The tongue (lingua) is a muscular organ involved in mixing food, the act of swallowing, taste perception and articulation.

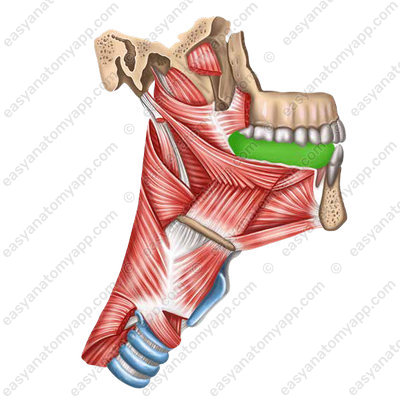
The tongue has the following parts:
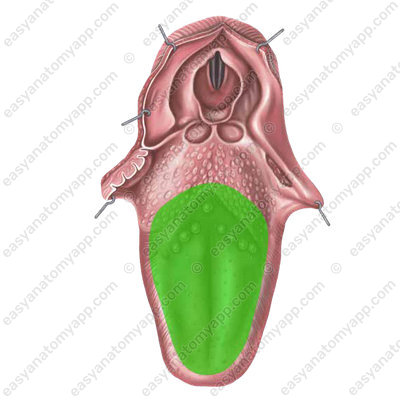
1. Apex of the tongue (apex linguae)
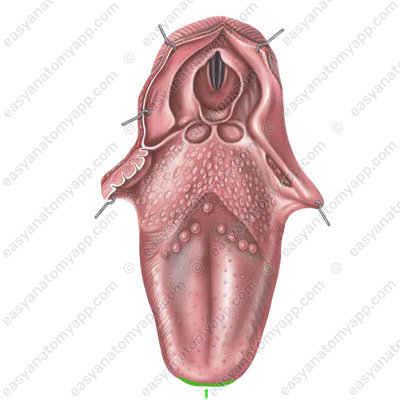
2. Body of the tongue (corpus linguae)

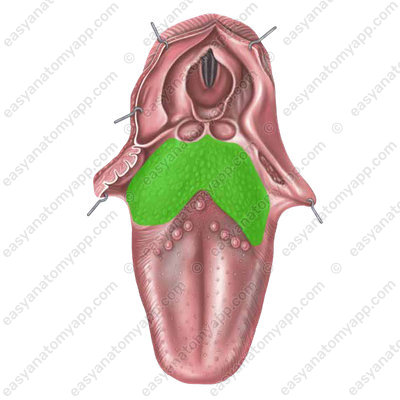
3. Root or base of the tongue (radix linguae)
The superior surface of the organ is called from the dorsum of the tongue (dorsum linguae).
The median sulcus (sulcus medianus linguae) runs along the median line anteroposteriorly.
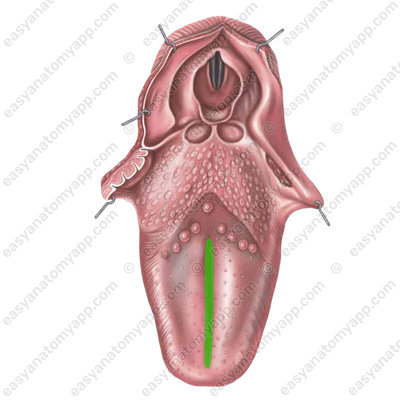
In the thickness of the tongue, this sulcus corresponds to a fibrous plate dividing the tongue into right and left halves.
The median sulcus ends with a foramen caecum (foramen caecum linguae).
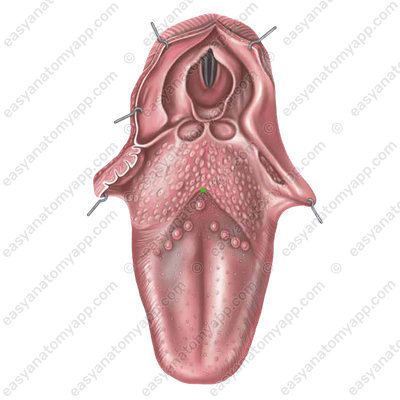
On the sides of it, there is a terminal sulcus (sulcus terminalis linguae), which is V-shaped. This sulcus is the border between the root and the body of the tongue.

