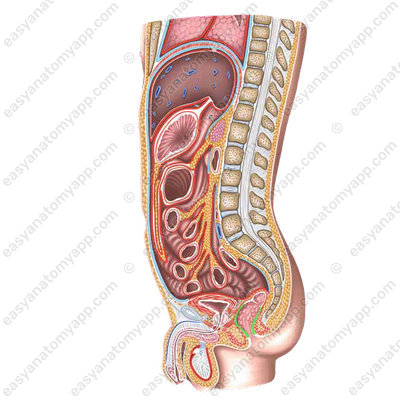
In this note, we will consider the anatomy of the rectum (rectum).
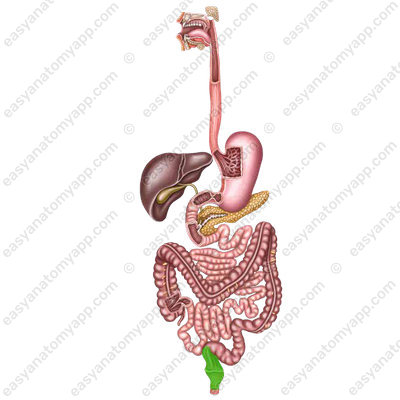
It is the terminal part of the large intestine. Characteristic features, such as haustrae and taeniae, are absent in the rectum. It performs the function of removing the formed fecal masses.
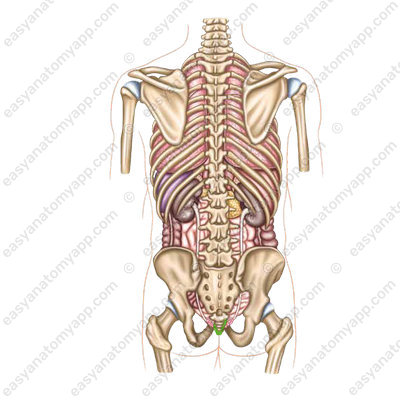
It is located in the pelvic cavity from the level of the left sacro-iliac joint to the perineum.
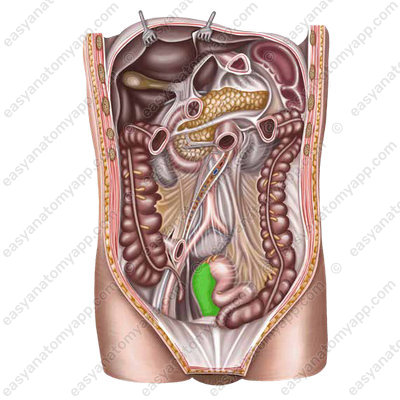
Anteriorly from the rectum in men, there are the urinary bladder, seminal vesicles, and prostate.
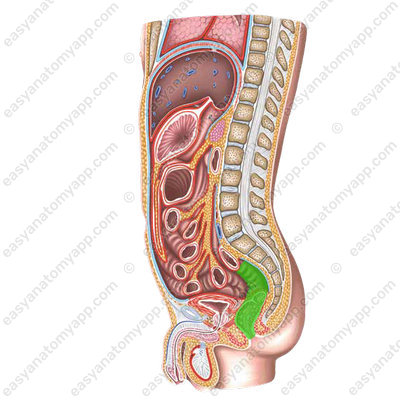
In women, this is the location of the uterus and vagina.
Posteriorly, there is the sacrum.
Laterally, there are iliac vessels.
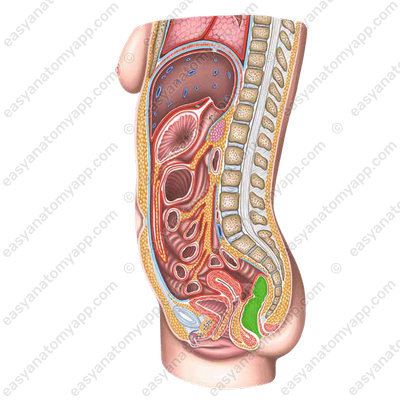
The rectum consists of three parts:
1. Supraampular part (pars supraampullaris)
2. Ampulla (ampulla recti)
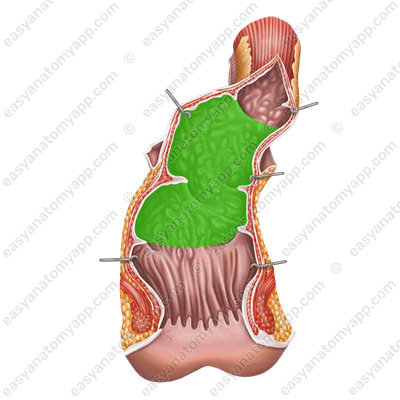
3. Anal canal (canalis analis),
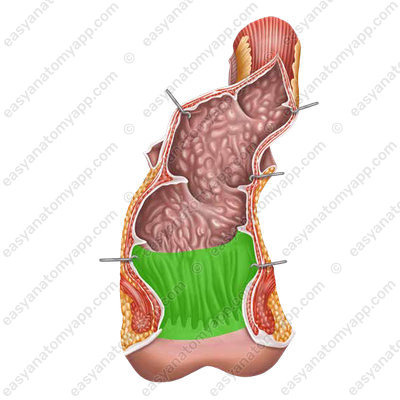
which ends with the anus (anus).
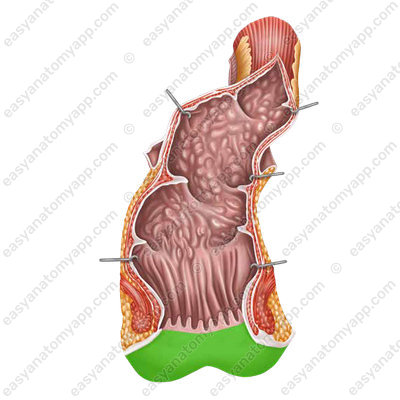
In the sagittal plane, the rectum has 2 flexures:
1. Sacral flexure (flexura sacralis)
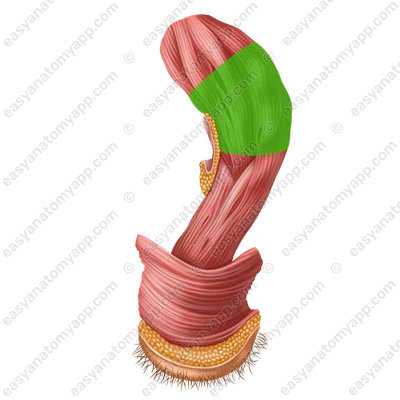

