The thoracic cage (compages thoracis), sometimes simply thorax)) is formed by 12 pairs of ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and the sternum.

The ribs are connected to the sternum by the sternocostal joints (articulationes sternocostales), and to the vertebrae by the joint of the head of the rib (articulatio capitis costae) and the costotransverse joint (articulatio costotransversaria).
Let’s learn about the structure of the joint of the head of the rib (articulatio capitis costae).
.jpg)
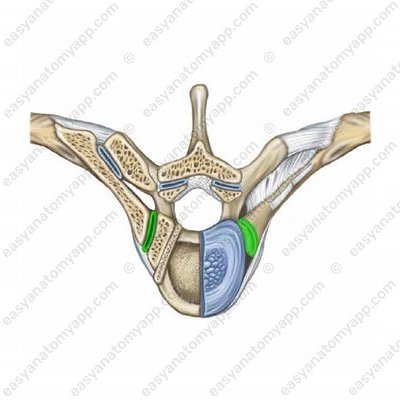
It is formed between the articular surface of the rib of the head (facies articularis capitis costae);
and the costal facets, as well as the semi-facets on the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae (foveae costales).
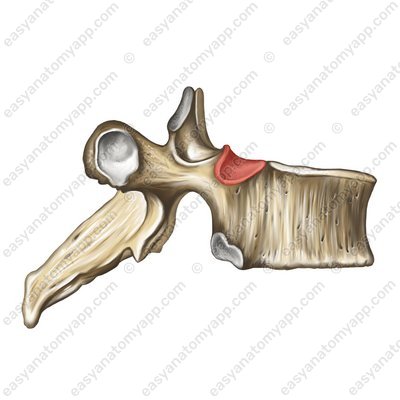
The joint capsule is attached along the edge of the articular surfaces, it is quite dense.
According to the classification, the joint is simple, uniaxial, combined (with costotransverse and sternocostal joints) and saddle-shaped (for ribs 2-10) or ball-and-socket type (for ribs 1, 11 and 12).
The following range of motions takes place in the joint: lifting and lowering of the thoracic cage. In this case, the axis around which this motion takes place passes through the neck of the rib.
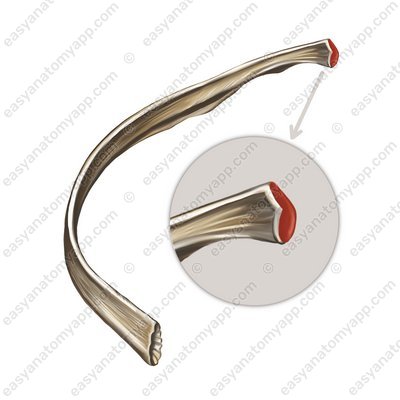
The fixing apparatus of the joint is the radiate ligament of the head of the rib (ligamentum capitis costae radiatum), which begins on the anterior surface of the head of the rib and attaches to the intervertebral disc, as well as the bodies of adjacent vertebrae.
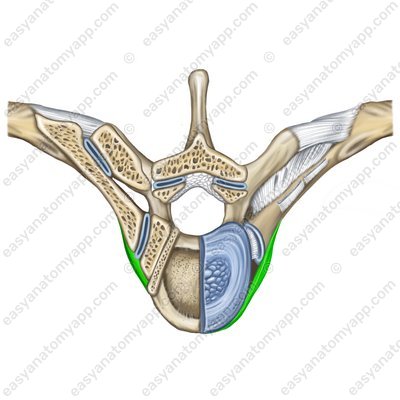
The additional structures include the intra-articular ligament of the head of the rib (ligamentum capitis costae intraarticulare).