The mucous membrane of the tongue has processes covered with epithelium called lingual papillae (papillae linguales). There are no papillae in the root area. In this area, there is a cluster of lymphoid tissue called the lingual tonsil (tonsilla lingualis).
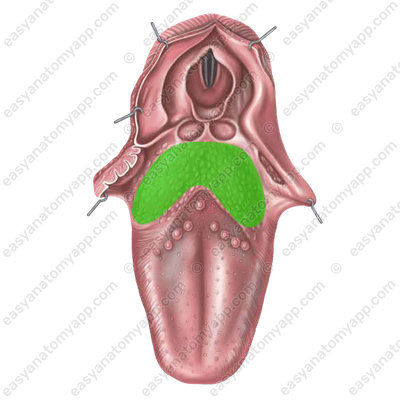
Humans have four types of papillae:
Filiform papillae (papillae filiformes)
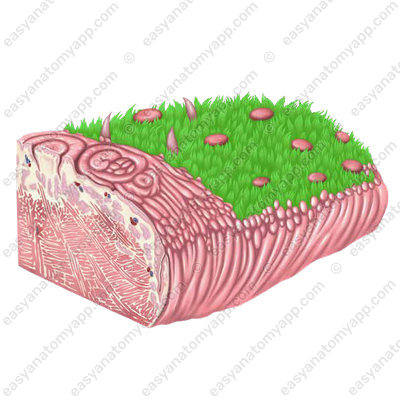


Conic papillae (papillae conicae), which cover the anterior two-thirds of the dorsum of the tongue and provide sensitivity to pain, temperature, and touch.
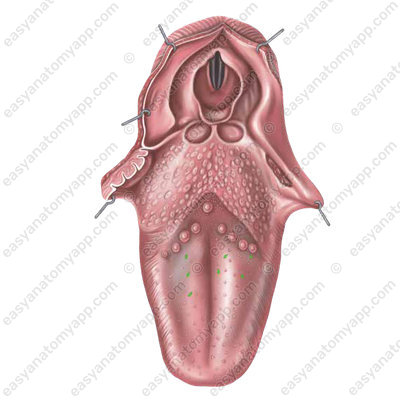
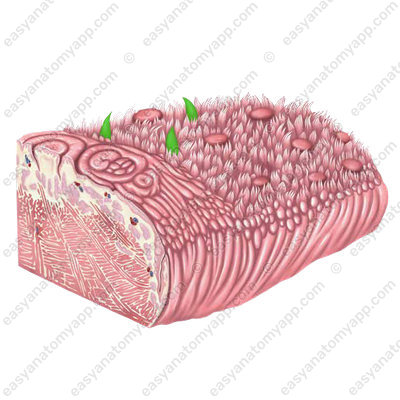
Fungiform papillae (papillae fungiformes), which have a rounded shape and are located mainly on the apex and body of the tongue.
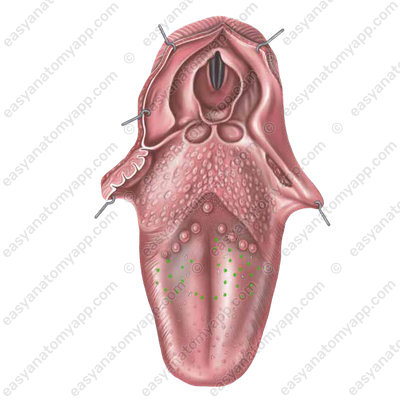
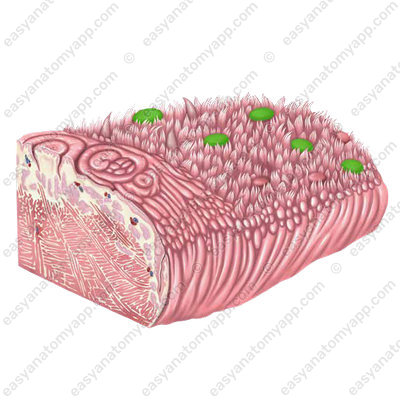
Vallate papillae (papillae vallatae), which are located on the border between the dorsum and the root of the tongue.
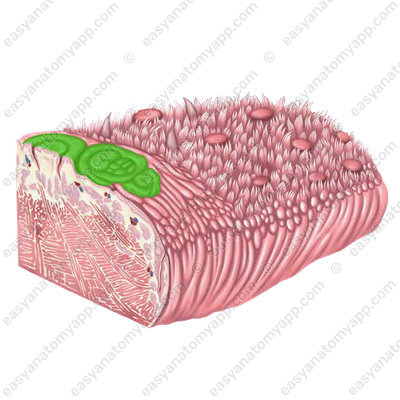
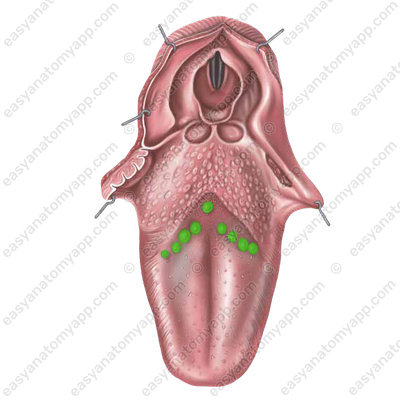

