The vertebral column is connected to the skull with three joints: the atlanto-occipital, the median atlanto-axial and the lateral atlanto-axial joint.
Let’s learn about the structure of the atlanto-occipital joint (articulatio atlantooccipitalis).
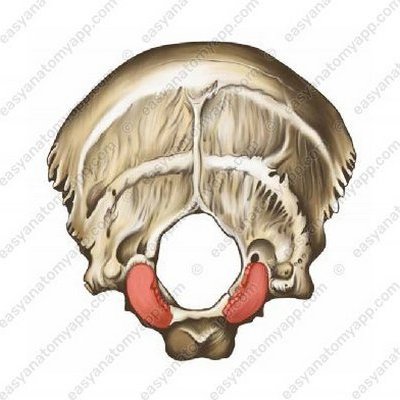
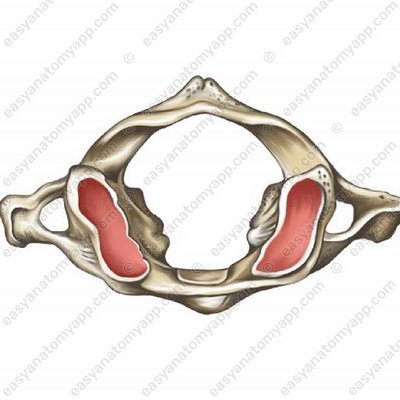
This joint is formed between the articular surface on the occipital condyle (condylus occipitalis) and the superior articular surface of the atlas (facies articularis superior).
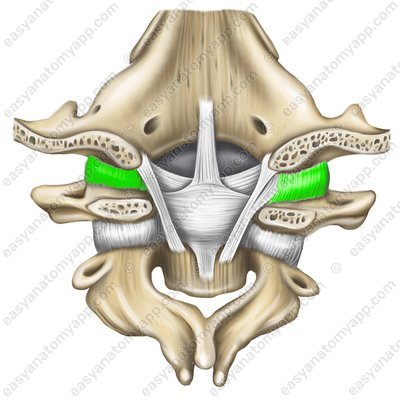
The articular capsule (capsula articularis) is attached along the border of the articular surfaces, it is thin, fibrous, and elastic.
.jpg)
According to the classification, this joint is ellipsoid, biaxial, simple and combined (with the same joint of the opposite side).
The following range of motions is possible in the joint:
Around the frontal axis – the head tilts back and forth (nodding).
Around the sagittal axis – the head tilts to the right and left.
And when moving from one axis to another — circular motion (circumductio)
The fixing apparatus of the joint is represented by several ligaments:
The anterior atlanto-occipital membrane (membrana atlantooccipitalis anterior) is stretched between the basilar part of the occipital bone and the superior margin of the anterior arch of the atlas
Anterior atlanto-occipital membrane (membrana atlantooccipitalis anterior) 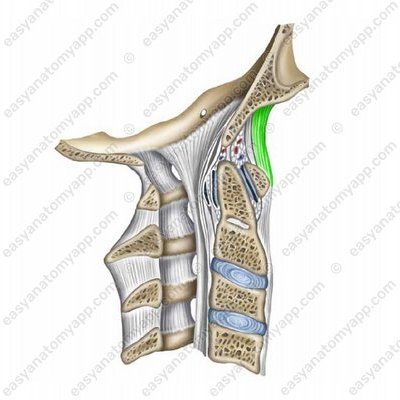
Cruciate ligament of the atlas (ligamentum cruciforme atlantis). It consists of three bundles:
Cruciate ligament of the atlas (lig. cruciforme atlantis) 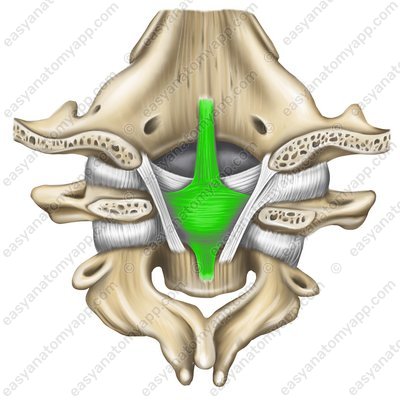
Superior longitudinal fasciculus (fasciculus longitudinalis superior)
Superior longitudinal fasciculus (fasciculus longitudinalis superior) 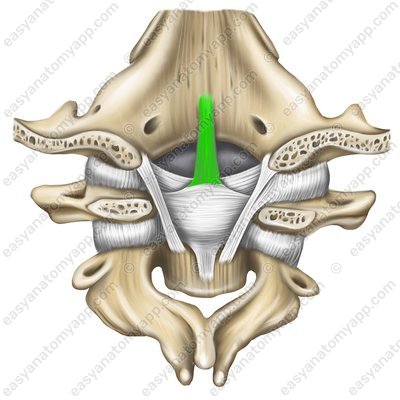
Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (fasciculus longitudinalis inferior)