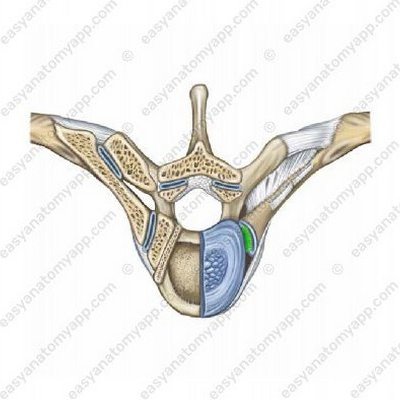
Only the joints 2-10 have it. It arises from the ridge of the head of the rib and inserts into the intervertebral disc, which separates the articular semifossae of the superimposed and the underlying vertebrae.
The following vessels and nerves take part in the blood supply and innervation of the joint.
Arteries: supreme intercostal artery, posterior intercostal arteries 1-10
Nerves: posterior branches of spinal nerves (C8-T11)
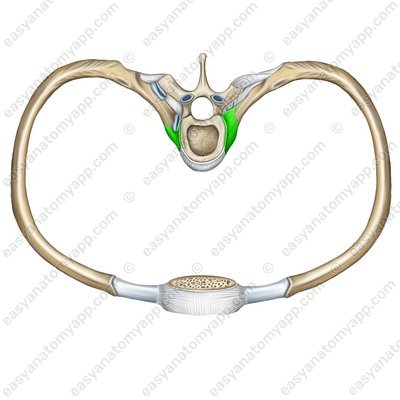
Now let’s learn about the structure of the costotransverse joint (articulatio costotransversaria).
Costotransverse joint (art. costotransversaria) 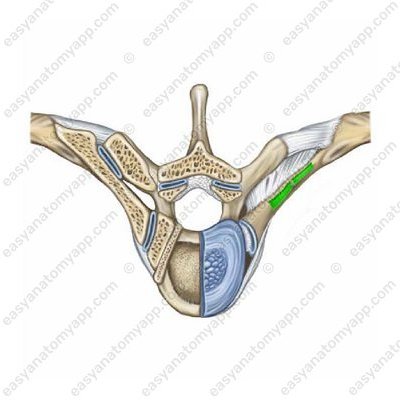
Costotransverse joint – cracked open (art. costotransversaria) .jpg)
It is present only in pairs of ribs 1-10 and is formed between the articular surface on the transverse costal facet (fovea costalis transversalis) and the articular facet (tuberculum costae).
Transverse costal facet (fovea costalis transversalis) 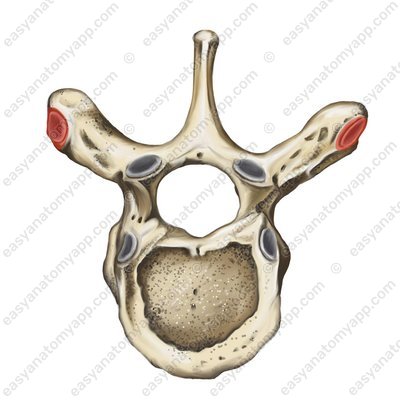
Articular facet (tuberculum costae) .jpg)
The joint capsule is attached along the edge of the articular surfaces, it is quite dense.
According to the classification, the joint is cylindrical, uniaxial, simple and combined (with a joint of the head of the rib and sternocostal joints)
The range of motion is similar to the joint of the head of the rib. It includes lifting and lowering of the thoracic cage.
The fixing apparatus of the joint is composed of several ligaments:
The costotransverse ligament (ligamentum costotransversarium) connects the dorsal part of the neck of the femur with the ventral part of the corresponding transverse process.
