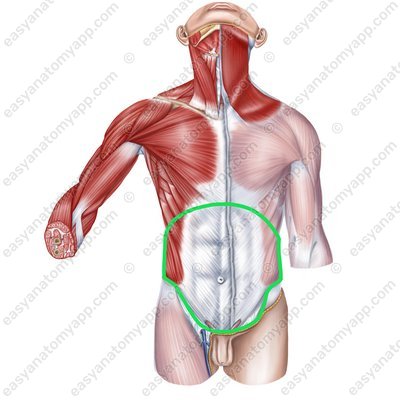
In this pdf-note, we’ll start with the borders of the abdomen:
The superior border passes through the xiphoid process of the sternum and the costal arch
The lateral border is the posterior median line (from the 12th rib to the iliac crest), also called the Lesgaft’s line
The inferior border passes through the iliac crest, inguinal ligament, and pubic symphysis
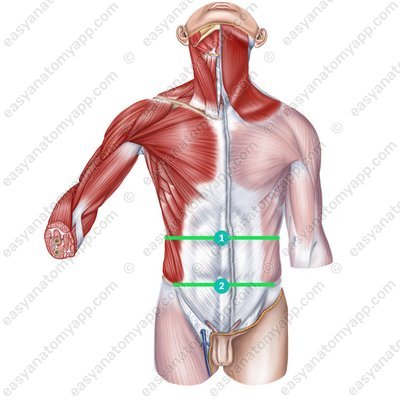
Two horizontal lines can be drawn through the abdominal region:
Intercostal line (linea bicostarum) is located between the inferior ends of 10th ribs (at the L3 level)
Interspinous line (linea bispinarum) is located between the superior anterior iliac spines (at the S2 level)
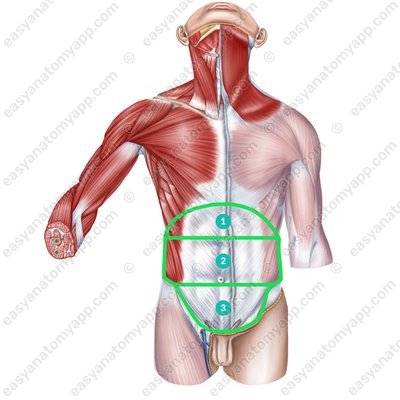
These lines divide the abdominal region into three socalled floors:
Epigastric fossa (epigastrium)
Mesogastrium (mesogastrium)
Pubic region (hypogastrium)
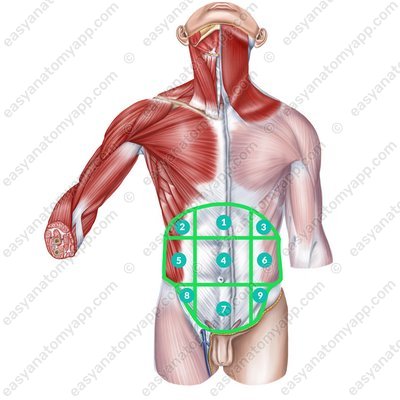
Also, two vertical lines can be drawn along the lateral borders of the rectus abdominis muscles, which divide these three floors into several anatomical regions:
Epigastric region (regio epigastrica)
Right hypochondrium (regio hypochondrica dextra)
Left hypochondrium (regio hypochondrica sinistra)
Umbilical region (regio umbilicalis)
Right lateral abdominal region (regio abdominalis lateralis dextra)
Left lateral abdominal region (regio abdominalis lateralis sinistra)
Pubic region (regio pubica)
Right inguinal region (regio inguinalis dextra)
Left inguinal region (regio inguinalis sinistra)
Muscles of the abdomen are autochthonous according to embryological classification. That means that during embryogenesis, they were laid in the region of the abdomen, and remained there in the postnatal period. The muscles are innervated by the anterior branches of the spinal nerves, which are also called intercostal nerves, as well as the superior branches of the lumbar plexus.
