In this note, we will consider the anatomy of the salivary glands.
They produce saliva, which performs the function of digestion in the oral cavity, as well as softens and moistens the food bolus.
By the nature of their secretions, the glands of the oral cavity are divided into:
- Serous glands, which secrete liquid rich in protein.
- Mucous glands, which secrete a liquid with a lower protein content.
- Mixed glands
All salivary glands have a common principle of structure, they consist of a secretory unit and duct.
There are minor and major salivary glands.
Minor salivary glands are located in the thickness of the oral mucosa and are distinguished by their localization:
- Labial glands (glandulae labiales)
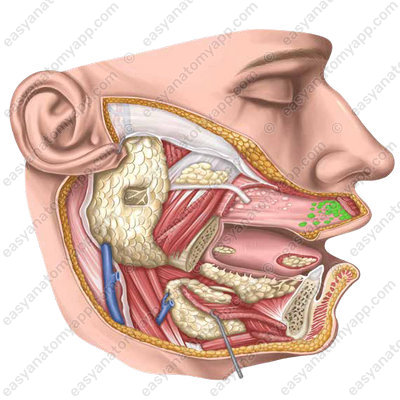
- Buccal glands (glandulae buccales)

- Palatal glands (glandulae palatinae)
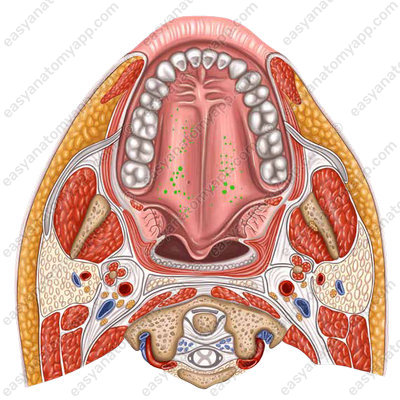
- Molar glands (glandulae molares)

- Lingual glands (glandulae linguales)
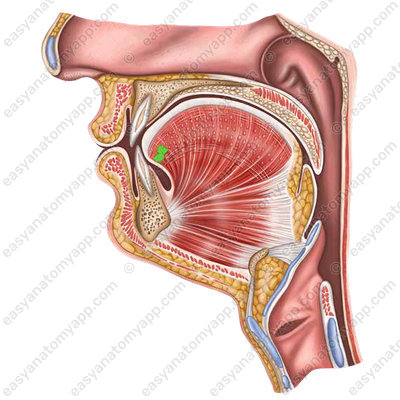
Major salivary glands are located outside the walls of the oral cavity, but open into it with their ducts. These include:
Parotid gland (glandula parotidea)
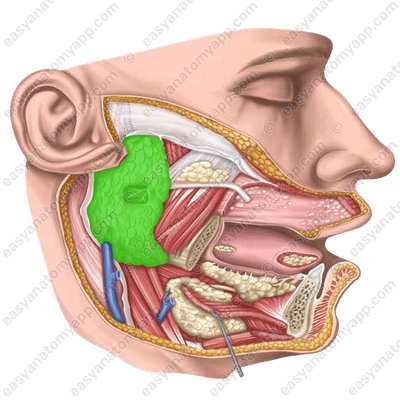
Submandibular gland (glandula submandibularis)
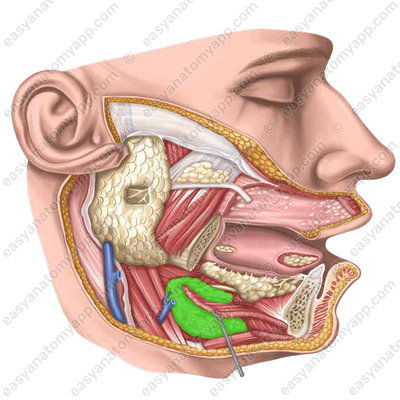
Sublingual gland (glandula sublingualis)
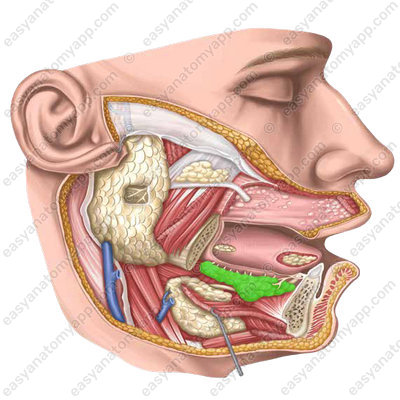
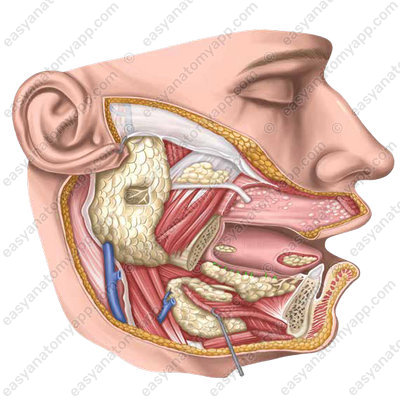
Parotid salivary gland
The parotid salivary gland is a paired gland of serous type.