Costotransverse ligament (lig. costotransversarium) 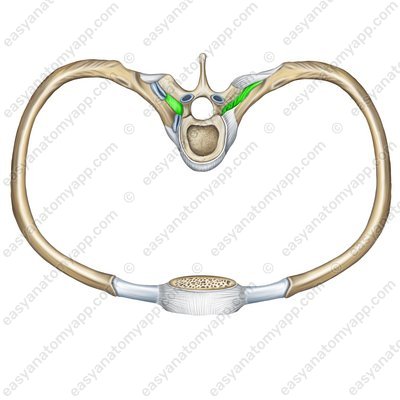
Costotransverse ligament (lig. costotransversarium) 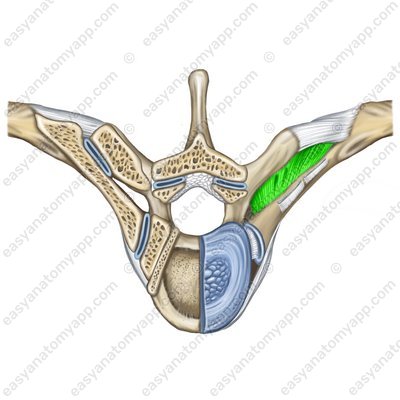
The superior costotransverse ligament (ligamentum costotransversarium superius) connects the neck of the femur with the superposed transverse process.
Superior costotransverse ligament (lig. costotransversarium superius) 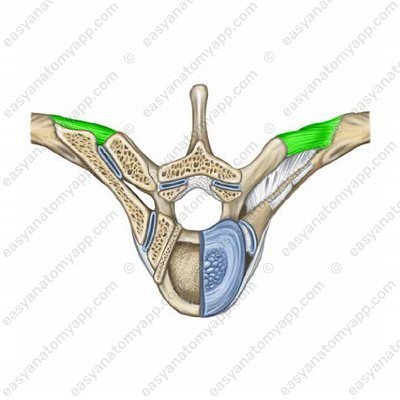
The lateral costotransverse ligament (ligamentum costotransversarium laterale) connects the tubercle of the rib with the end of the transverse process.
Lateral costotransverse ligament (lig. costotransversarium laterale) 
Lateral costotransverse ligament (lig. costotransversarium laterale) 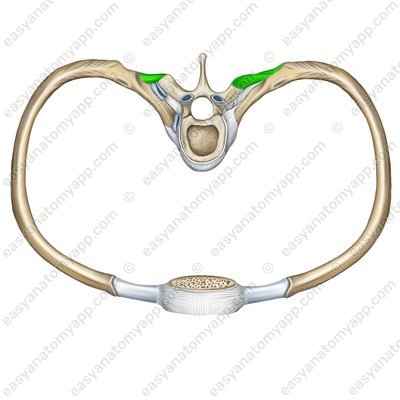
Let’s learn about the structure of the sternocostal joint (articulatio sternocostalis).
Sternocostal joint (artt. sternocostales) .jpg)
Such joints are formed between the anterior ends of the cartilages of the ribs 2-7 and the costal notches of the sternum.
The articular capsule is a direct continuation of the perichondrium of the costal cartilages and is strenghened by radiate sternocostal ligaments (ligamenta sternocostalia radiata). Anteriorly, they fuse with the periosteum of the sternum, forming a dense membrane of the sternum.
Radiate sternocostal ligaments (ligg. sternocostalia radiata) 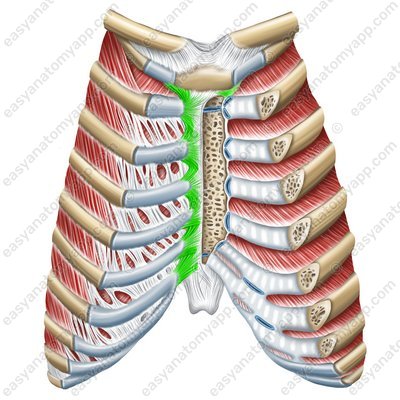
Radiate sternocostal ligaments (ligg. sternocostalia radiata) 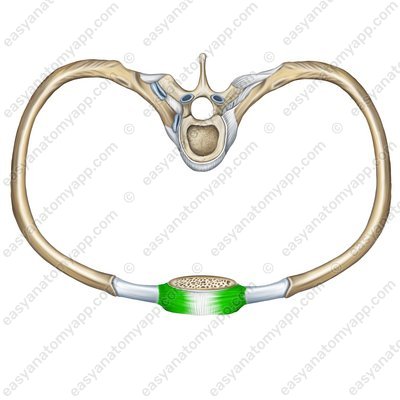
The cartilages of the ribs 8-10 do not connect to the sternum but fuse together to form a costal arch (arcus costalis).