They resemble fungiform papillae in shape, but their superior surface is flattened, and there is a narrow deep sulcus around the papilla, into which the ducts of the glands open.
Foliate papillae (papillae foliatae), which lie along the margins of the tongue in the form of folds of the mucous membrane.


Several folds form on the inferior surface of the tongue.
Fimbriated fold (plica fimbriata)
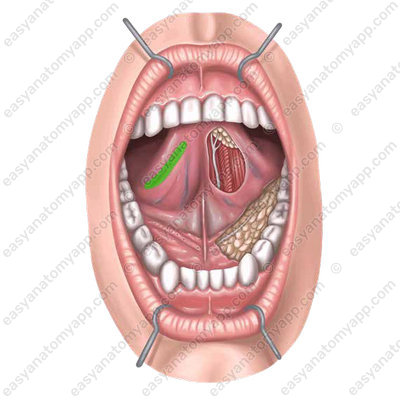
Frenulum of the tongue (frenulum linguae)

Sublingual fold (plica sublingualis)
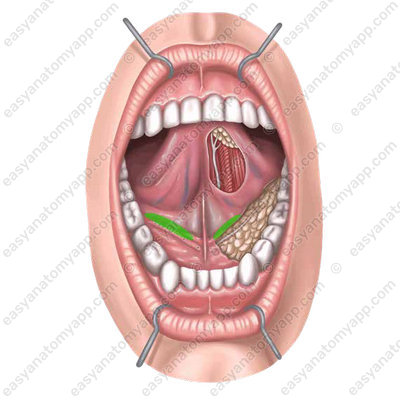
On the sides of the frenulum is a paired sublingual caruncle (caruncula sublingualis), on which the excretory ducts of the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands open
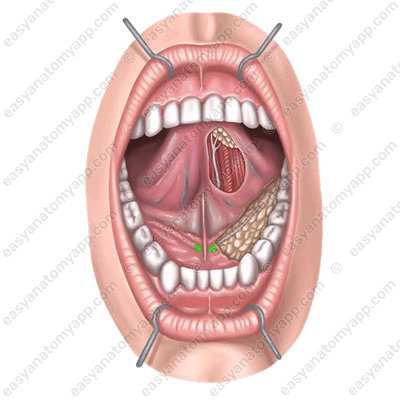
The tongue is predominantly composed of transversely striated muscles covered with a mucous membrane on the outside.
Muscles of the tongue
The muscles of the tongue are paired, and they are divided into two groups:
- Skeletal or extrinsic muscles
- Proper or intrinsic muscles
The extrinsic muscles of the tongue arise from the bones of the skull and from the hyoid bone and insert deep into the tongue. The contraction of these muscles change the position of the tongue in the oral cavity. These include:
The genioglossus muscle (m. genioglossus), which arises from the mental spine of the mandible. The contraction of this muscle pulls the tongue anteriorly and inferiorly.
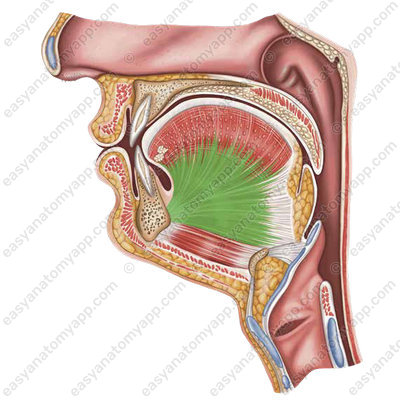
The hyoglossus muscle (m. hyoglossus), which arises from the greater horn and from the body of the hyoid bone. It pulls the tongue posteriorly and inferiorly.
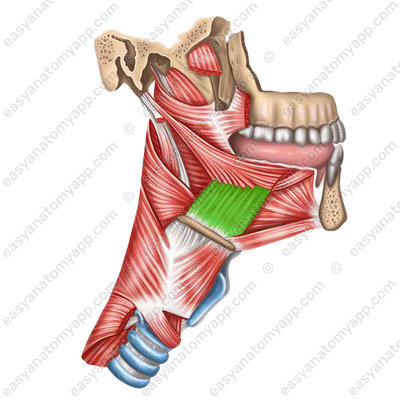
The styloglossus muscle (m. styloglossus), which arises from the styloid process of the temporal bone and the stylohyoid ligament. It pulls the tongue to the side.
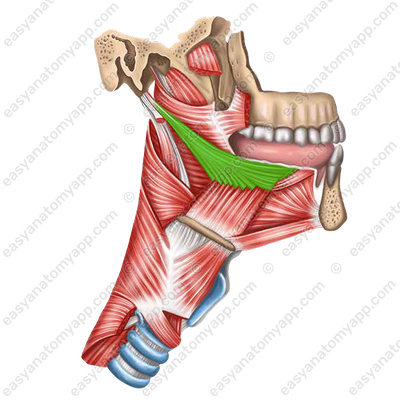
The palatoglossus muscle (m. palatoglossus), which is located in the thickness of the eponymous arc. It lifts the root of the tongue.

