In this note, we will consider the anatomy of the small intestine (intestinum tenue).
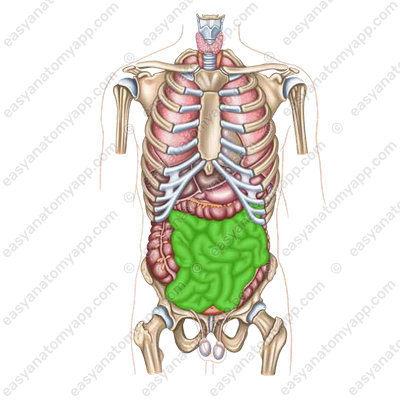
This is the part of the digestive tract located between the stomach and large intestine.
In the small intestine, food is exposed to intestinal and pancreatic secretions, as well as bile. In the lumen of the intestine, the final digestion of food and the absorption of its products takes place. The remains move into the large intestine.
The small intestine has three parts:
- Duodenum (duodenum)
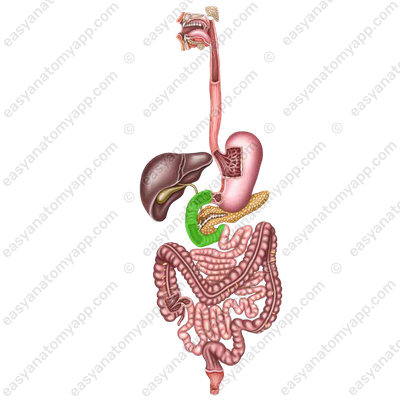
- Jejunum (jejunum)

- Ileum (ileum)
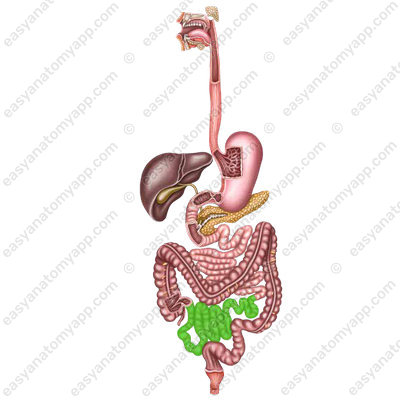
The last two parts are combined into the so-called mesenteric section of the small intestine, because they have a mesentery, which is a duplication of the peritoneum.
Let’s consider each part in greater detail.
The duodenum (duodenum) has the shape of a horseshoe, circumflexing the head of the pancreas.
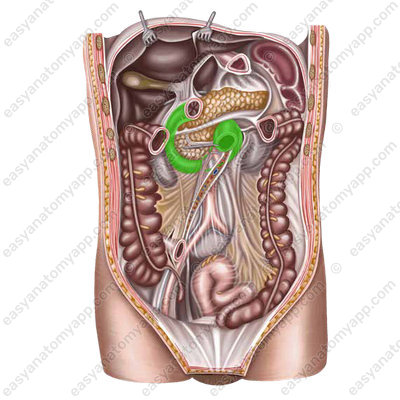
It begins from the pylorus of the stomach to the right of the 8th thoracic or 1st lumbar vertebra and ends at the left border of the body of the 2nd lumbar vertebra.
There are several parts of the duodenum.
- Superior part (pars superior)
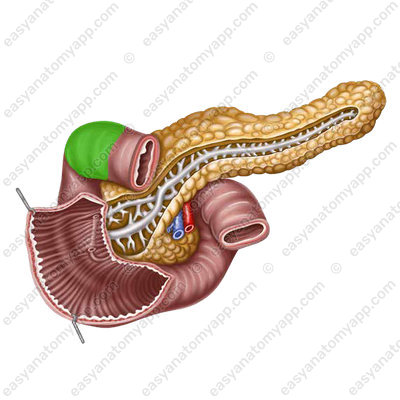
It forms the superior duodenal flexure (flexura duodeni superior) and passes into the descending part.

- Descending part (pars descendens) begins from the superior duodenal flexure at the level of the 1st lumbar vertebra and descends along the right border of the spine.
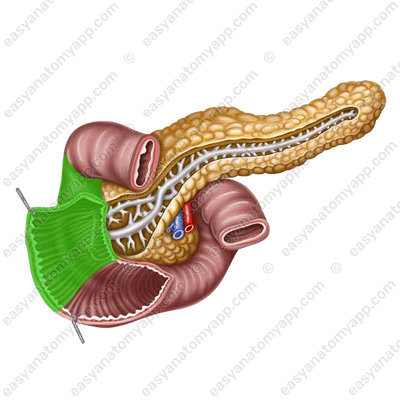
At the level of the 3rd lumbar vertebra, the intestine takes a sharp turn to the left, resulting in the inferior duodenal flexure (flexura duodeni inferior).
