The humerus is connected to the bones of the forearm by the elbow joint (articulatio cubiti).
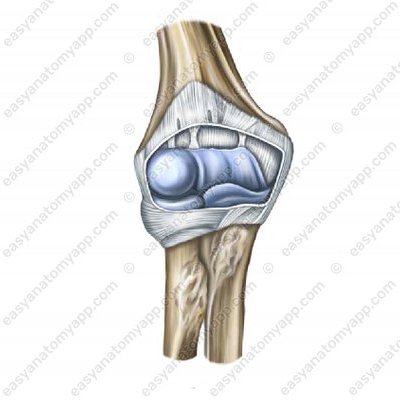
This is a complex joint that consists of 3 simple joints:
The humero-ulnar joint (articulatio humeroulnaris)
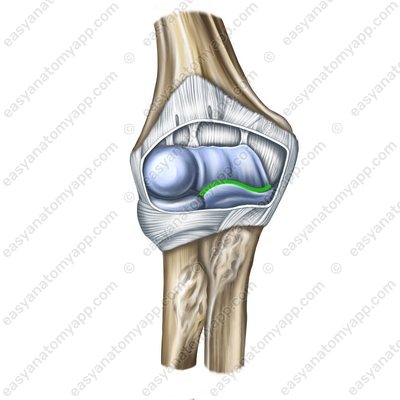
The humero-radial joint (articulatio humeroradialis)
Humero-radial joint (art. humeroradialis) 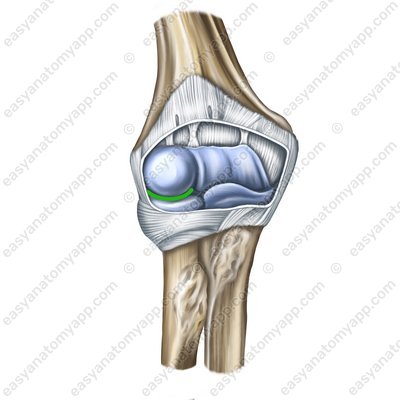
The proximal radio-ulnar joint (articulatio radioulnaris proximalis)
Proximal radio-ulnar joint (art. radioulnaris proxirnalis) 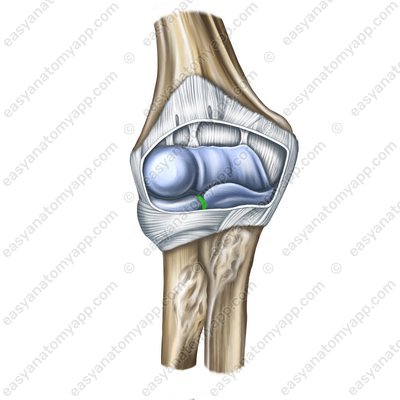
The articular capsule on the humerus covers the fossa of the olecranon fossa, the coronoid fossa, the radial fossa, leaving the condyles outside the articular cavity. On the ulna, the capsule is attached along the edge of the articular surface, and on the radius – along its neck.
Articular capsule (capsula articularis) .jpg)
Let’s learn about the structure of the humero-ulnar joint (articulatio humeroulnaris).
It is formed between the articular surfaces on the trochlea (trochlea humeri) and the trochlear notch of the ulna (incisura trochlearis ulnae).
Trochlea (trochlea humeri) 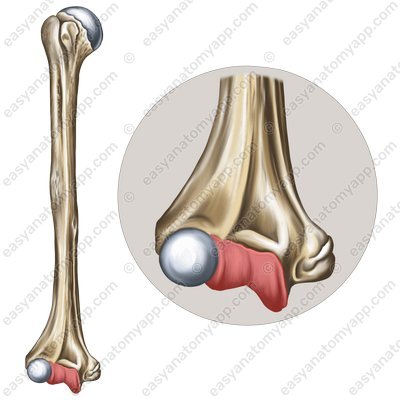
Trochlear notch of the ulna (incisura trochlearis ulnae) 
According to the classification, the joint is helical, hinge, uniaxial, and combined (with the humeroradial joint).
In the joint, flexion and extension motions around the frontal axis take place.
The ligamentous apparatus of the joint consists of several ligaments (they are common to the entire elbow joint):
The collateral ulnar ligament (ligamentum collaterale ulnare) arises from the base of the medial epicondyle of the humerus, expands in the inferior direction and inserts into the medial edge of the trochlear notch of the ulna.