Costal arch (arcus costalis) 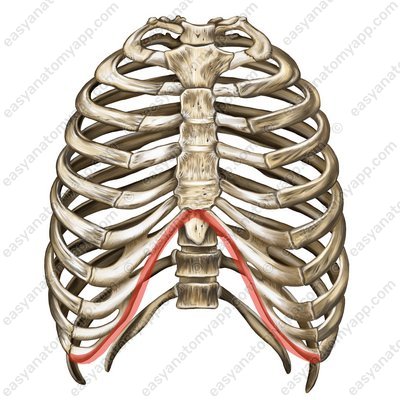
The anterior sections of all ribs are additionally connected to each other by means of an external intercostal membrane (membrana intercostalis externa)
External intercostal membrane (membrana intercostalis externa) 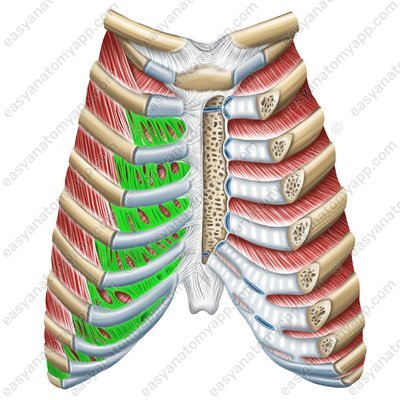
And the posterior sections of the ribs are additionally connected to each other by an internal intercostal membrane (membrana intercostalis interna).
Internal intercostal membrane (membrana intercostalis interna) 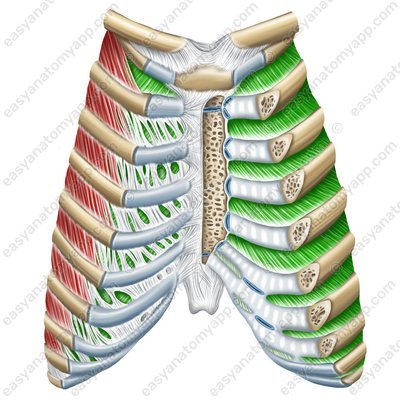
During breathing, the posterior ends of the ribs rotate in the joint of the head of the rib and the costotransverse joint. Upon inhalation, the anterior ends of the ribs and the sternum lift, the intercostal spaces widen. Upon exhalation, the front ends of the ribs and the sternum are lowered.
The joint of the first rib with the sternum is called the sternocostal synchondrosis (synchondrosis sternocostalis).
There are two apertures (in and out openings) at the thoracic cage.
The superior aperture (apertura thoracis superior) is located between the first thoracic vertebra and the first rib.
Superior aperture (apertura thoracis superior) 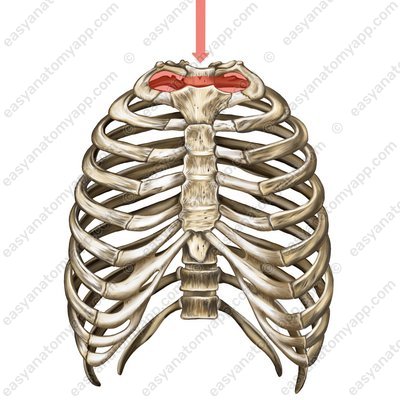
The inferior aperture (apertura thoracis inferior) is located between the xiphoid process, the costal arch (arcus costalis) and the tenth (according to some sources – the twelfth) thoracic vertebra. This aperture is covered by a special respiratory muscle – the diaphragm.