The intrinsic muscles of the tongue arise and end in the thickness of the tongue. The contraction of these muscles changes the shape of the tongue. The intrinsic muscles include:
The superior longitudinal muscle (m. longitudinalis superior), which is located in the superior parts of the tongue. The contraction of this muscle shortens the tongue and lifts its apex.
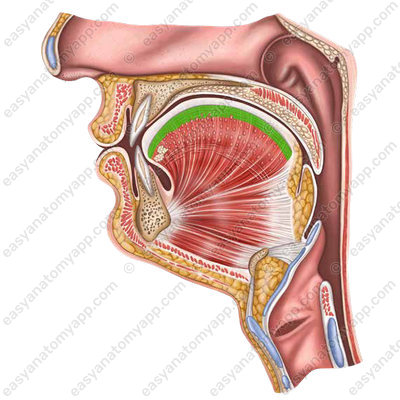
The inferior longitudinal muscle (m. longitudinalis inferior), which is located in the inferior parts of the tongue. It also shortens the tongue but lowers its apex.

The transverse muscle of the tongue (m. transversus linguae) consists of bundles running transversely from the septum of the tongue to its margin. It narrows the tongue and lifts its back.
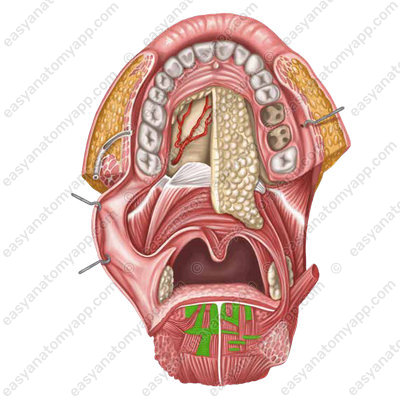
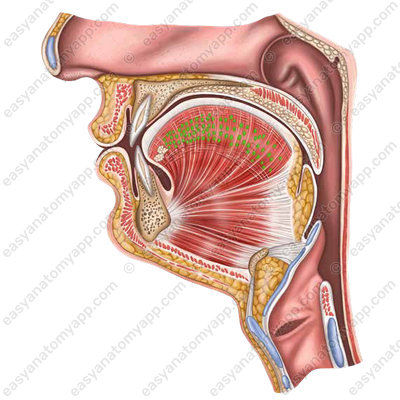
The vertical muscle of the tongue (m. verticalis linguae) is located mainly in the lateral parts of the tongue. It flattens the tongue.
(m. verticalis linguae)
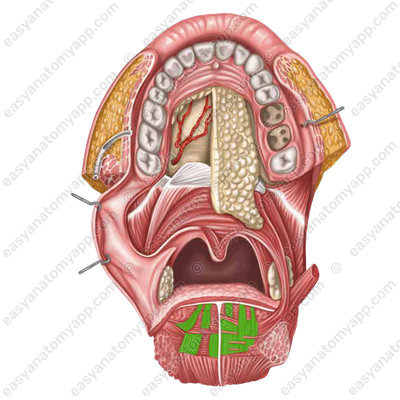
Blood supply
A branch of the external carotid artery called the lingual artery (arteria lingualis) supplies the tongue with arterial blood.

