The bones of the hand include the bones of the wrist (ossa carpi), metacarpal bones (ossa metacarpi) and the bones of the fingers, or phalanges (phalanges/ossa digitorum).
All of them are connected to each other with various joints. Let’s start with the carpal joints.
The first is the midcarpal joint (articulatio mediocarpalis). Essentially it is not a single, but several joints that are formed between the proximal and distal rows of the wrist bones.
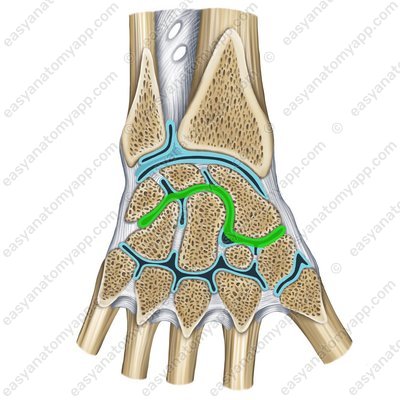
The joint gap is S-shaped. The joint has two compartments of sorts. One of them is formed by the navicular bone, which articulates with the trapezium bone and trapezoid bone. The other compartment consists of the capitate and hamate bones, which are connected to the triquetrum, lunate and navicular bones.
The articular capsule is relatively loose and very thin on the dorsal side, it inserts along the edge of the articular surfaces.
According to the classification, the joint is simple, hinge, uniaxial, and combined (with the radiocarpal joint (articulatio radiocarpea))
Almost no motions take place in this joint.
The ligamentous apparatus of this joint, as well as other wrist joints, contains several ligaments.
The palmar and dorsal intercarpal ligaments (ligamenta intercarpalia palmaria et dorsalia)
Palmar intercarpal ligaments (ligg. intercarpalia palmaria) .jpg)
Dorsal intercarpal ligaments (ligg. intercarpalia dorsalia) 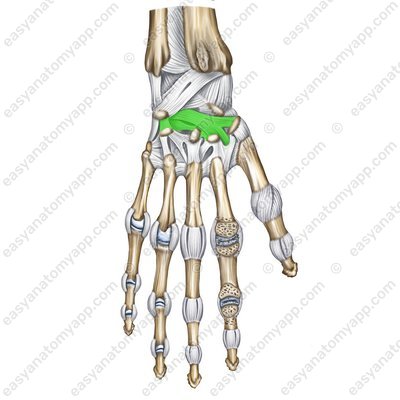
The radiate carpal ligament (ligamentum carpi radiatum)
Radiate carpal ligament (lig. carpi radiatum) 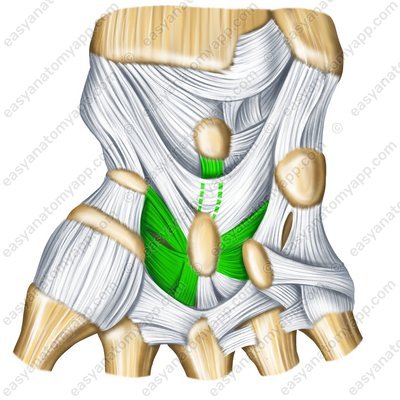
Radiate carpal ligament (lig. carpi radiatum) 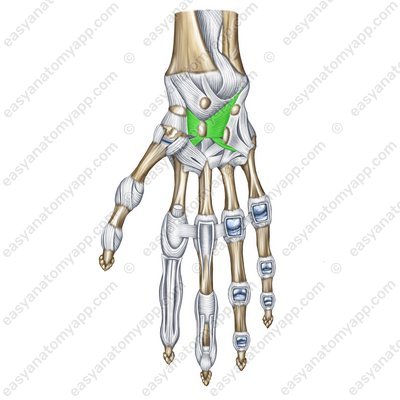