2. Perineal flexure (flexura perinealis)
The wall of the rectum consists of several layers:
Mucous membrane (tunica mucosa).

The suprampullar part and the rectal ampulla contain transverse folds (plicae transversales).

There are several longitudinal folds in the anal canal, which are called anal columns (columnae anales).
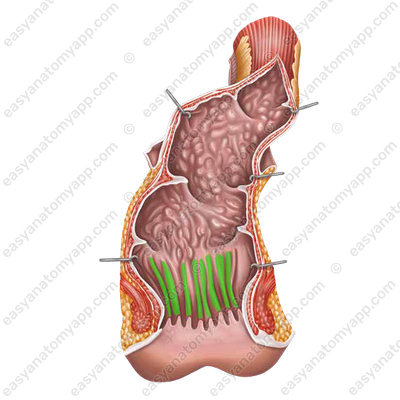
Between them are the recesses called the anal sinuses (sinus anales),
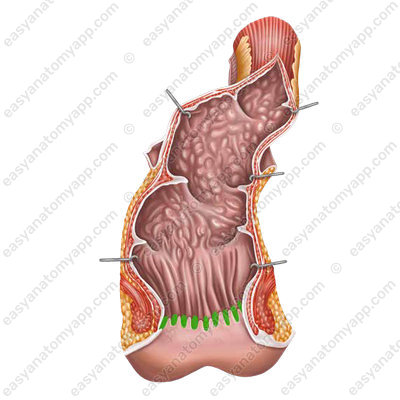
into which the excretory ducts of the anal glands open. Transverse folds called anal valves (valvulae anales) are formed between the inferior ends of the anal columns.
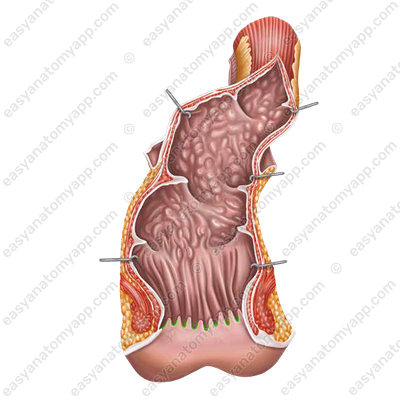
At the border of the ampulla and the anal canal, there is a small mucous torus called the anorectal line (linea anorectalis).
The second layer of the wall is the submucosa (tela submucosa). The hemorrhoidal venous plexus (plexus venosus haemorrhoidalis) is located here.

Next follows the muscular layer (tunica muscularis).
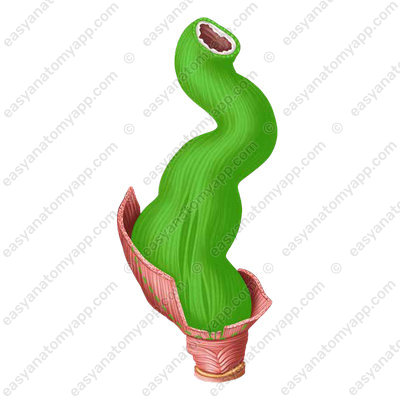
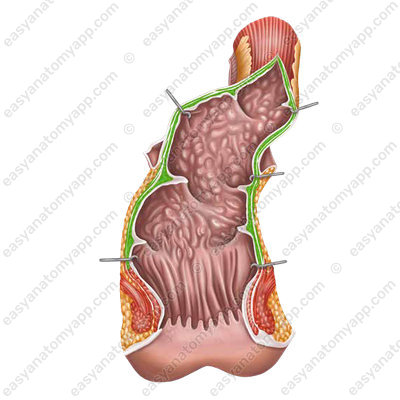

