In this note, we will consider the anatomy and main functions of the pancreas (pancreas).
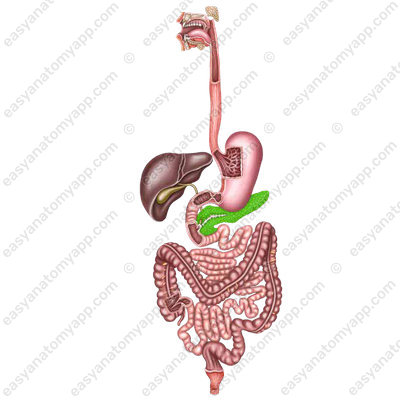
It is a gland of mixed secretion. It is located in the epigastric and left subcostal regions.
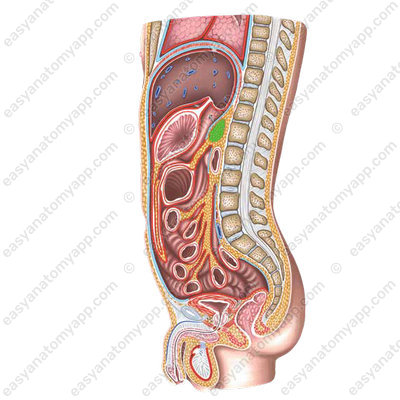
It is projected at the level of lumbar vertebrae 1-2.

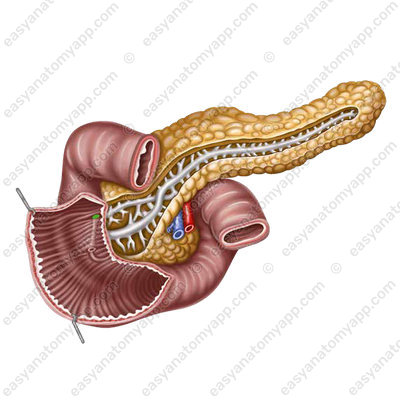
The pancreas consists of three parts:
1. Head of the pancreas (caput pancreatis),
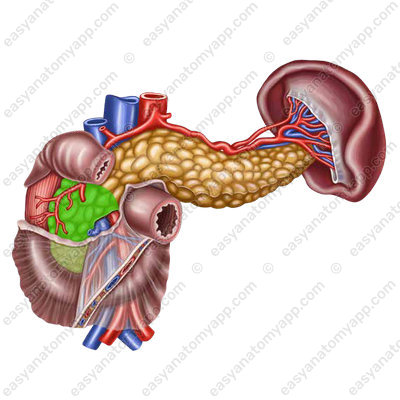
which sometimes has an additional process, the so-called uncinate process (processus uncinatus).
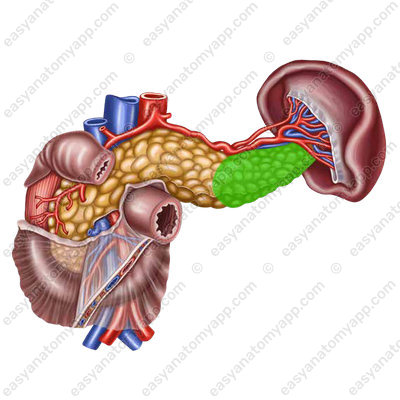
2. Body of the pancreas (corpus pancreatis).
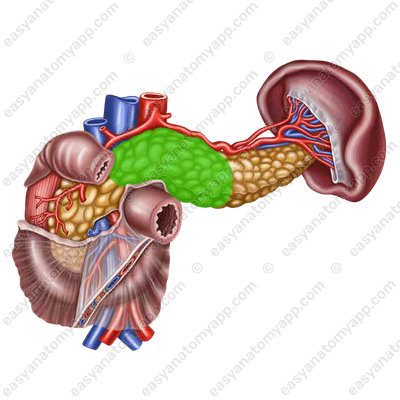
3. Til of the pancreas (cauda pancreatis)
There is a notch (incisura pancreatis) between the head and the body.