It is located in the retromandibular fossa (fossa retromandibularis).
The gland is covered with a thin layer of subcutaneous tissue and skin.
The external carotid artery, the retromandibular vein, the facial and auriculotemporal nerves pass through this gland. The parotid nerve plexus and deep parotid lymph nodes are located in the thickness of the gland.
The parotid duct (ductus parotideus) passes along the external surface of the masseter muscle and pierces the buccal muscle, after which it opens on the mucous membrane of the oral vestibule at the level of the second upper molar tooth.
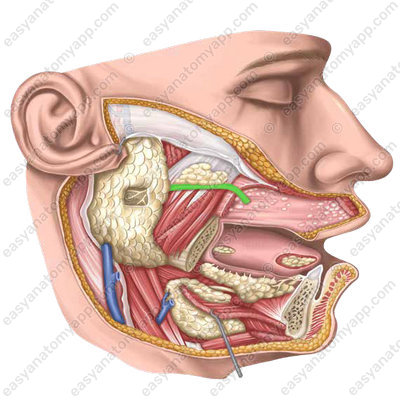
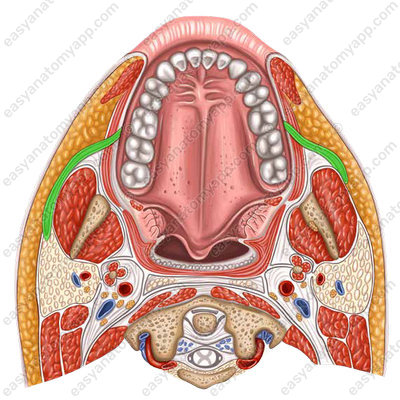
Blood supply
- Branches of the parotid gland (rr. parotidei) provide blood supply from the superficial temporal artery (a. temporalis superficialis)
Venous drainage
- Parotid veins (vv. parotidei) drain blood to the pterygoid venous plexus (plexus venosus pterygoideus)
- Parotid branches (rr. parotidei) drain blood to the facial vein (v. facialis)
Lymphatic drainage
- Lymph nodes of the parotid salivary gland (nody lymphatici parotidei)
Innervation
Afferent innervation
- Branches of the parotid salivary gland (rr. parotidei) from the auriculotemporal nerve (n. auriculotemporalis)
Sympathetic innervation
- The superior cervical ganglion (g. cervicale superius) arising from the sympathetic trunk (truncus sympathicus)
Parasympathetic innervation
- The otic ganglion (g. oticum) from the lesser petrosal nerve (n. petrosus minor)
Submandibular gland
The submandibular salivary gland is a paired gland of a mixed type of secretion.