The circular layer of the muscular coat forms the internal anal sphincter (m. sphincter ani internus),

while the external anal sphincter (m. sphincter ani externus) is formed by the striated muscles of the perineum.
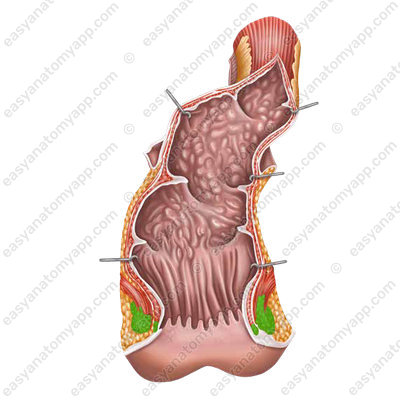
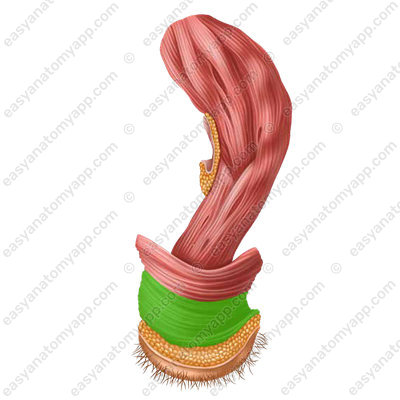
The superior part of the rectum is covered with the peritoneum intraperitoneally, the middle part is covered mesoperitoneally, and the inferior part is covered with adventitia.
Blood supply
- Superior rectal artery (a. rectalis superior)
- Middle rectal artery (a. rectalis media)
- Anterior rectal artery (a. rectalis inferior)
Venous drainage
The venous blood drains through the eponymous veins into the inferior mesenteric vein (v. mesenterica inferior).
Lymph drainage
- Superior rectal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici rectales superiores)
- Middle rectal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici rectales medii)
- Inferior rectal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici inferiores)
- Pararectal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici pararectales)
- Sacral lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici sacrales)
- Left colic lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici colici sinistri)
- Inferior mesenteric lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici mesenterici inferiores)
- Inguinal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici inguinales), which drain lymph from the anal area.
Innervation
Rectal plexus (plexus rectalis) forms along the course of the rectum.
- Afferent innervation is carried out by fibers from the sacral plexus, and the anal region is innervated by the pudendal nerve (n. pudendus).
- Sympathetic innervation is provided by fibers of the inferior pancreatic plexus (plexus hypogastricus inferior).
- Parasympathetic innervation is carried out by the pelvic splanchnic (nn. splanchnici pelvini).
- Efferent innervation of the external anal sphincter is provided by the fibers of the pudendal nerve.
Anatomy of the rectum
- Digestive system
- systema digestorium
- Lips
- labium
- Oral cavity
- cavitas oris
- Cheeks
- buccae
- Tongue
- lingua
- Pharynx
- pharynx
- Esophagus
- oesophagus
- Stomach
- ventriculus/gaster
- Duodenum
- duodenum
- Liver
- hepar
- Pancreas
- pancreas
- Gallbladder
- vesica fellea
- Jejunum
- jejunum
- Ileum
- ilium
- Caecum
- intestinum caecum
- Vermiform appendix
- appendix vermiformis
- Ascending colon
- colon ascendens
- Transverse colon
- colon transversum
- Descending colon
- colon descendens
- Sigmoid colon
- colon sigmoideum
- Rectum
- rectum
- Supraampullar part
- pars supraampullaris
- Rectal ampulla
- ampulla recti
- Anal canal
- canalis analis
- Sacral flexure
- flexura sacralis
- Perineal flexure
- flexura perinealis
- Transverse folds
- plicae transversales
- Anal columns
- columnae anales
- Anorectal line
- linea anorectalis
- Anal valves
- valvulae anales
- Anal sinuses
- sinus anales
- Anal pecten
- pecten anales
- Anocutaneous line
- linea anocutanea
- Linea alba
- linea alba
- Mucous membrane
- tunica mucosa
- Muscular layer
- tunica muscularis
- Serous coat or adventitia
- tunica serosa / adventitia
- Hemorrhoidal venous plexus
- plexus venosus haemorrhoidalis
- Internal anal sphincter
- m. sphincter ani internus
- External anal sphincter
- m. sphincter ani externus
- Mesentery of the rectum
- mesorectum
- Superior rectal artery
- a. rectalis superior
- Middle rectal artery
- a. rectalis media
- Inferior mesenteric vein
- v. mesenterica inferior
- Superior rectal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici rectales superiores
- Middle rectal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici rectales medii
- Inferior rectal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici inferiores
- Pararectal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici pararectales
- Sacral lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici sacrales
- Left colonic lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici colici sinistri
- Inferior mesenteric lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici mesenterici inferiores
- Inguinal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici inguinales
- Rectal plexus
- plexus rectalis
- Pudendal nerve
- n. pudendus
- Inferior pancreatic plexus
- plexus hypogastricus inferior
- Pelvic splanchnic nerves
- nn. splanchnici pelvini