(flexura duodeni inferior)
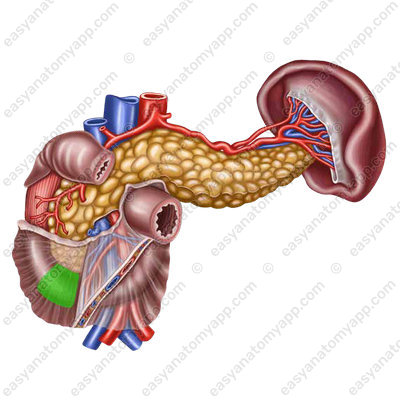
- Horizontal part (pars horizontalis) begins from the inferior duodenal flexure and goes horizontally to the left at the level of the body of the 3rd lumbar vertebra.
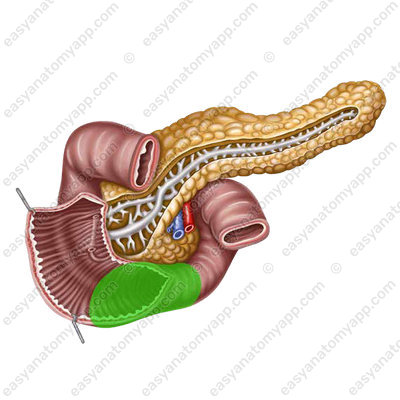
- Ascending part (pars ascendens)
It ends with a sharp flexure down, forward and to the left at the left border of the body of the 2nd lumbar vertebra. This is the duodenojejunal flexure (flexura duodenojejunalis).
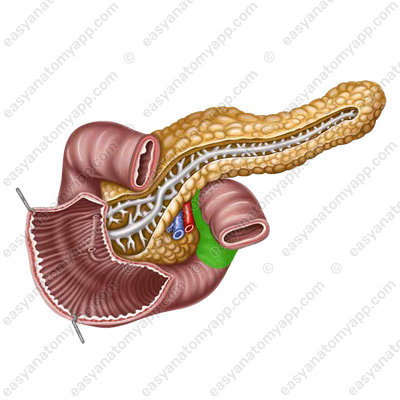
Behind the superior part, the portal vein and the common bile duct are located, and the superior surface of this part of the intestine is in contact with the quadrate lobe of the liver.
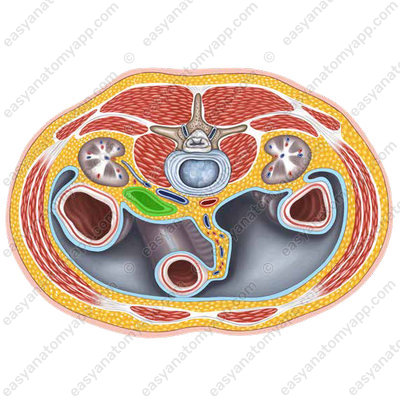
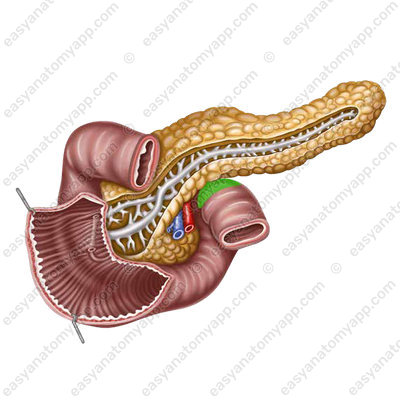
The right kidney is located posteriorly from the descending part, and the common bile duct passes to the left and somewhat posteriorly. In front of the duodenum, the root of the mesentery of the transverse colon and the liver adhere to the duodenum.
The horizontal part crosses the inferior vena cava lying on the spine anteriorly.
Behind the ascending part, there is the abdominal part of the aorta, and at the place of transition of the horizontal part to the ascending one, the superior mesenteric artery and vein located at the root of the mesentery of the small intestine pass over the duodenum.