The intra-articular interosseous intercarpal ligaments (ligamenta intercarpalia interossea intraarticularia)
Intra-articular interosseous intercarpal ligaments (ligg. intercarpalia interossea) 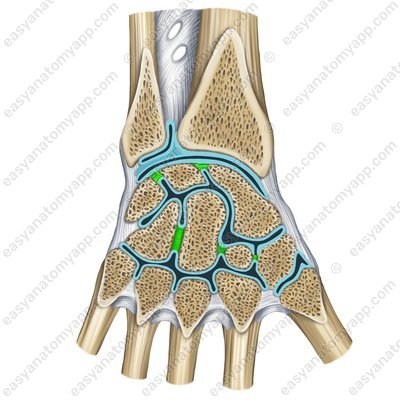
The radial collateral ligament of the wrist joint (ligamentum collaterale carpi radiale)
Radial collateral ligament of the wrist joint – palmar surface (lig. collaterale carpi radiale) 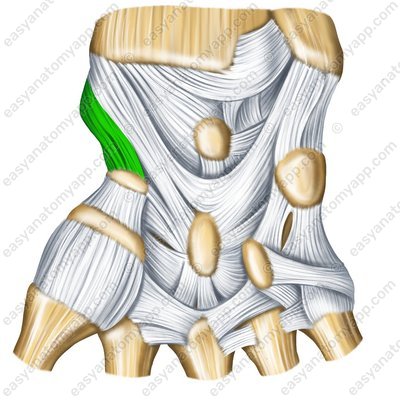
Radial collateral ligament of the wrist joint – back surface (lig. collaterale carpi radiale) 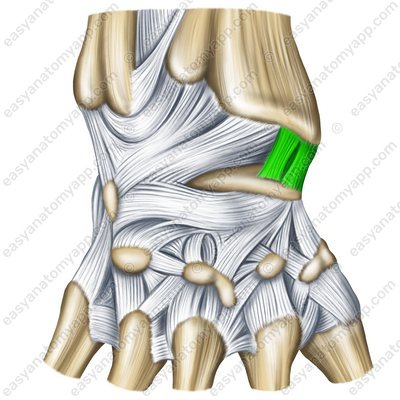
Radial collateral ligament of the wrist joint – sawing (lig. collaterale carpi radiale) 
The ulnar collateral ligament of wrist joint (ligamentum collaterale carpi ulnare)
Ulnar collateral ligament of wrist joint – palmar surface (lig. collaterale carpi ulnare) 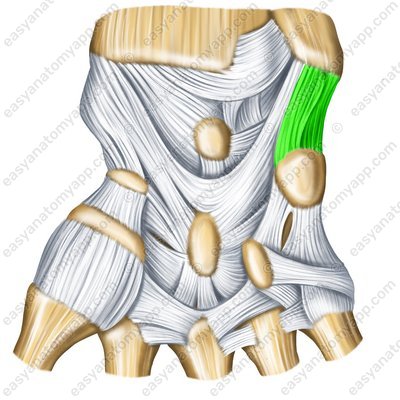
Ulnar collateral ligament of wrist joint – back surface (lig. collaterale carpi ulnare) 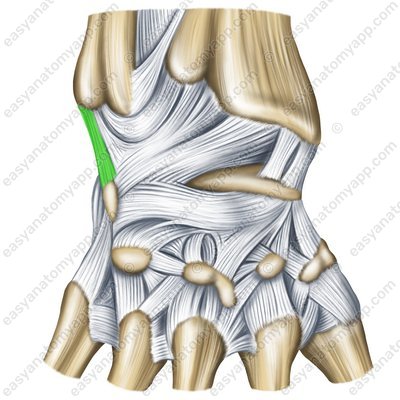
Ulnar collateral ligament of wrist joint – sawing (lig. collaterale carpi ulnare) 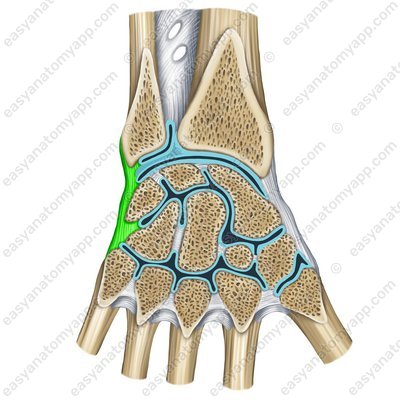
The pisohamate ligament (ligamentum pisohamatum)
Pisohamate ligament (lig. pisohamatum) 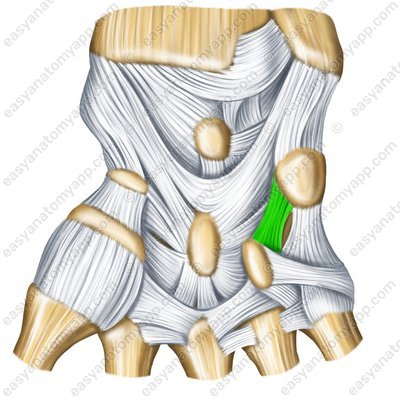
Pisohamate ligament (lig. pisohamatum) 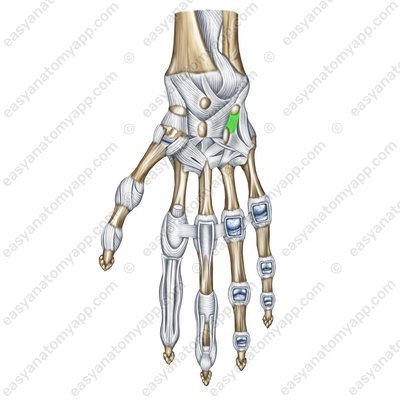
The pisometacarpal ligament (ligamentum pisometacarpale)
Pisometacarpal ligament (lig. pisometacarpale) 
Pisometacarpal ligament (lig. pisometacarpale) 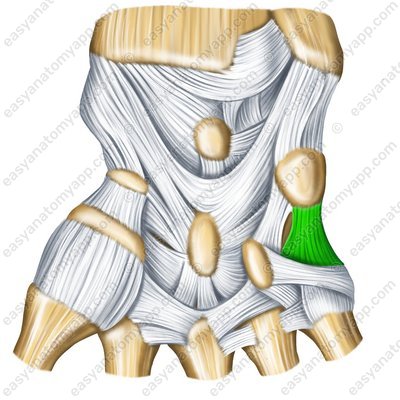
Next, let’s learn about the intercarpal joints (articulationes intercarpales). They are formed between the articular surfaces of the carpal bones facing each other.
