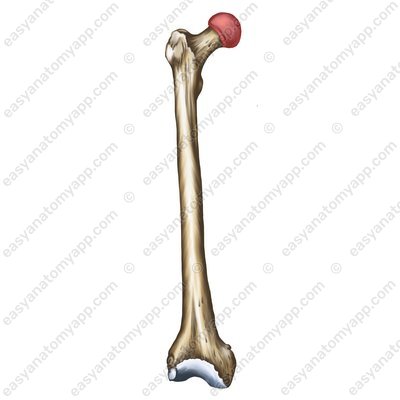
The femur is connected to the pelvic bone by the hip joint (articulatio coxae).
.jpg)
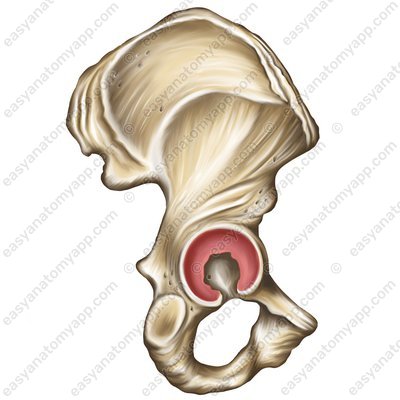
This joint is formed between the acetabular lunate articular surface (facies lunata acetabuli) and the articular surface on the head of the femur (caput femoris).
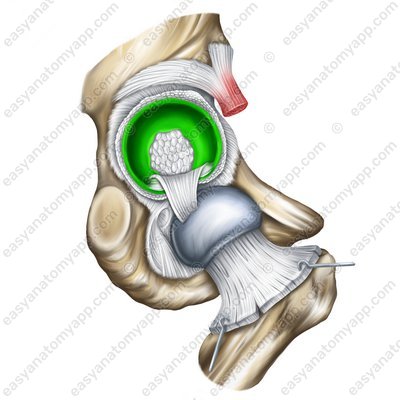
The articular capsule is attached to the pelvic bone along the edge of the acetabular labrum (labrum acetabulare), on the femur — anteriorly along the intertrochanteric line (linea intertrochanterica), from the posterior side – medially from the intertrochanteric ridge (crista intertrochanterica), and the lateral part of the neck of the femur remains outside the joint cavity.
According to the classification, the joint is cotyloid, multiaxial, simple, not combined, and complex.
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
around the frontal axis: flexion and extension
around the sagittal axis: abduction and adductio
around the vertical axis: rotation
When shifting from the frontal axis to the sagittal, circumduction may be carried out.
The fixing apparatus of the joint is composed of several ligaments:
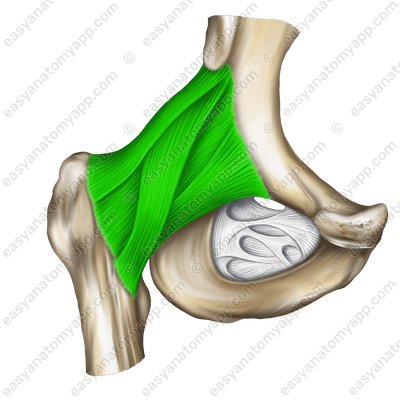
The iliofemoral ligament (ligamentum iliofemorale) arises from the anterior border of the anterior inferior iliac spine (crista iliaca anterior inferior), passes inferiorly and inserts into the intertrochanteric line (linea intertrochanterica).
Iliofemoral ligament (lig. iliofemorale) 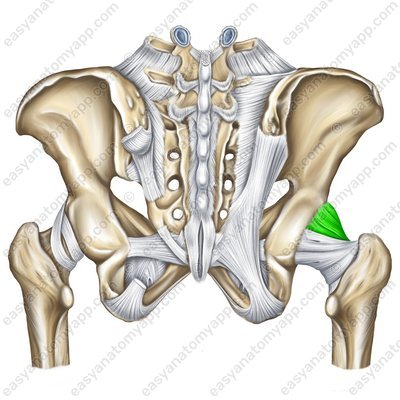
Iliofemoral ligament (lig. iliofemorale) 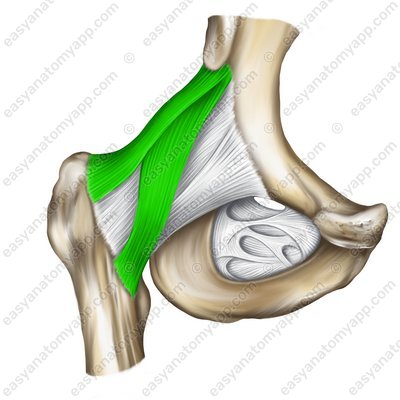
The pubofemoral ligament (ligamentum pubofemorale) arises from the superior branch of the pubis and the body of the ilium. It inserts into the medial border of the intertrochanteric line of the femur.