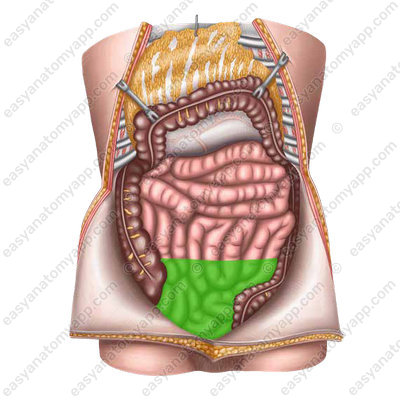
- Jejunum (jejunum)
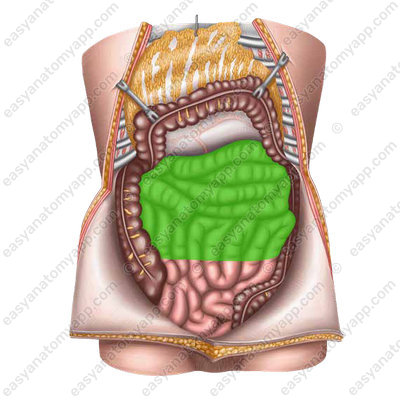
Its loops lie in the superior left part of the abdominal cavity and without a clear border pass into the loops of the ileum (ileum), which occupies mainly the inferior right part of the abdominal cavity.
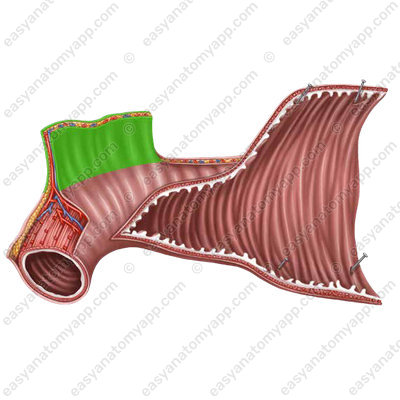
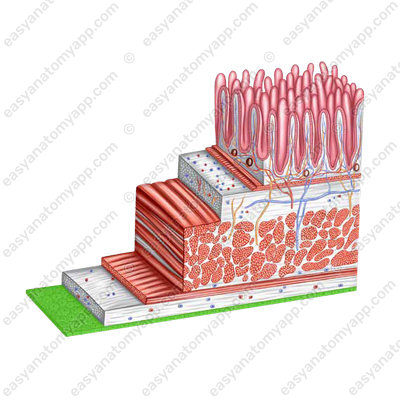
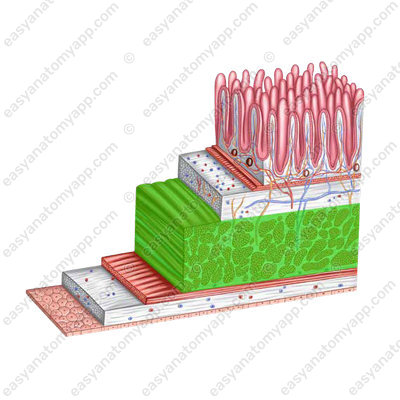
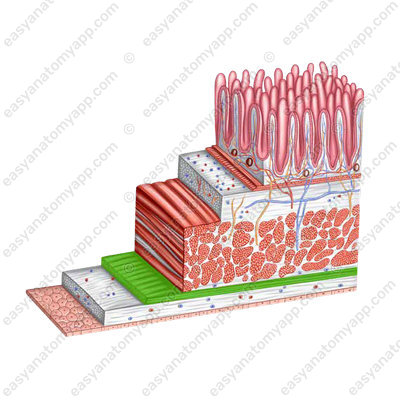
The wall of the small intestine consists of several layers:
- Mucous membrane (tunica mucosa)
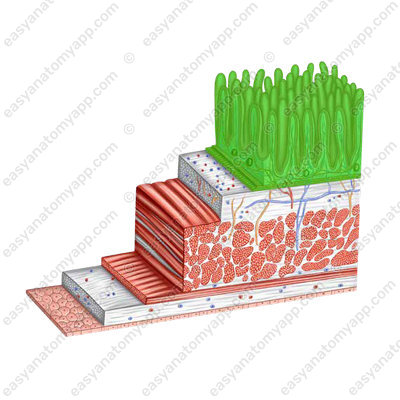
- Submucosa (tela submucosa)
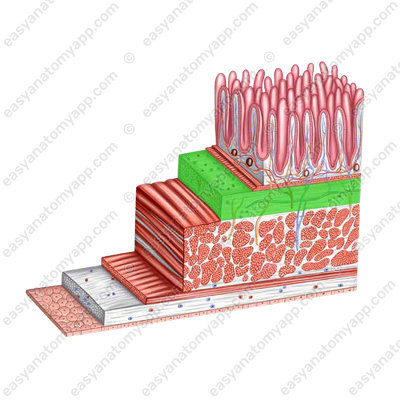
- Muscular layer (tunica muscularis)
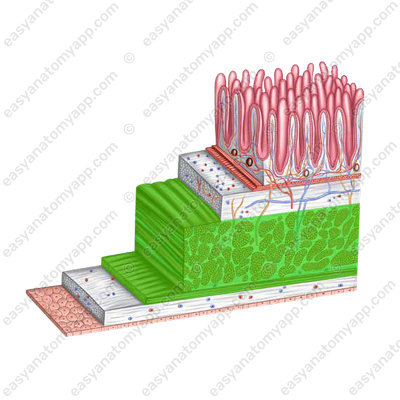
- Serosa or peritoneum (tunica serosa)

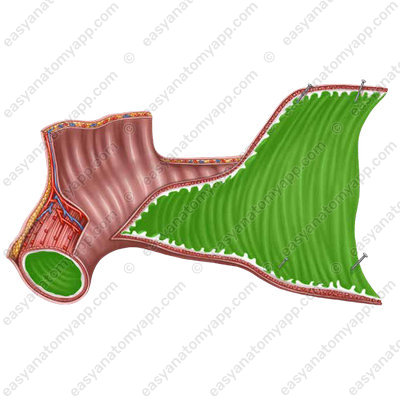
