In this note, we will consider the anatomy of the gallbladder and biliary tract.
Gallbladder (vesica fellea или vesica biliaris) is a hollow organ in which bile accumulates and concentrates.
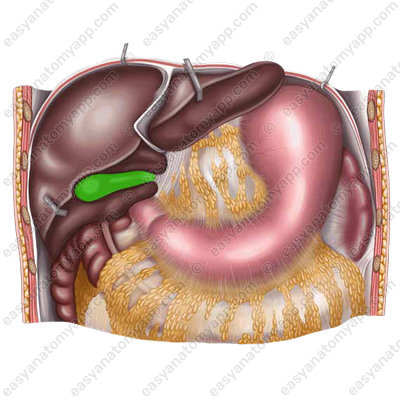
After meal, the gallbladder contracts, and bile is excreted through the bile ducts into the duodenum. The role of bile is to break down fats, caffeine, and chlorophyll. In addition, being an alkaline liquid, it helps to neutralize the increased acidity of gastric juice before it enters the intestines.
It is located in the right hypochondriac region (regio hypochondriaca dextra).
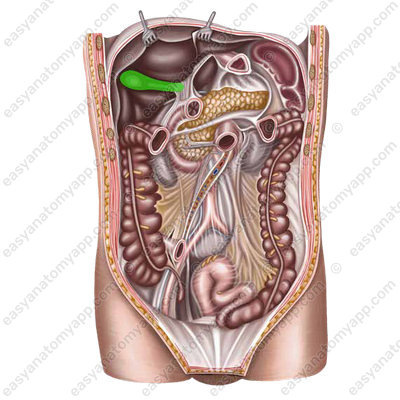
It adheres to the visceral surface of the liver. The fundus of the gallbladder is projected to the right at the junction of the cartilages of the ribs 8 and 9.
There are three parts in the gallbladder:
1. Fundus (fundus vesicae felleae)
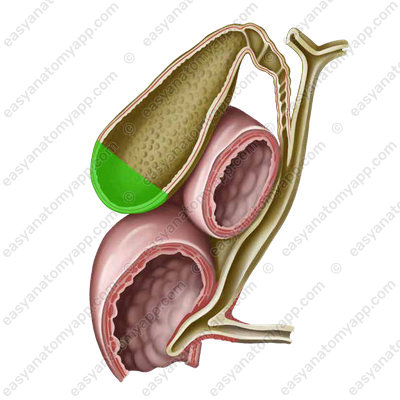
2. Body (corpus vesicae felleae)

3. Neck (collum vesicae felleae)
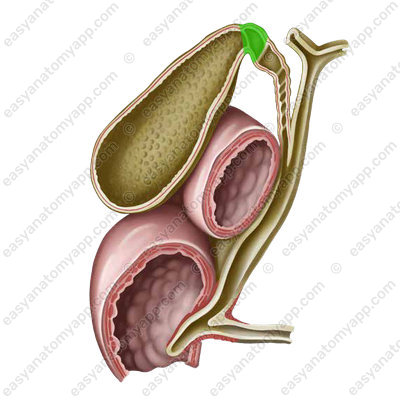
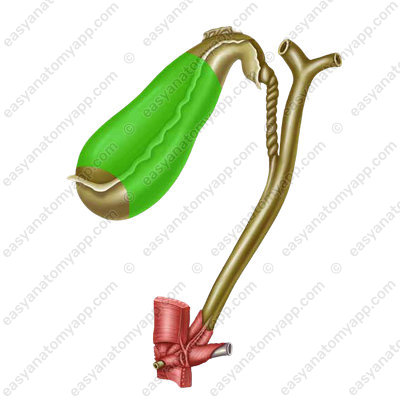
The cystic duct (ductus cysticus) branches off from the neck
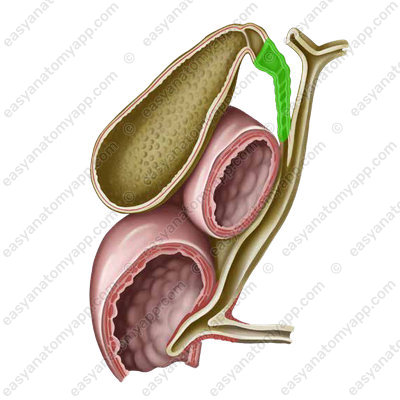
If we dissect the gallbladder and take a look at its mucous membrane, we will find a spiral fold (plica spiralis), which spirally passes in the cystic duct.