Inferior aperture (apertura thoracis inferior) 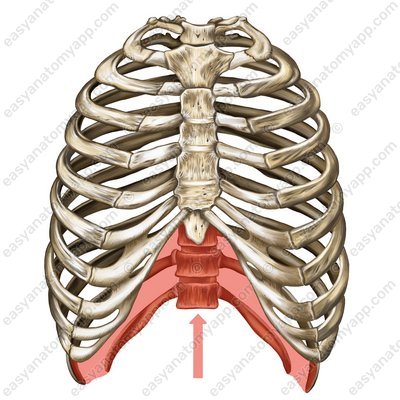
Between two adjacent ribs there is an intercostal space (spatium intercostale), which is covered by muscles and ligaments.
Intercostal space (spatia intercostales) 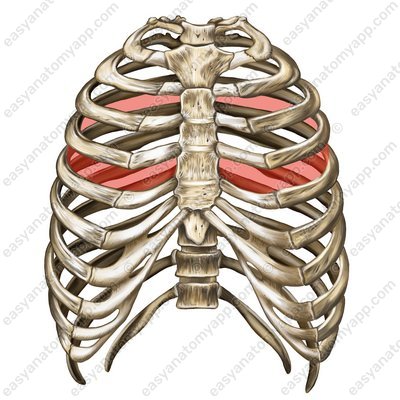
At the junction of the costal arches with the sternum, an infrasternal angle (angulus infrasternalis) is formed.
Infrasternal angle (angulus infrasternalis) 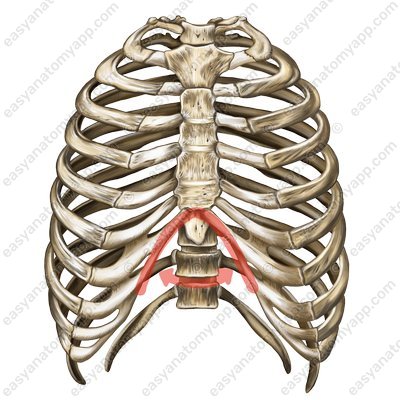
Between the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae and the inner surface of the ribs, there is the so-called pulmonary groove (sulcus pulmonalis) adjacent to the lungs.
Depending on the type of physique, there are different types of the thoracic cage:
Asthenic type: the thoracic cage is narrow with wide intercostal spaces. Infrasternal angle <90°
Normosthenic type: the thoracic cage is of medium width. Infrasternal angle = 90°
Hypersthenic type: the thoracic cage is wide, with narrow intercostal spaces. Infrasternal angle >90°
In men, the thoracic cage is cone-shaped, longer and wider, and in women it is cylindrical, shorter and narrower.
Joints and Ligaments of the Thorax
- Thoracic cavity
- cavitas thoracis
- Thoracic cage
- compages thoracis
- Costotransverse joint
- art. costotransversaria
- Vertebra
- vertebra
- Rib
- costa
- Transverse costal facet
- fovea costalis transversalis
- Tubercle of the rib
- tuberculum costae
- Joint of the head of the rib
- art. capitis costae
- Sternocostal joints
- artt. sternocostales
- Costotransverse ligament
- lig. costotransversarium
- Superior costotransverse ligament
- lig. costotransversarium superius
- Lateral costotransverse ligament
- lig. costotransversarium laterale
- Superior and inferior costal foveae
- foveae costales superior et inferior
- Head of the rib
- caput costae
- Radiate ligament of the head of the rib
- lig. capitis costae radiatum
- Intra-articular ligament of the head of the rib
- lig. capitis costae intraarticulare
- Posterior intercostal arteries
- aa. intercostales posteriores
- Sternocostal synchondrosis
- synchondrosis sternocostalis
- Radiate sternocosta ligaments
- ligg. sternocostalia radiata
- Costal arc
- arcus costalis
- Interchondral joints
- artt. interchondrales
- External intercostal membrane
- membrana intercostalis externa
- Internal intercostal membrane
- membrana intercostalis interna
- Intercostal spaces
- spatia intercostales
- Superior thoracic aperture
- apertura thoracis superior
- Inferior thoracic aperture
- apertura thoracis inferior
- Thoracic cavity
- cavitas thoracis
- Thoracic cage
- compages thoracis
- Costotransverse joint
- art. costotransversaria