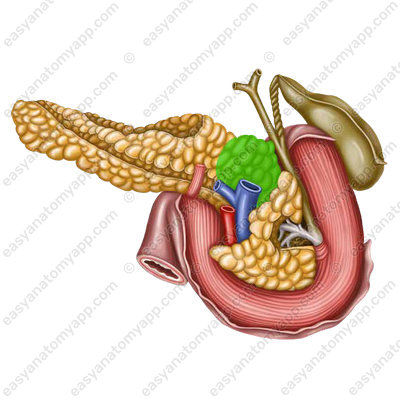
The pancreas also has three surfaces:
- Posterior surface (facies posterior)
- Anterior surface (facies anterior)
- Inferior surface (facies inferior)
At the places of transition of one surface to another, margins are formed, there are also three of them:
1. Superior margin (margo superior), which forms the omental tuberosity (tuber omentale)
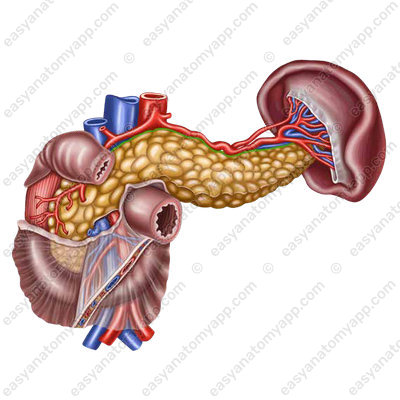
2. Anterior margin (margo anterior)

3. Inferior margin (margo inferior)
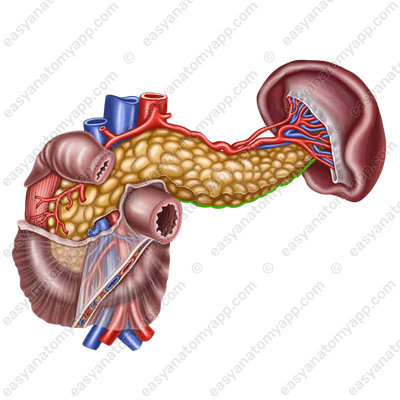
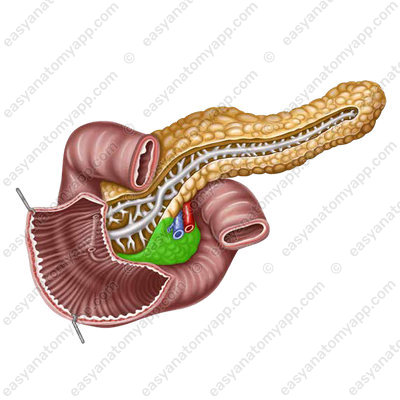
The structural and functional unit of the exocrine part of the gland is the acinus, which consists of secretory cells and an excretory duct.
The set of acini forms a lobule of the gland. The excretory ducts coming out of the lobules form the main pancreatic duct (ductus pancreaticus) or the duct of Wirsung,
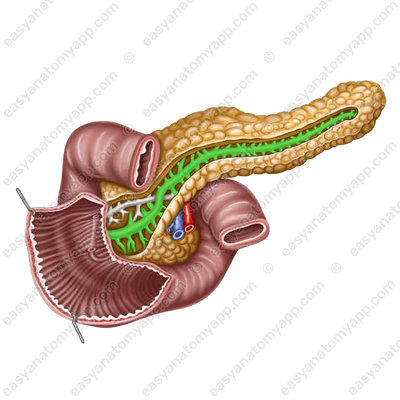
which passes in the thickness of the organ from the tail to the head and passes into the ampulla of the pancreas (ampulla pancreatis).
Together with the common bile duct, the pancreatic duct opens in the descending part of the duodenum, forming a major duodenal papilla (papilla duodeni major).
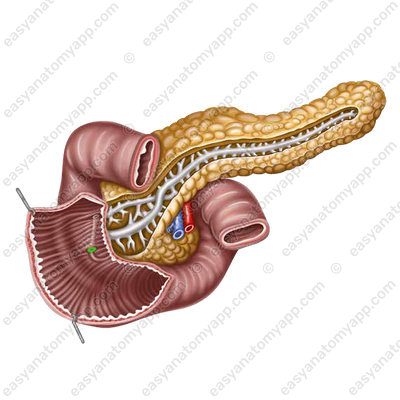
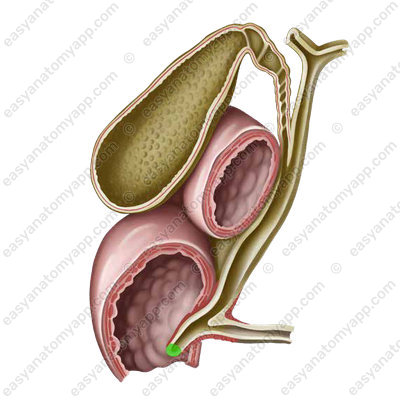
There is the so-called sphincter of Oddi in its thickness.