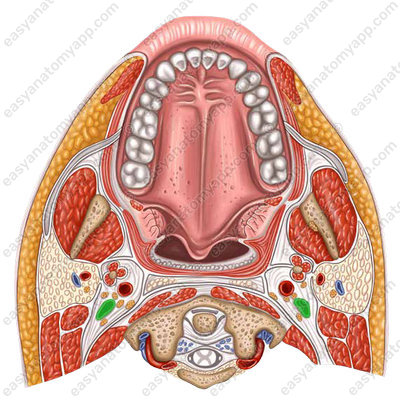
Venous drainage
The lingual vein (v. lingualis), which ends by the internal jugular vein (v. jugularis interna), drains venous blood from the tongue.
Innervation
The sublingual nerve (nervus hypoglossus) provides motor innervation of the muscles of the tongue.
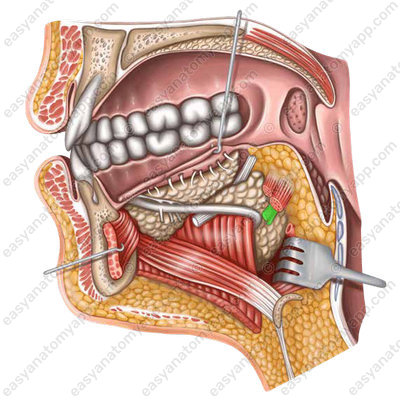
Sensory innervation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is provided by the lingual nerve (n. lingualis), of the posterior third — by the glossopharyngeal nerve (n. glossopharyngeus), of the root of the tongue — by the superior branch of the laryngeal nerve (n. laryngeus superior).
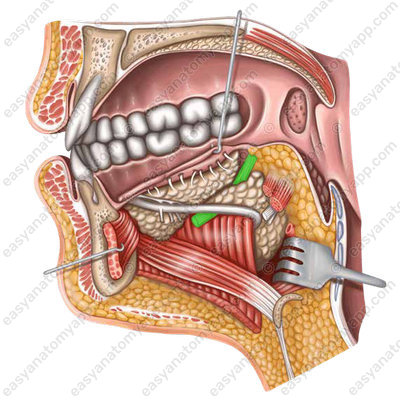
The glossopharyngeal nerve (n. glossopharyngeus) provides the posterior third of the tongue with gustatory innervation, while the two anterior thirds are innervated by the chorda tympani (chorda tympani).
Lymphatic drainage
Lymphatic vessels from the tongue are directed to the submandibular, mental, and lateral deep cervical lymph nodes.
Anatomy of the tongue
- Tongue
- lingua
- Apex of the tongue
- apex linguae
- Body of the tongue
- corpus linguae
- Root of the tongue
- radix linguae
- Dorsum of the tongue
- dorsum linguae
- Papillae of the tongue
- papillae linguales
- Lingual tonsil
- tonsilla lingualis
- Filiform papillae
- papillae filiformes
- Conic papillae
- papillae conicae
- Fungiform papillae
- papillae fungiformes
- Vallate papillae
- papillae vallatae
- Foliate papillae
- papillae foliatae
- Median sulcus of the tongue
- sulcus medianus linguae
- Foramen caecum of the tongue
- foramen caecum linguae
- Genioglossus muscle
- m. genioglossus
- Hyoglossus muscle
- m. hyoglossus
- Styloglossus muscle
- m. styloglossus
- Palatoglossus muscle
- m. palatoglossus
- Superior longitudinal muscle
- m. longitudinalis superior
- Inferior longitudinal muscle
- m. longitudinalis inferior
- Transverse muscle of the tongue
- m. transversus linguae
- Vertical muscle of the tongue
- m. verticalis linguae