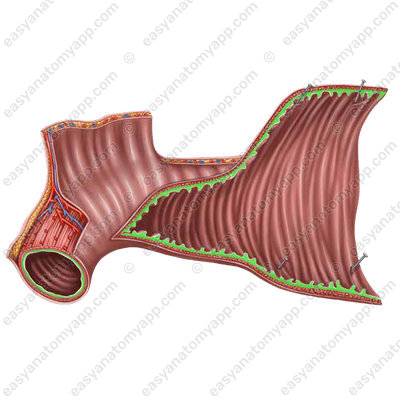
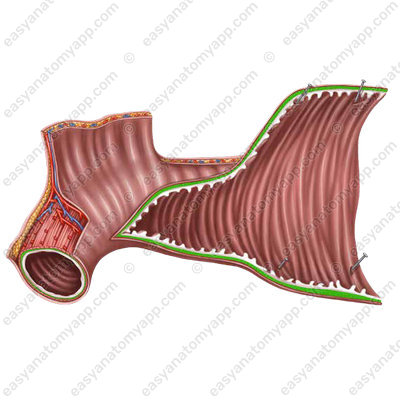
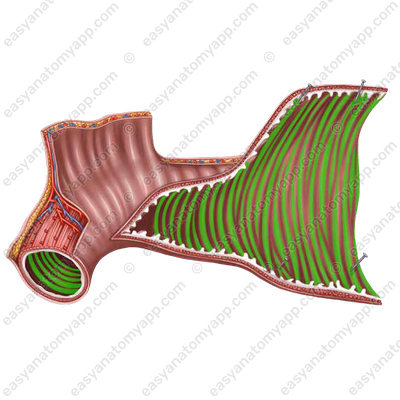
A distinct feature of the mucous membrane is the presence of circular folds or valves of Kerckring (plice circulares),
as well as numerous intestinal villi (villi intestinales).

In addition, there are longitudinal folds in the duodenum, mainly in the descending part. One of these folds ends with an eminence called the major duodenal papilla, or the papilla of Vater (papilla duodeni major);
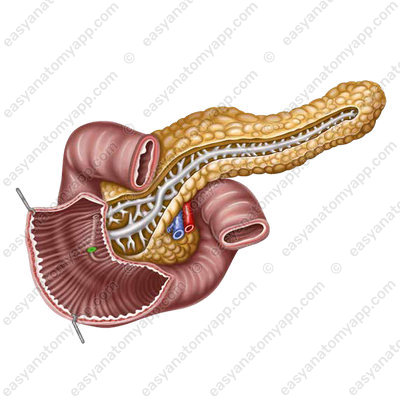
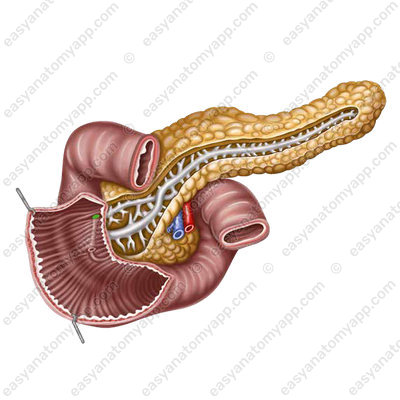
The common bile duct and the main pancreatic duct open at its top. The minor duodenal papilla (papilla duodeni minor) is located superiorly to the major papilla, there is an opening of the accessory pancreatic duct on it.