Among the muscles of the abdomen, the following groups are distinguished:
Lateral wall muscles (passing to the anterior wall, they form large tendon laminae called aponeuroses)
External oblique muscle (m. obliquus externus abdominis)
External oblique muscle (m. obliquus externus abdominis) 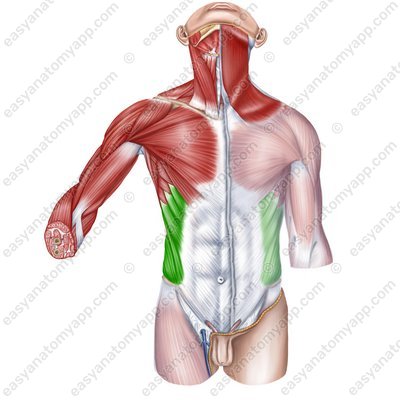
External oblique muscle (m. obliquus externus abdominis) 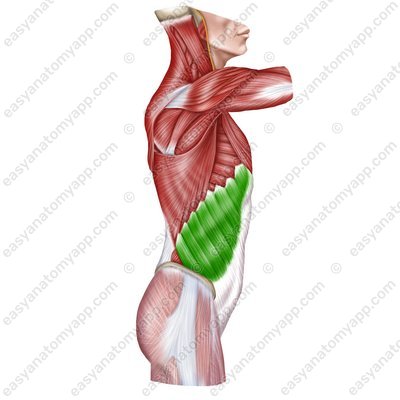
External oblique muscle (m. obliquus externus abdominis)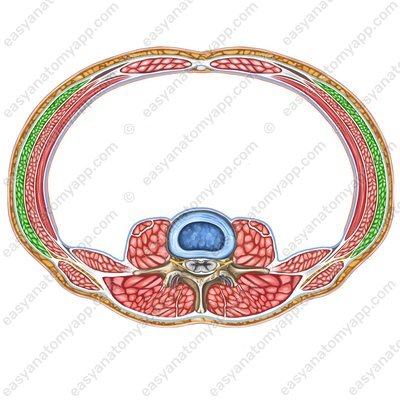 
External oblique muscle
(m. obliquus externus abdominis)Origin: external surface of the ribs 5-12
Insertion: linea alba of the abdomen, outer lip of the iliac crest, pubic symphysis
Function: with bilateral contraction, it flexes the trunk, compresses the internal organs (the muscle of the “abdominal press”), and participates in the act of exhalation; with unilateral contraction, it turns the trunk contralaterally (in the opposite direction)
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th7-Th11), subcostal nerve (Th12), iliopubic nerve (Th12-L1), ilio-inguinal nerve (L1)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, lateral thoracic artery, superficial circumflex iliac artery
Internal oblique muscle (m. obliquus internus abdominis), which lies deeper
Internal oblique muscle (m. obliquus internus abdominis) 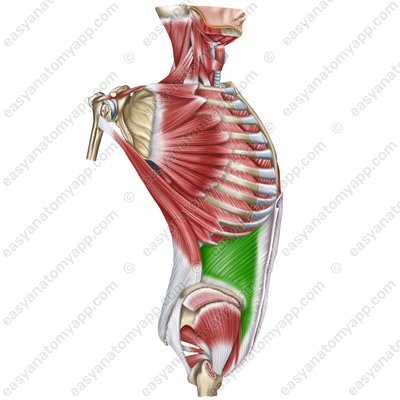
Internal oblique muscle (m. obliquus internus abdominis) .jpg)
Internal oblique muscle (m. obliquus internus abdominis)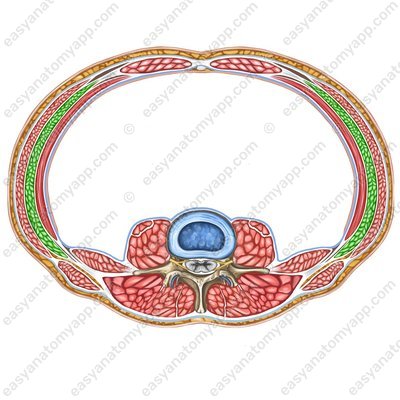 
Internal oblique muscle
(m. obliquus internus abdominis)Origin: intermediate zone of the iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia, inguinal ligament
Insertion: inferior surface of the ribs 10-12, linea alba of the abdomen
Function: with bilateral contraction, it flexes the trunk, compresses the internal organs (the muscle of the “abdominal press”), and participates in the act of exhalation; with unilateral contraction, it turns the trunk ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th7-Th11), subcostal nerve (Th12), iliopubic nerve (Th12-L1), ilio-inguinal nerve (L1)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, superior epigastric artery, inferior epigastric artery, musculophrenic arteries