Pubofemoral ligament (lig. pubofemorale) 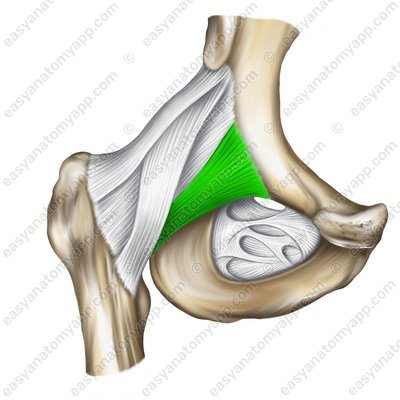
The ischiofemoral ligament (ligamentum ischiofemorale) arises from the body of the ischium, passes almost horizontally in the external direction and inserts into the trochanteric fossa of the greater trochanter.
Ischiofemoral ligament (ligamentum ischiofemorale) 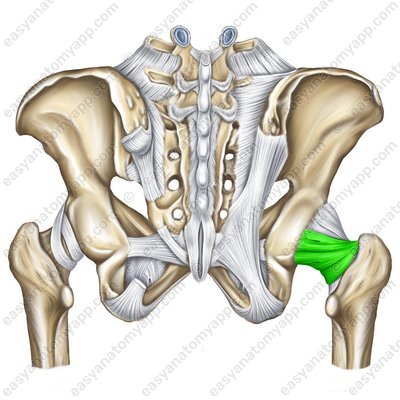
The zona orbicularis (zona orbicularis) is a bundle of circular fibers that cover the neck of the femur forming a loop and attach to the ilium under the anterior inferior iliac spine (crista iliaca anterior inferior).
Zona orbicularis (zona orbicularis) 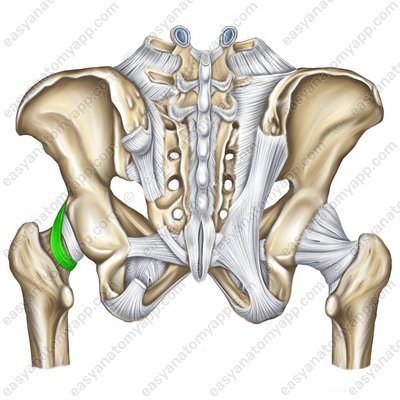
Zona orbicularis (zona orbicularis) 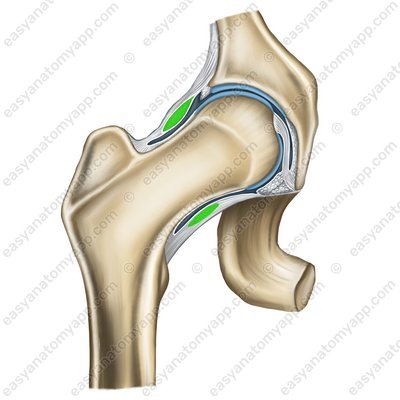
There are several additional structures to this joint.
The acetabular labrum (labrum acetabulare), which fuses with the edge of the acetabulum, deepening it. There are also two so-called intracapsular ligaments.
