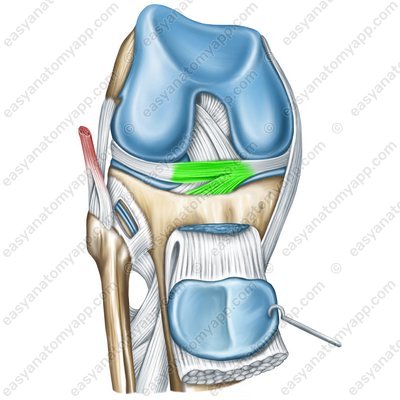
In addition to the menisci, several ligaments belong to the additional structures:
The anterior cruciate ligament (ligamentum cruciatum anterius) arises from the medial surface of the lateral condyle of the femur and attaches to the anterior intercondylar area of the tibia.
Transverse ligament of the knee (lig. cruciatum anterius genus) 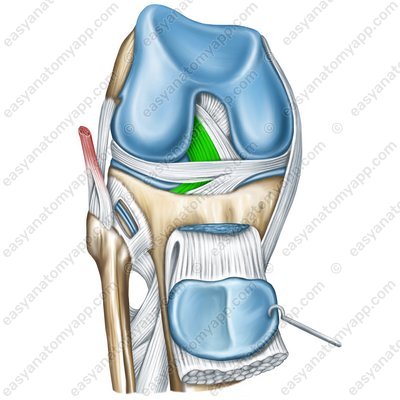
Transverse ligament of the knee (lig. cruciatum anterius genus) .jpg)
The posterior cruciate ligament (ligamentum cruciatum posterius) arises from the lateral surface of the medial condyle, and inserts into the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia.
Posterior cruciate ligament (lig. cruciatum posterius genus) 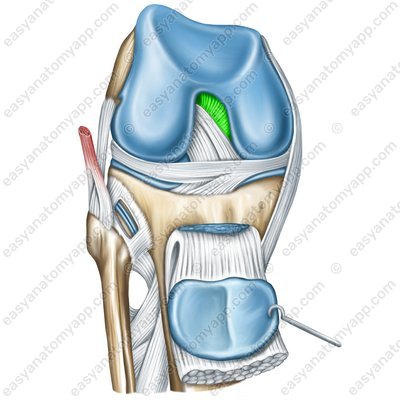
Posterior cruciate ligament (lig. cruciatum posterius genus) .jpg)
The transverse ligament of the knee (ligamentum transversum genus)
Transverse ligament of the knee (lig. transversum genus) 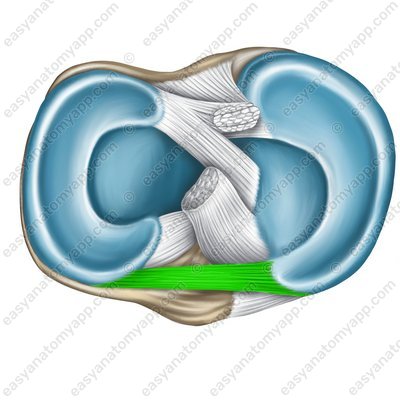
Two meniscofemoral ligaments:
The anterior meniscofemoral ligament (ligamentum meniscofemorale anterius)
Anterior meniscofemoral ligament (ligamentum meniscofemorale anterius) 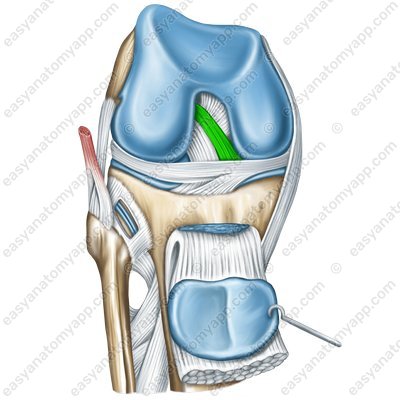
The posterior meniscofemoral ligament (ligamentum meniscofemorale posterius)
Posterior meniscofemoral ligament (ligamentum meniscofemorale posterius) 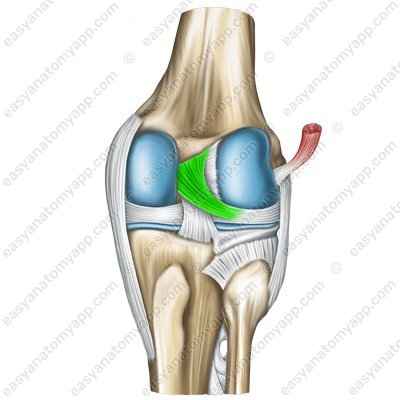