Intercarpal joints (artt. intercarpales) 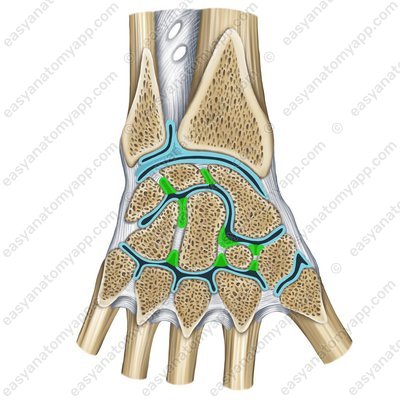
These are triquetrum bone (os triquetrum), lunate bone (os lunatum), scaphoid bone (os scaphoideum), trapezium bone (os trapezium), trapezoid bone (os trapezoideum), capitate bone (os capitatum), hamate bone (os hamatum) and pisiform bone (os pisiforme).
The capsules of this joints are thin, they insert along the edges of the articular surfaces.
The joint cavities of the midcarpal and intercarpal joints communicate with each other.
According to the classification, the joint is simple and plane. Almost no motions take place in this joint.
Let’s move on to the carpometacarpal joints (articulationes carpometacarpales).
Carpometacarpal joints (artt. carpometacarpales) 
Carpometacarpal joints (artt. carpometacarpalis) .jpg)
These joints are formed between the distal articular surfaces of the second row of wrist bones and articular surfaces on the bases of the 2nd-5th metacarpals.
The articular capsule is thin, common to all four carpometacarpal joints, and stretched tightly.
Carpometacarpal joints (artt. carpometacarpales) .jpg)
The joint gap is also common, it is an angled line that connects to the cavities of the intercarpal and midcarpal joints.
According to the classification, carpometacarpal joints are simple and plane, there are practically no motions in them.
The fixing apparatus of the joint is composed of several ligaments:
The palmar carpometacarpal ligaments (ligamenta carpometacarpalia palmaria) are located on the palmar surface of the hand
Palmar carpometacarpal ligaments (ligg. carpometacarpalia palmaria) 
The dorsal carpometacarpal ligaments (ligamenta carpometacarpalia dorsalia) are located on the back surface of the hand.