In the mesenteric part of the small intestine, mainly in the ilium, there are so-called Peyer’s patches, which are part of gastrointestinal associated lymphoid tissue (GALT).
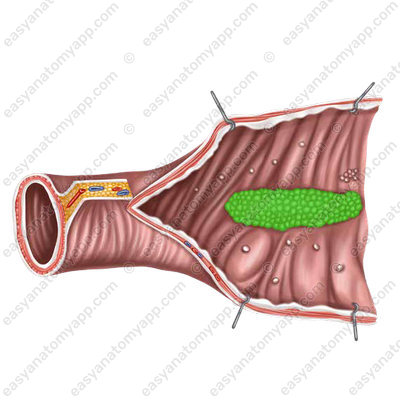
The muscular layer of the small intestine consists of two sub-layers: internal circular (stratum circulare) and external longitudinal (stratum longitudinale).
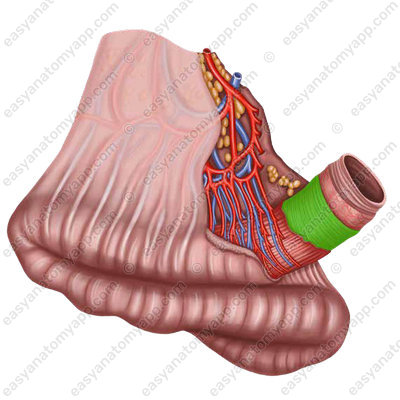
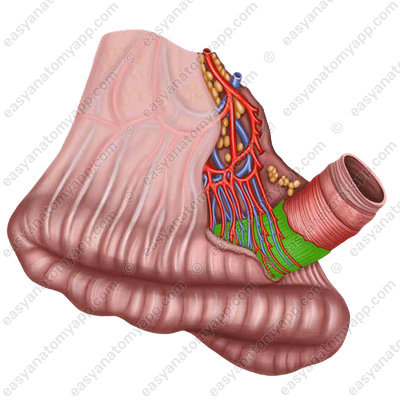
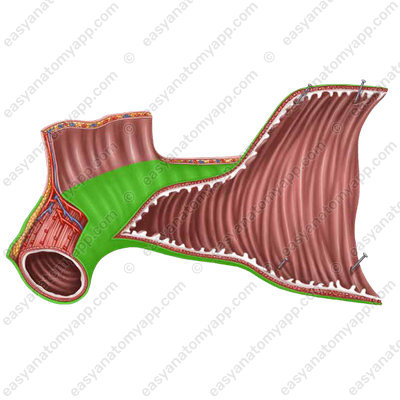
In relation to the peritoneum, the small intestine is covered intraperitoneally, except for the duodenum, which is covered with the peritoneum only on the anterior side.
With intraperitoneal covering, the sheaths of the peritoneum approach the intestine from one side. Therefore, there is a smooth free border covered with the peritoneum in the intestine, and the mesenteric border opposite to it, where the peritoneum covering the intestine passes into its mesentery.
Between the two mesentery sheaths, vessels and nerves lie in the fibrous layer.
Blood supply
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery (a. pancreatoduodenalis superior) which is a branch of the gastroduodenal artery (a. gastroduodenalis)
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (a. pancreatoduodenalis inferior) which is a branch of the superior mesenteric artery (a. mesenterica superior)
Venous drainage
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal vein (v. pancreatoduodenalis superior) which flows into the portal vein (v. portae)
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal vein (v. pancreatoduodenalis inferior) which flows into the portal vein (v. portae)
Lymphatic drainage
- Pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici pancreatoduodenales)
- Pyloric lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici pylorici)
- Superior mesenteric lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici mesenterici superiores)
- Coeliac lymph nodes (nodi lymphatici coeliaci)
Innervation
Along the course of the organ, nerve fibers form the duodenal plexus (plexus duodenalis).
- The vagus nerve (n. vagus)
- Branches of the coeliac plexus (plexus coeliacus)
Anatomy of the small intestine
- Small intestine
- intestinum tenue
- Duodenum
- duodenum
- Superior part
- pars superior
- Superior duodenal flexure
- flexura duodeni superior
- Descending part
- pars descendens
- Inferior duodenal flexure
- flexura duodeni inferior
- Horizontal part
- pars horizontalis
- Ascending part
- pars ascendens
- Duodenojejunal flexure
- flexura duodenojejunalis
- Major duodenal papilla
- papilla duodeni major
- Minor duodenal papilla
- papilla duodeni minor