Acetabular labrum (labrum acetabuli) 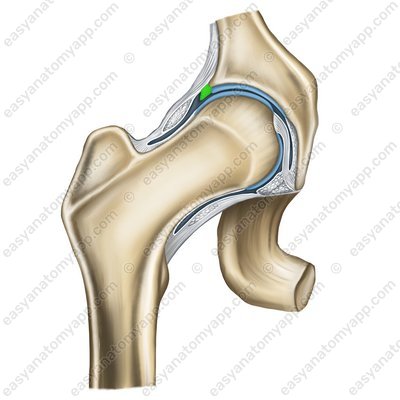
The transverse ligament of the acetabulum (ligamentum transversum acetabuli)
Transverse ligament of the acetabulum (lig. transversum acetabuli) 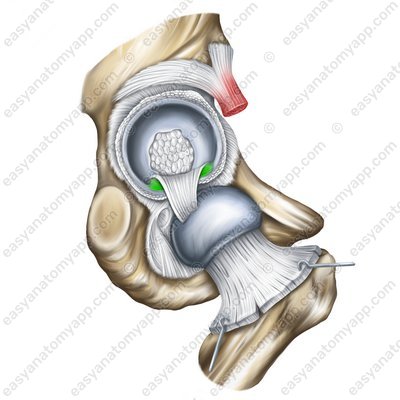
Transverse ligament of the acetabulum (lig. transversum acetabuli) 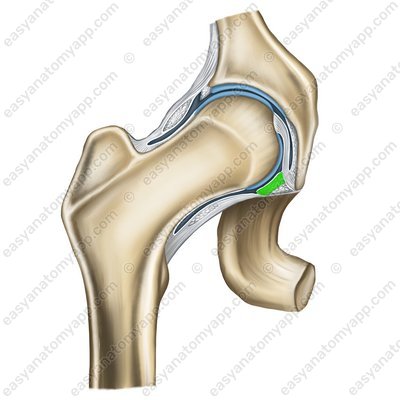
The ligament of the head of the femur (ligamentum capitis femoris)
Ligament of the head of the femur (lig.capitis femoris) 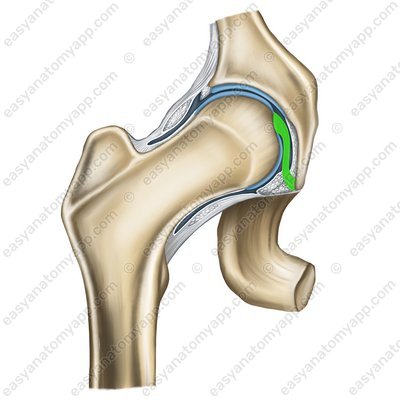
Ligament of the head of the femur (lig.capitis femoris) 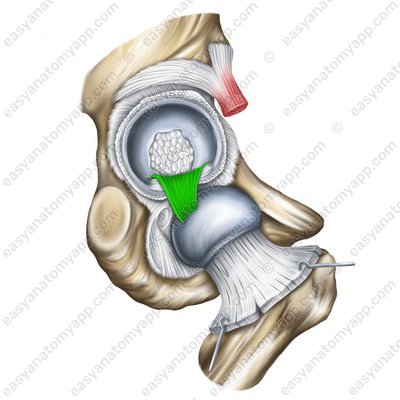
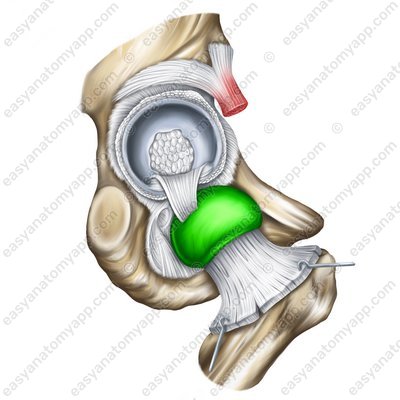
In addition, the additional structures of the hip joint include the acetabular fat pad (corpus adiposum acetabuli).
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the joint.
Arteries: obturator artery (arteria obturatoria), medial circumflex femoral artery (arteria circumflexa femoris medialis)
Veins: the blood outflows through the veins with the same name
Nerves: obturator nerve (nervus obturatorius), femoral nerve (nervus femoralis), sciatic nerve (nervus ischiadicus)
Hip joint
- Hip joint
- articulatio coxae
- Pelvic bone
- os coxae
- Femur
- femur
- Acetabular lunate articular surface
- facies lunata acetabuli
- Head of the femur
- caput femoris
- Labrum
- labrum acetabuli
- Intertrochanteric line
- linea intertrochanterica
- Intertrochanteric crest
- crista intertrochanterica
- Iliofemoral ligament
- ligamentum iliofemorale
- Anterior inferior iliac spine
- crista iliaca anterior inferior
- Pubofemoral ligament
- ligamentum pubofemorale
- Ischiofemoral ligament
- ligamentum ischiofemorale
- Zona orbicularis
- zona orbicularis
- Transverse ligaments of the acetabulum
- ligamentum transversum acetabuli
- Acetabular notch
- incisura acetabuli
- Ligament of the head of the femur
- ligamentum capitis femoris
- Acetabular fat pad
- corpus adiposum acetabuli