Dorsal carpometacarpal ligaments (ligg. carpometacarpaliadorsalia) 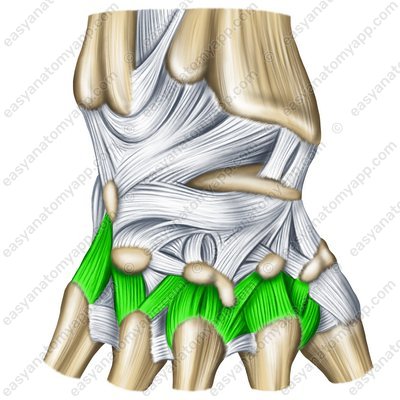
Let’s learn about the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb (articulatio carpometacarpalis pollicis).
Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb – sawing (artt. carpometacarpalis pollicis) 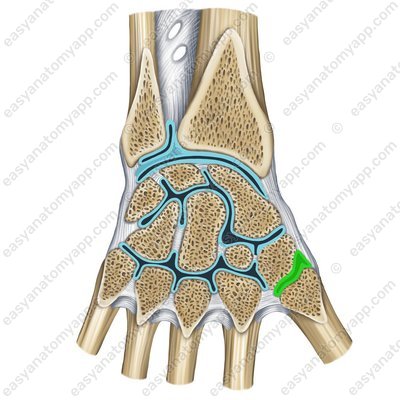
The articular surfaces involved in the formation of the joint are the articular surface of the trapezium bone and the articular surface of the base of the first metacarpal bone.
The joint capsule is loose, thin.
According to the classification, the joint is simple, saddle-shaped, and not combined.
Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb – palmar surface (artt. carpometacarpalis pollicis) .jpg)
Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb – palmar surface (artt. carpometacarpalis pollicis) .jpg)
Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb – back surface (artt. carpometacarpalis pollicis) _1.jpg)
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
Around the frontal axis: flexion and extension. Since the frontal axis is located at an angle with respect to the frontal plane, the thumb tilts towards the palm during flexion, it is opposed to the rest of the fingers.
Around the sagittal axis, the thumb is adducted (adductio) to the index finger (index).
With a combination of movements around the frontal and sagittal axes, circumduction takes place.
Let’s move on to the intermetacarpal joints (articulationes intermetacarpales).
Intermetacarpal joints (artt. intermetacarpalis) 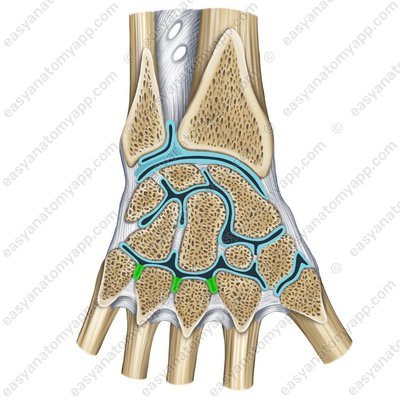
The articular surfaces involved in the formation of the joint are the adjacent articular surfaces of the bases of the 2nd- 5th metacarpals.
The joint capsules are common with the capsule of the carpometacarpal joints.