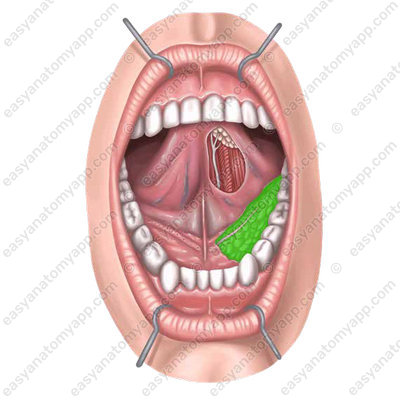
It is located in the area of the submandibular triangle of the neck.
From the external side, it is covered with the superficial layer of the cervical fascia and skin.
A small anterior process of the gland lies on the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle. Here the submandibular duct, also known as Wharton’s duct (ductus submandibularis), comes out of the gland;
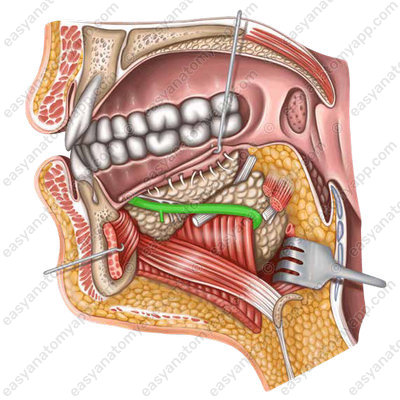
It opens with a small foramen on the sublingual caruncle (caruncula sublingualis), next to the frenulum of the tongue.


Blood supply
- Sublingual branches (rr. sublinguales) supply blood from the submental artery (a. submentalis)
Venous drainage
- Sublingual branches (rr. sublinguales) drain blood into the facial vein (v. facialis)
Lymphatic drainage
- Submandibular lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici submandibulares)
Innervation
Afferent innervation
- Sublingual branches (rr. sublinguales) arising from the lingual nerve (n. lingualis)
Sympathetic innervation
- The superior cervical ganglion (g. cervicale superius) arising from the sympathetic trunk (truncus sympathicus)
Parasympathetic innervation
- The submandibular ganglion (g. submandibulare) from the chorda tympani (chorda tympani)
Submandibular gland
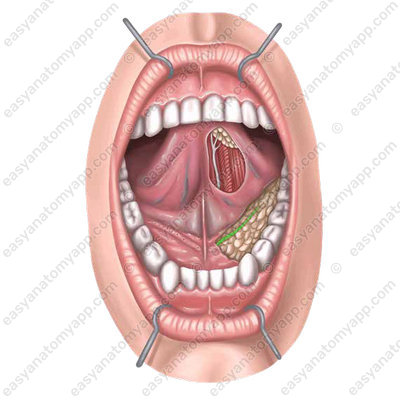
The sublingual salivary gland is a paired gland, predominantly of the mucous type of secretion.

It is located on the mylohyoid muscle.
From the lateral side, it comes into contact with the internal surface of the mandible in the area of the sublingual fossa
The major sublingual duct (ductus sublingualis major) opens on the sublingual caruncle together with the submandibular duct.
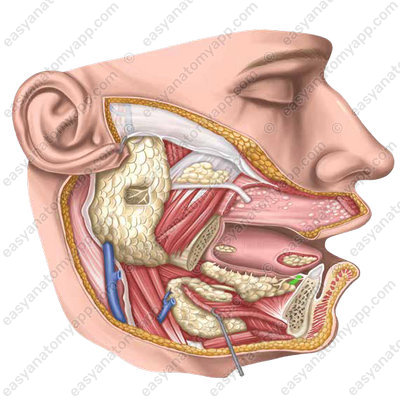
Several minor sublingual ducts (ductus sublinguales minores) flow into the oral cavity independently on the surface of its mucous membrane along the sublingual fold.
Blood supply
- The sublingual artery (a. sublingualis) supplies blood from the lingual artery (a. lingualis)
Venous drainage
- The lingual vein (v. lingualis) drains blood to the internal jugular vein (v. jugularis interna)
Lymphatic drainage
- Submandibular lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici submandibulares)
Innervation
Afferent innervation
- Sublingual branches (rr. sublinguales) arising from the lingual nerve (n. lingualis)
Sympathetic innervation
- The superior cervical ganglion (g. cervicale superius) arising from the sympathetic trunk (truncus sympathicus)
Parasympathetic innervation
- The sublingual ganglion (g. sublinguale) from the chorda tympani (chorda tympani)
Anatomy of the salivary glands
- Labial glands
- glandulae labiales
- Buccal glands
- glandulae buccales
- Palatine glands
- glandulae palatinae
- Molar glands
- glandulae molares
- Lingual glands
- glandulae linguales
- Parotid gland
- glandula parotidea
- Retromadibular fossa
- fossa retromandibularis
- Parotid duct
- ductus parotideus