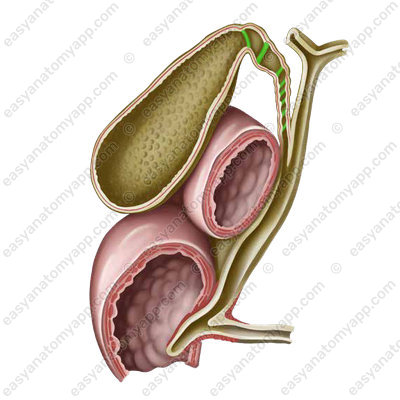
The wall of the gallbladder consists of several layers.
1. Mucous membrane (tunica mucosa)
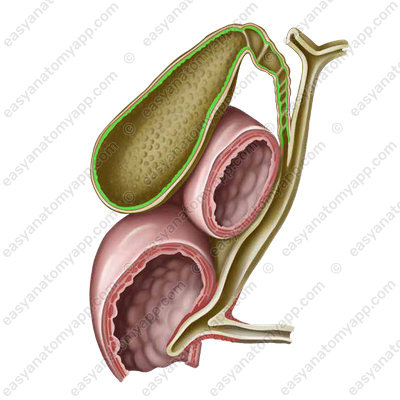
2. Muscular coat (tunica muscularis), which formed by two layers.
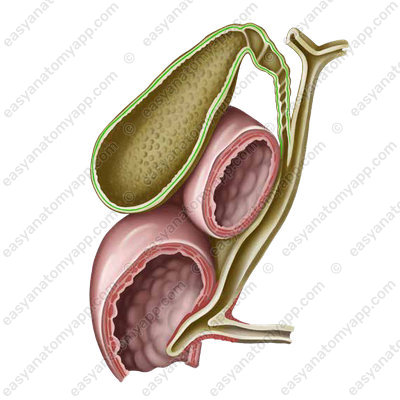
- Internal layer, which is circular (stratum circulare)
- External layer, which is longitudinal (stratum longitudinale)
3. Tunica externa (tunica externa) is represented by both adventitia and serosa (tunica serosa).
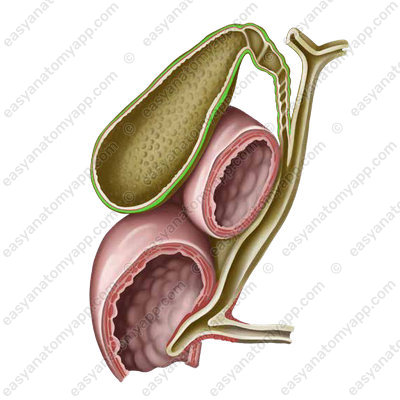
The part of the bladder that adheres to the liver is not covered by the peritoneum and has the adventitia.
An unfilled gallbladder lies extraperitoneally, and a filled one lies mesoperitoneally.
Blood supply
Arterial blood flow is carried out through its proper artery, which is a branch of the proper hepatic artery.
- Cystic artery (a. cystica)
Venous drainage
The blood drainage is carried out through the eponymous vein into the portal vein.
- Cystic vein (v. cystica)
Lymph drainage
The following groups of lymph nodes are regional for the gallbladder:
- Hepatic lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici hepatici)
- Coeliac lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici coeliaci)
Innervation
- Afferent innervation is carried out by the anterior branches of the inferior thoracic spinal nerves and the vagus nerve.
- Sympathetic innervation is provided by branches of the hepatic plexus.
- Parasympathetic innervation is carried out by branches of the vagus nerve.
Biliary tract
Let’s move on to the consideration of the biliary tract.
It can be divided into two categories:
- Intraorganic (or intrahepatic) biliary tract
- Extraorganic (or extrahepatic) biliary tract
The intraorganic biliary tract includes several structures.