The ligamentous apparatus of the joint includes the palmar and dorsal metacarpal ligaments (ligamenta metacarpalia palmaria et dorsalia)
Palmar metacarpal ligaments (lig. metacarpalia palmaria) 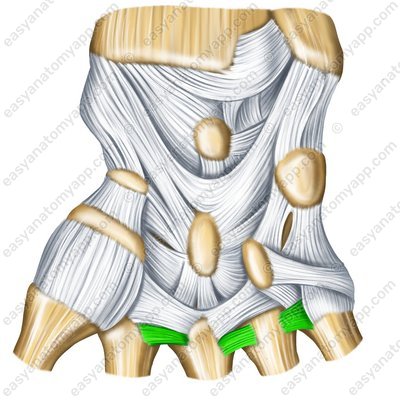
Dorsal metacarpal ligaments (lig. metacarpalia dorsalia) 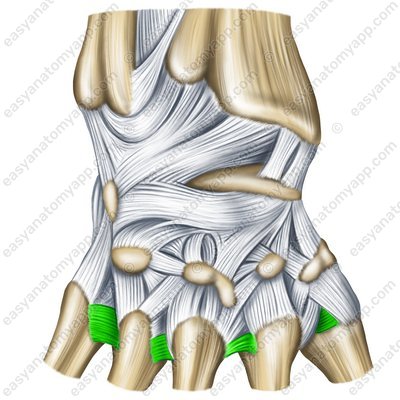
Palmar metacarpal ligaments (lig. metacarpalia palmaria) 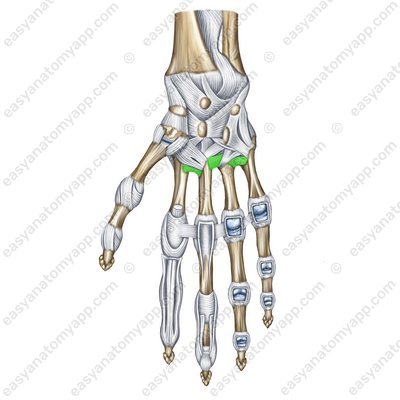
Next come the metacarpophalangeal joints (articulationes metacarpophalangeae).
They are formed between the articular surfaces on the base of the proximal phalanx (phalanx proximalis) and the corresponding head of the metacarpal bone (os metacarpale).
Metacarpophalangeal joints – palmar surface (artt. metacarpophalangeae) .jpg)
Metacarpophalangeal joints – back surface (artt. metacarpophalangeae) .jpg)
The joint capsule is loose, attached along the edges of the articular surfaces.
According to the classification, the joint is condylar, ellipsoid, biaxial and not combined.
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
around the frontal axis: flexion and extension
around the sagittal axis: abduction and adductio
Circular motion takes place with a shift from one axis to another.
The fixing apparatus of the joint is composed of several ligaments:
The lateral collateral ligaments (ligamenta collateralia) fix the joints along the lateral surfaces.
Lateral collateral ligaments – palmar surface (lig. collateralia) 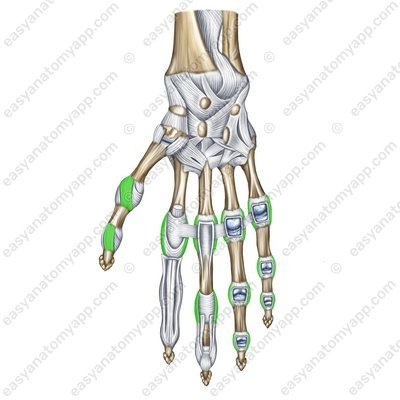
Lateral collateral ligaments – back surface (lig. collateralia) 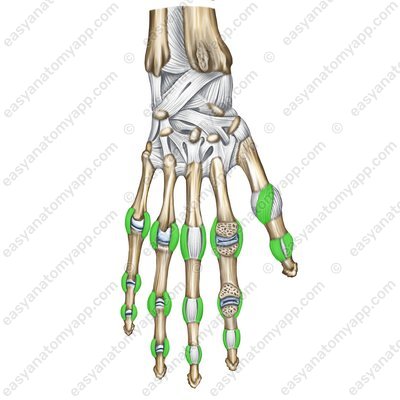
The palmar ligaments (ligamenta palmaria) fix joints on the palmar surface.
Palmar ligaments (lig. palmaria) 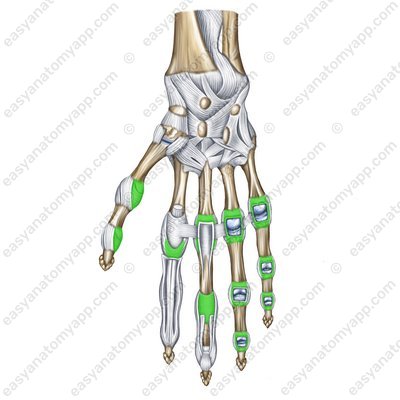
The deep transverse metacarpal ligaments (ligamenta metacarpalia transversa profunda) are stretched between the heads of the 2nd-5th metacarpals.