Collateral ulnar ligament (lig. collaterale ulnare) 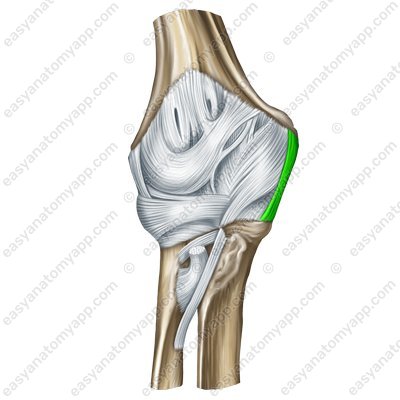
Collateral ulnar ligament(lig. collaterale ulnare) 
The collateral radial ligament (ligamentum collaterale radiale) arises from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. Descending to the head of the radius, it divides into two bundles. The anterior bundle passes anteriorly and inserts into the anterior-exterior edge of the trochlear notch of the ulna. The posterior bundle passes behind the neck of the radius, covers it in the form of a lemniscus and inserts into the annular ligament of the radius.
Collateral radial ligament (lig. collaterale radiale) 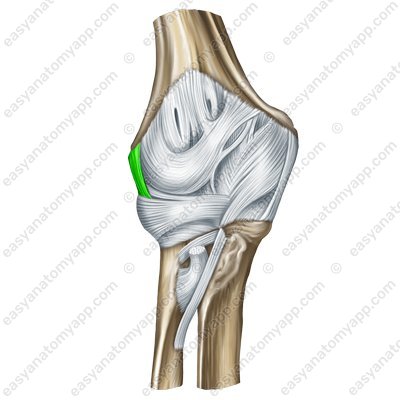
Collateral radial ligament (lig. collaterale radiale) 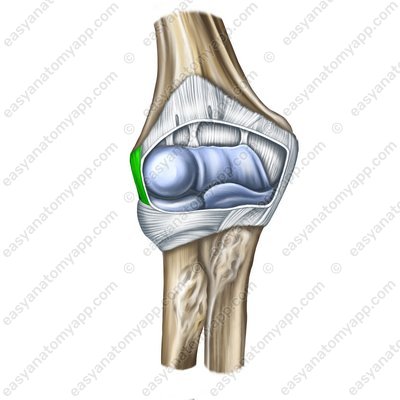
The annular ligament of the radius (ligamentum anulare radii) covers the neck of the radius and inserts at the anterior and posterior edges of the radial notch of the ulna, holding it at the lateral surface of the ulna.
This joint has no additional structures.
Annular ligament of the radius (lig. anulare radii) 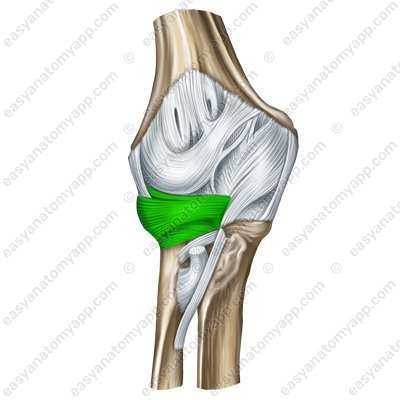
Annular ligament of the radius (lig. anulare radii) 
Let’s learn about the structure of the humero-radial joint (articulatio humeroradialis).
Humero-radial joint (art. humeroradialis) 
It is formed between the articular surfaces on the capitulum of the humerus (capitulum humeri) and the fossa of the head of the radius (fovea articularis radii).
Capitulum of the humerus (capitulum humeri) 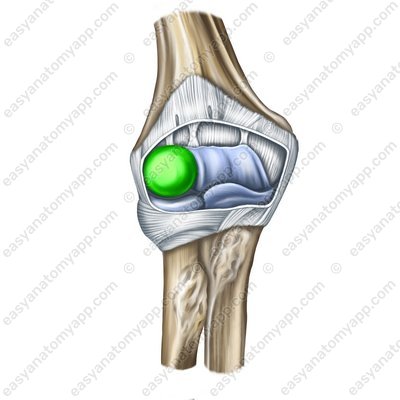
Radial fossa (fossa radialis) 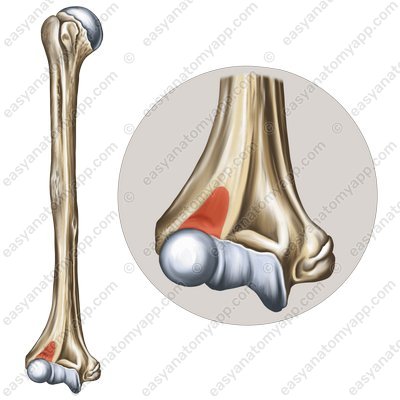
According to the classification, the joint is spherical, biaxial, and combined (with the humero-ulnar, proximal radio-ulnar and distal radio-ulnar joints).