And two ligaments supporting the patella:
The medial patellar retinaculum (retinaculum patellae mediale)
Medial patellar retinaculum (retinaculum patellae mediale) 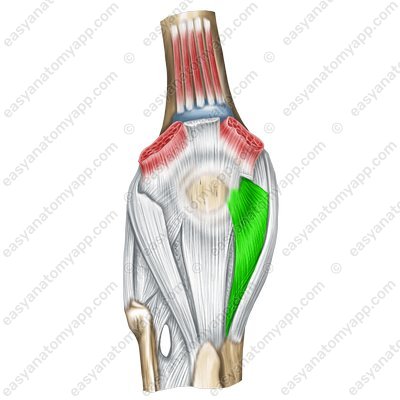
The lateral patellar retinaculum (retinaculum patellae laterale)
Lateral patellar retinaculum (retinaculum patellae laterale) 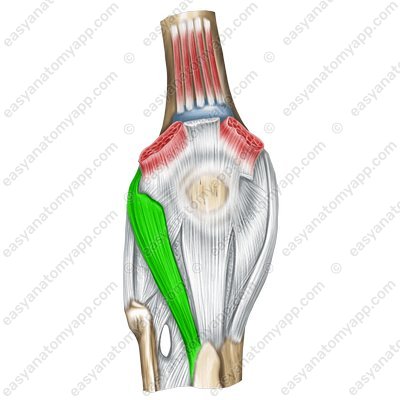
Also , several synovial folds belong to the additional structures:
The alar folds (plicae alares) are located inferiorly and laterally to the patella, they seem to be embedded in the joint cavity between the articulating bones.
Alar folds (plicae alares) 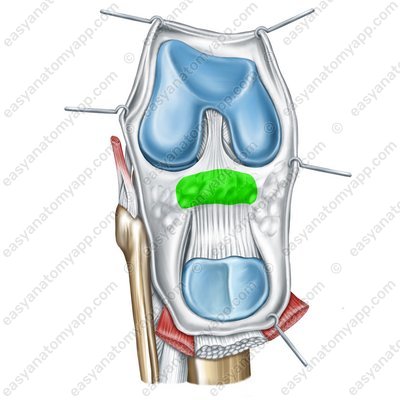
The infrapatellar synovial fold (plica synovialis infrapatellaris) goes from the patella down to the anterior intercondylar area, dividing the joint cavity into left and right parts.
Infrapatellar synovial fold (plica synovialis) 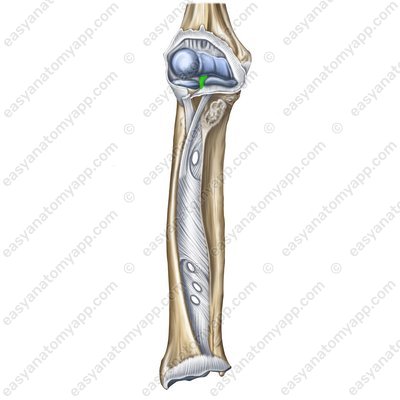
Infrapatellar synovial fold (plica synovialis) 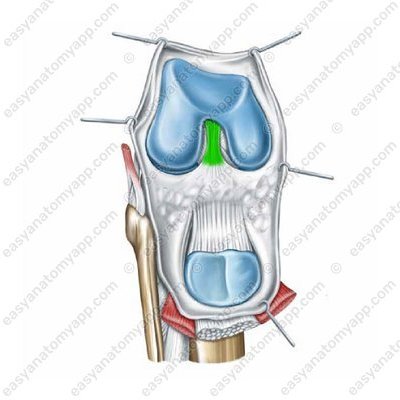
Several synovial bursae are connected to the knee joint cavity.
The suprapatellar articular bursa (bursa suprapatellaris) is located between the distal epiphysis of the femur and the tendon of the quadriceps femoris.
The deep infrapatellar bursa (bursa infrapatellaris profunda) lies between the patellar ligament and the proximal epiphysis of the tibia.