Deep transverse metacarpal ligaments (ligamenta metacarpalia transversa profunda) 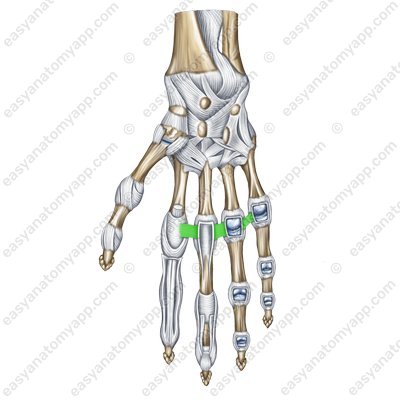
And the last joints of the hand are the interphalangeal joints (articulationes interphalangeae manus)
They are formed between the articular surfaces on the corresponding bases and the heads of the phalanges.
The joint capsule is attached along the edge of the articular surfaces.
Interphalangeal joints – back surface (artt. interphalangeae) .jpg)
Interphalangeal joints – palmar surface (artt. interphalangeae) .jpg)
According to the classification, the joint is simple, hinge, uniaxial and not combined.
In the joint, flexion and extension motions around the frontal axis take place.
The fixing apparatus of the joint is composed of several ligaments:
The lateral collateral ligaments (ligamenta collateralia) fix the joints along the lateral surfaces.
Lateral collateral ligaments – palmar surface (lig. collateralia) 
Lateral collateral ligaments – back surface (lig. collateralia) 
The palmar ligaments (ligamenta palmaria) fix the joints on the palmar surface.
Palmar ligaments (lig. palmaria) 
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the hand joints.
Arteries: branches of the deep arterial arch of the hand, branches of the palmar and dorsal plexuses of the hand
Veins: veins of the same name
Nerves: branches of the ulnar, median, and radial nerves
Joints of the wrist
- Midcarpal joint
- art. mediocarpalis
- Triquetrum bone
- os triquetrum
- Lunate bone
- os lunatum
- Scaphoid bone
- os scaphoideum
- Trapezium bone
- os trapezium
- Trapezoid bone
- os trapezoideum
- Capitate bone
- os capitatum
- Hamate bone
- os hamatum
- Wrist joint
- art. radiocarpea
- Intercarpal joints
- art. intercarpales
- Pisiform bone
- os pisiforme
- Palmar and dorsal intercarpal ligaments
- ligg. intercarpalia palmaria et dorsalia
- Radiate carpal ligament
- lig. carpi radiatum
- Interosseous intercarpal ligaments
- ligg. intercarpalia interossea
- Pisohamate ligament
- lig. pisohamatum
- Pisometacarpal ligament
- lig. pisometacarpale
- Carpometacarpal joints of the fingers 2-5
- artt. carpometacarpales II-V
- Metacarpal bones 2-5
- ossa metacarpalia II-V
- Palmar carpometacarpal ligaments
- ligg. carpometacarpalia palmaria
- Dorsal carpometacarpal ligaments
- ligg. carpometacarpalia dorsalia
- 1st metacarpal bone
- os metacarpale I
- Index finger
- index
- Intermetacarpal joints
- artt. intermetacarpales
- Palmar and dorsal metacarpal ligaments
- ligg. metacarpalia palmaria et dorsalia
- Wrist joint
- art. manus
- Metacarpophalangeal joints
- art. metacarpophalangeae
- Proximal phalanx
- phalanx proximalis
- Metacarpal bone
- os metacarpale
- Collateral ligaments
- ligg. collateralia
- Palmar ligaments
- ligg. palmaria
- Deep transverse metacarpal ligaments
- ligg. metacarpalia transversa profunda
- Interphalangeal joints
- artt.interphalangeaephalanges
- Phalanges of the fingers
- phalanges
- Dorsal carpal arch
- rete carpale dorsale
- Deep palmar arch
- arcus palmaris profundus
- Superficial palmar arch
- arcus palmaris superficialis
- Ulnar nerve
- n. ulnaris
- Median nerve
- n. medianus