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
Around the frontal axis: flexion and extension.
Around the vertical axis: pronation upon inward rotation, and supination upon outward rotation.
This joint has no additional structures.
Let’s learn the structure of the proximal radio-ulnar joint (articulatio radioulnaris proximalis).
Proximal radio-ulnar joint (art. radioulnaris proxirnalis) 
It is formed between the articular surfaces on the articular circumference of the radius (circumferentia articularis radii) and the radial notch of the ulna (incisura radialis ulnae).
Articular circumference of the radius (circumferentia articularis radii) 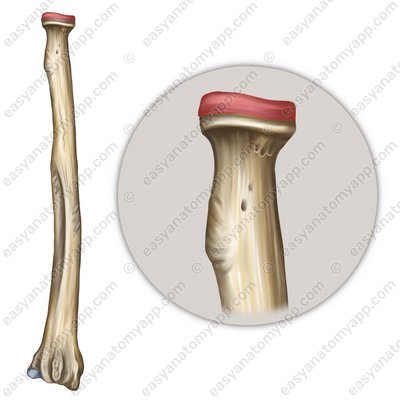
Radial notch of the ulna (incisura radialis ulnae) 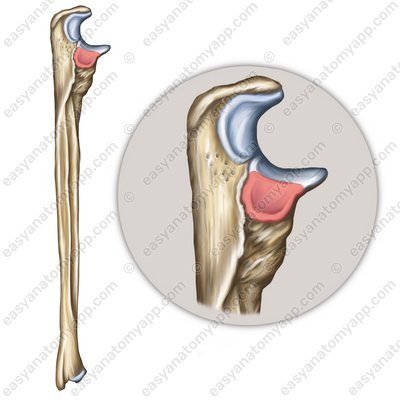
According to the classification, the joint is cylindrical, uniaxial, and combined (with the humeroradial and distal radio-ulnar joints).
Motions around the frontal axis, namely rotation, are possible in this joint.
In addition to the already mentioned ligaments, the ligamentous apparatus consists of the quadrate ligament (ligamentum quadratum). It connects the distal edge of the radial notch of the ulna with the neck of the radius.
Quadrate ligament (lig. quadratum) 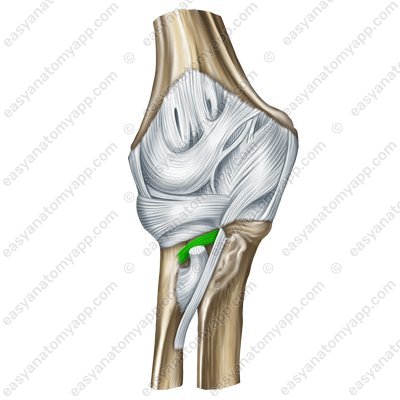
This joint has no additional structures.
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the elbow joint.
Arteries: cubital anastomosis (rete articulare cubiti)
Veins: the blood outflows through the veins with the same name
Nerves: ulnar nerve (n. ulnaris)
Elbow joint
- Elbow joint
- art. cubiti
- Humero-ulnar joint
- art. humeroulnaris
- Humeroradial joint
- art. humeroradialis
- Proximal radio-ulnar joint
- art. radioulnaris
- Humerus
- proximalis
- Ulna
- humerus ulna
- Radius
- radius
- Olecranon fossa
- fossa olecrani
- Coronoid fossa
- fossa coronoidea
- Radial fossa
- fossa radialis
- Trochlea
- trochlea humeri
- Trochlear notch of the ulna
- incisura trochlearis ulnae
- Collateral ulnar ligament
- lig. collaterale ulnare
- Collateral radial ligament
- lig. collaterale radiale
- Anular ligament of the radius
- lig. anulare radii
- Capitulum of the humerus
- capitulum humeri
- Articular circumference of the radius
- circumferentia articularis radii
- Radial notch of the ulna
- incisura radialis ulnae
- Distal radio-ulnar joint
- art. radioulnaris distalis