Inferior longitudinal fasciculus (fasciculus longitudinalis inferior) 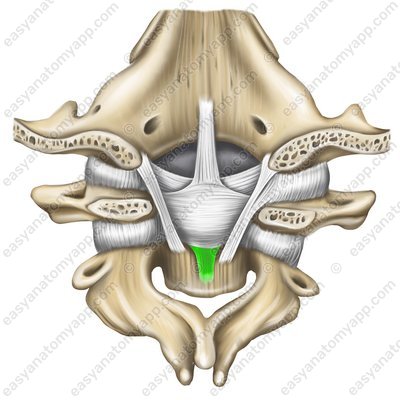
Transverse ligament of the atlas (ligamentum transversum atlantis)
Transverse ligament of the atlas (lig. transversum atlantis) 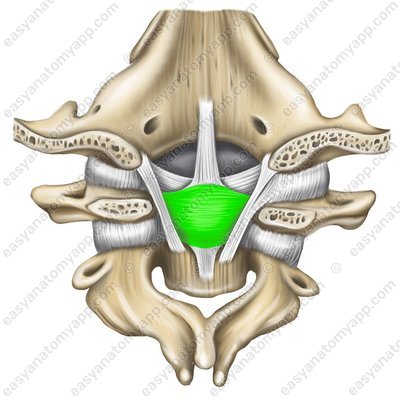
Other ligaments that strengthen the joint are:
Alar ligaments (ligamenta alaria)
Alar ligaments (ligg. alaria) 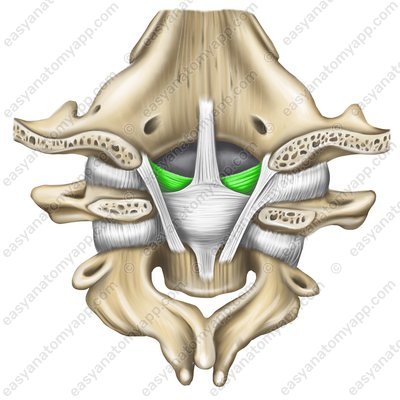
Tectorial membrane (membrana tecroria)
Tectorial membrane (membrana tectoria) 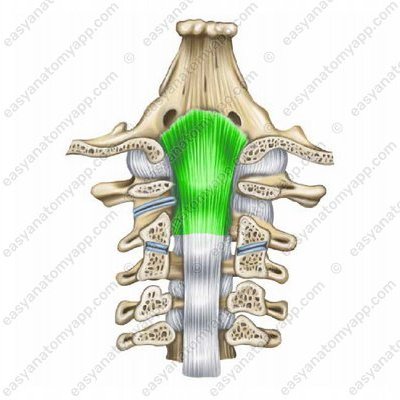
The following muscles act on the joint.
Head tilt forward (with bilateral contraction) – m. longus capitis, m. rectus capitis anterior, m. rectus capitis lateralis, m. sternocleidomastoideus
Head tilt backwards (with bilateral contraction) – mm. rectus capitis posterior major et minor, m. sternocleidomastoideus, m. obliquus capitis superior, m. trapezius, m. splenius capitis, m. longissimus capitis, m. semispinalis capitis
Side tilts – the above muscles of the right or left side.
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the joint.
Arteries: muscular branches of the vertebral artery (rami musculares a. vertebralis)
Veins: vertebral venous plexus (plexus venosi vertebrales)
Nerves: posterior branches of the II spinal nerve (r. dorsalis n. spinalis II)
Atlanto-occipital joint
- Atlanto-occipital joint
- articulatio atlantooccipitalis
- Condyle of the occipital bone
- condylus occipitalis
- Superior articular fissure of the atlas
- facies articularis superior
- Anterior atlanto-occipital membrane
- membrana atlantooccipitalis anterior
- Cruciate ligament of the atlas
- lig. cruciforme atlantis
- Transverse ligament of the atlas
- lig. transversum atlantis
- Superior longitudinal fasciculus
- fasciculus longitudinalis superior
- Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
- fasciculus longitudinalis inferior
- Alar ligaments
- ligg. alaria
- Tectorial membrane
- membrana tectoria