- Bile ducts (ductuli biliferi), where the bile is formed
- Interlobular bile duct (ductuli interlobulares), to which the bile formed in the bile ducts goes
- Segmental ducts (ducti segmentales), which are the next on the path of bile
- Right and left hepatic ducts (ductus hepaticus dexter et ductus hepaticus sinister) are two large ducts that provide the drainage of bile from the corresponding lobes of the liver.
Next, the ducts exit the liver and pass into the next group of ducts called extraorganic.
- Common hepatic duct (ductus hepaticus communis) is formed when the right and left hepatic ducts merge.
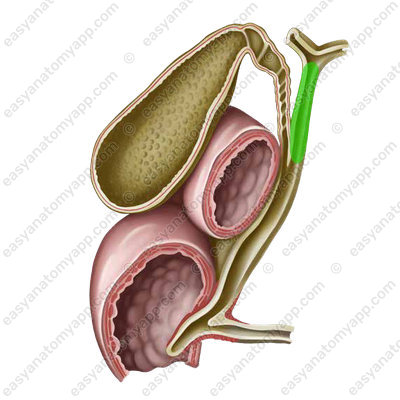
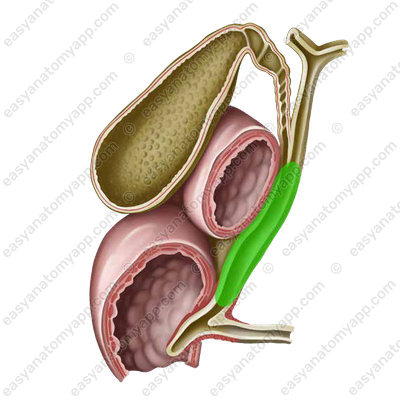
- Cystic duct (ductus cysticus) is a duct that drains bile from the gallbladder

- Common bile duct or choledochus (ductus choledochus) is formed by the fusion of the cystic and common hepatic ducts.
- Hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla hepatopancreatica) is where the choledochus and the pancreatic duct merge.
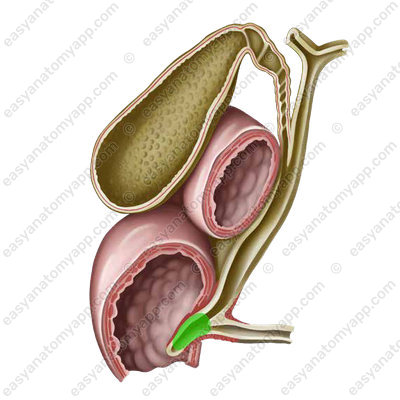
In the descending part of the duodenum, this ampulla opens into the lumen of the intestine, forming the major duodenal papilla (papilla duodeni major).
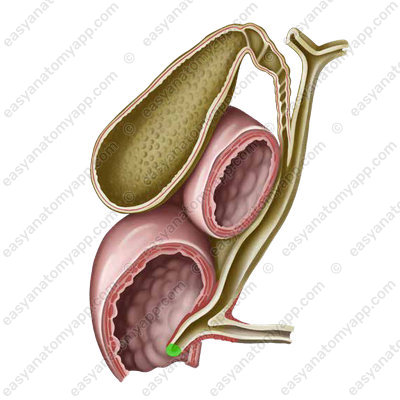
There is the so-called sphincter of Oddi in its thickness.
Anatomy of the gallbladder and biliary tree
- Gallbladder
- vesica fellea
- Fundus of the gallbladder
- fundus vesicae felleae
- Body of the gallbladder
- corpus vesicae felleae
- Neck of the gallbladder
- collum vesicae felleae
- Spiral fold
- plica spiralis
- Mucous membrane
- tunica mucosa
- Muscular layer
- tunica muscularis
- Circular layer
- stratum circulare
- Longitudinal layer
- stratum longitudinale
- Tunica externa
- tunica externa
- Bile ducts
- ductuli biliferi
- Interlobular bile ducts
- ductuli interlobulares
- Segmental ducts
- ducti segmentales
- Right and left hepatic ducts
- ductus hepaticus dexter et ductus hepaticus sinister
- Common hepatic duct
- ductus hepaticus communis
- Cystic duct
- ductus cysticus
- Common bile duct
- ductus choledochus
- Hepatopancreatic ampulla
- ampulla hepatopancreatica
- Major duodenal papilla
- papilla duodeni major