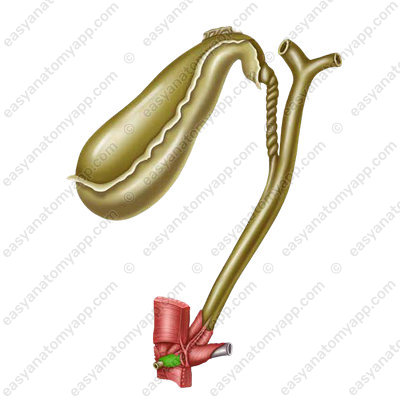
In the area of the gland head, an accessory duct (or the duct of Santorini) is formed,

which opens in the minor duodenal papilla (papilla duodeni minor).
Functions
- The pancreas is the primary source of enzymes for the digestion of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. These enzymes predominantly include trypsin (protease) and chymotrypsin, pancreatic lipase, and amylase. The main pancreatic secretion of ductal cells also contains bicarbonate ions involved in neutralizing acidic gastric chyme. The secretion of the pancreas is collected in the interlobular ducts, which merge with the main excretory duct, which opens into the duodenum.
- Interspersed between the lobules are numerous groups of cells that do not have excretory ducts, i.e. islets of Langerhans, which function as endocrine glands , releasing glucagon and insulindirectly into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate carbohydrate metabolism. These hormones have the opposite effects: glucagon increases blood glucose level, while insulin lowers it.
- Proteolytic enzymes are secreted into the lumen of the acinus in the form of zymogens(proenzymes, inactive forms of enzymes). These enzymes are called trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen. When released into the intestine, they are exposed to enterokinase present in the wall mucus, which activates trypsinogen, converting it into trypsin. Free trypsin further cleaves the remaining trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen to their active forms. The formation of enzymes in an inactive form is an important factor preventing enzyme damage to the pancreas, often observed in pancreatitis.
- Hormonal regulation of the exocrine function of the pancreas is provided by gastrin, cholecystokinin and secretin, which are hormones produced by the cells of the stomach and duodenum in response to stretching, as well as the secretion of pancreatic juice.
Blood supply
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery (a. pancreatoduodenalis superior)
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (a. pancreatoduodenalis inferior)
- Pancreatic arteries (aa. pancreatici)
Blood drainage
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal vein (v. pancreatoduodenalis superior)
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein (v. pancreatoduodenalis inferior)
- Pancreatic veins (vv. pancreatici)
All these veins end by the portal vein of the liver.
Lymph drainage
- Pancreatic lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici pancreatici)
- Pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici pancreatoduodenales)
- Splenic lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici lienales)
- Coeliac lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici coeliaci)
Innervation
- Afferent innervation is provided by branches of the inferior thoracic spinal nerves.
- Sympathetic innervation is provided by the pancreatic (plexus pancreaticus)
- Parasympathetic innervation is carried out by branches of the vagus nerve.
Anatomy of the pancreas
- Digestive system
- systema digestorium
- Lips
- labium
- Oral cavity
- cavitas oris
- Cheeks
- buccae
- Tongue
- lingua
- Pharynx
- pharynx
- Esophagus
- oesophagus
- Stomach
- ventriculus/gaster
- Duodenum
- duodenum
- Liver
- hepar
- Pancreas
- pancreas
- Gallbladder
- vesica fellea
- Jejunum
- jejunum
- Ileum
- ilium
- Caecum
- intestinum caecum
- Vermiform appendix
- appendix vermiformis
- Ascending colon
- colon ascendens
- Transverse colon
- colon transversum
- Descending colon
- colon descendens
- Sigmoid colon
- colon sigmoideum
- Rectum
- rectum
- Head of the pancreas
- caput pancreatis
- Uncinate process
- processus uncinatus
- Body of the pancreas
- corpus pancreatis
- Tail of the pancreas
- cauda pancreatis
- Posterior surface
- facies posterior
- Anterior surface
- facies anterior
- Inferior surface
- facies inferior
- Superior margin
- margo superior
- Omental tuberosity
- tuber omentale
- Anterior border
- margo anterior
- Inferior border
- margo inferior
- Excretory duct
- ductus excretorius
- Pancreatic duct
- ductus pancreaticus
- Ampulla of the pancreas
- ampulla pancreatis
- Minor duodenal papilla
- papilla duodenalis minor
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- a. pancreatoduodenalis superior
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery
- a. pancreatoduodenalis inferior
- Pancreatic arteries
- aa. pancreatici
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal vein
- v. pancreatoduodenalis superior
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein
- v. pancreatoduodenalis inferior
- Pancreatic veins
- vv. pancreatici
- Pancreatic lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici pancreatici
- Pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici pancreatoduodenales
- Splenic lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici lienales
- Coeliac lymph nodes
- nodi lymphatici coeliaci
- Pancreatic plexus
- plexus pancreaticus