Deep infrapatellar bursa (bursa infrapatellaris profunda) 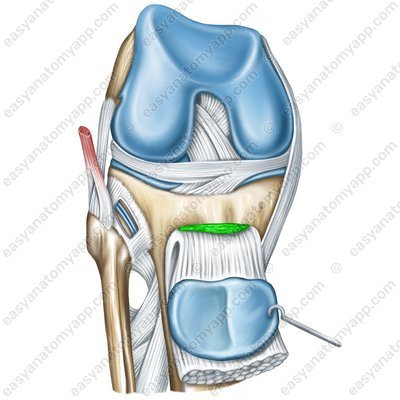
The popliteal bursa (bursa musculi poplitei)
The lateral subtendinous bursa of the gastrocnemius (bursa subtendinea musculi gastrocnemii lateralis)
The medial subtendinous bursa of the gastrocnemius (bursa subtendinea musculi gastrocnemii medialis)
Medial subtendinous bursa of the gastrocnemius (bursa subtendinea musculi gastrocnemii medialis) .jpg)
The semimembranosus bursa (bursa musculi semimembranosi)
There are also several bursae that are not communicated with the joint.
The subcutaneous prepatellar bursa (bursa subcutanea prepatellaris) is located on the anterior surface of the knee joint, at the level of the patella in the layer of subcutaneous tissue
The subtendinous prepatellar bursa (bursa prepatellaris subtendinea)
The superior bursa of the biceps femoris (bursa musculi biceps femoris superior)
The inferior bursa of the biceps femoris (bursa musculi biceps femoris inferior)
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the joint.
Arteries: descending genicular artery (a. genus descendens), lateral circumflex femoral artery (a. circumflexae femoris lateralis), popliteal artery (a. poplitea), anterior tibial artery (a. tibialis anterior), posterior tibialis artery (a. tibialis posterior)
Veins: the blood outflows through the veins with the same name
Nerves: sciatic nerve (n. ischiadicus)
Knee joint
- Knee joint
- articulatio genus
- Femur
- femur
- Tibia
- tibia
- Patella
- patella
- Articular surfaces on the condyles of the femur
- facies articularis condyli femoris
- Superior articular surface of the tibia
- facies articularis superior tibiae
- Patellar surface of the femur
- facies patellaris
- Articular surface of the patella
- facies articularis patellae
- Fibular collateral ligament
- ligamentum collaterale fibulare
- Tibial collateral ligament
- ligamentum collaterale tibiale
- Patellar ligament
- ligamentum patellae
- Oblique popliteal ligament
- ligamentum popliteum obliquum
- Arcuate popliteal ligament
- ligamentum popliteum arcuatum
- Lateral meniscus
- meniscus lateralis
- Medial meniscus
- meniscus medialis
- Transverse ligament of the knee
- ligamentum transversum genus
- Anterior cruciate ligament
- ligamentum cruciatum anterius
- Posterior cruciate ligament
- ligamentum cruciatum posterius
- Transverse ligament of the knee
- ligamentum transversum genus
- Anterior meniscofemoral ligament
- ligamentum meniscofemorale anterius
- Posterior meniscofemoral ligament
- ligamentum meniscofemorale posterius
- Medial patellar retinaculum
- retinaculum patellae mediale
- Lateral patellar retinaculum
- retinaculum patellae laterale
- Alar folds
- plicae alares
- Infrapatellar synovial fold
- plica synovialis infrapatellaris
- Suprapatellar articular bursa
- bursa suprapatellaris
- Deep infrapatellar bursa
- bursa infrapatellaris profunda
- Popliteal bursa
- bursa musculi poplitei
- Lateral subtendinous bursa of the gastrocnemius
- bursa subtendinea musculi gastrocnemii lateralis
- Medial subtendinous bursa of the gastrocnemius
- bursa subtendinea musculi gastrocnemii medialis
- Semimembranosus bursa
- bursa musculi semimembranosi
- Subcutaneous prepatellar bursa
- bursa subcutanea prepatellaris
- Subtendinous prepatellar bursa
- bursa prepatellaris subtendinea
- Superior bursa of the biceps femoris
- bursa musculi biceps femoris superior
- Inferior bursa of the biceps femoris
- bursa musculi biceps femoris inferior
- Descending genicular artery
- a. genus descendens
- Lateral circumflex femoral artery
- a. circumflexae femoris lateralis
- Popliteal artery
- a. poplitea
- Anterior tibial artery
- a. tibialis anterior
- Posterior tibialis artery
- a. tibialis posterior
- Sciatic nerve
- n. ischiadicus