Transverse abdominal muscle (m. transversus abdominis), which lies even deeper
Transverse abdominal muscle (m. transversus abdominis) 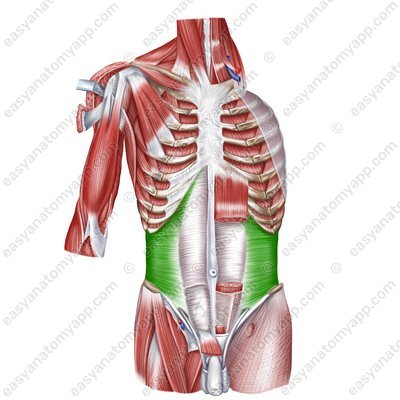
Transverse abdominal muscle (m. transversus abdominis)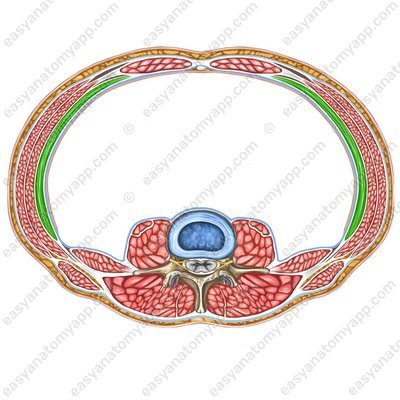 
Transversus abdominis muscle
(m. transversus abdominis)Origin: internal surface of the ribs 7-12, thoracolumbar fascia, internal lip of the iliac crest, inguinal ligament
Insertion: linea alba of the abdomen, aponeurosis of the internal oblique muscle
Function: with bilateral contraction, it compresses the internal organs (the primary muscle of the “abdominal press”), and participates in the act of exhalation; with unilateral contraction, it turns the trunk ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th7-Th11), iliopubic nerve (Th12-L1), ilio-inguinal nerve (L1)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, superior epigastric artery, inferior epigastric artery, musculophrenic arteries
Anterior wall muscles
Rectus abdominis (m. rectus abdominis)
Rectus abdominis muscle (m. rectus abdominis) 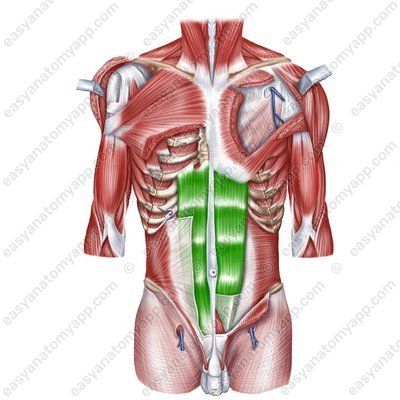
Rectus abdominis muscle (m. rectus abdominis) 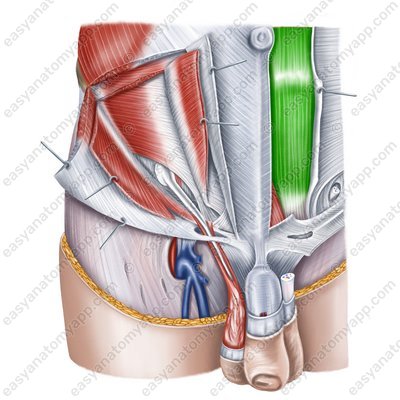
Rectus abdominis muscle (m. rectus abdominis) 
Rectus abdominis
(m. rectus abdominis)Origin: pubic crest, pubic symphysis
Insertion: external surface of the cartilages of the ribs 5-7, xiphoid process of the sternum
In its course it has several tendonous intersections (intersectiones tendineae)
Function: flexes the trunk, compresses the internal organs (the muscle of the “abdominal press”), participates in the act of exhalation; when the thorax is fixed, it lifts the pelvis
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th7-Th11), subcostal nerve (Th12), iliopubic nerve (Th12-L1)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, superior epigastric artery, inferior epigastric artery
Pyramidalis muscle (m. pyramidalis)
Pyramidalis muscle (m. pyramidalis) 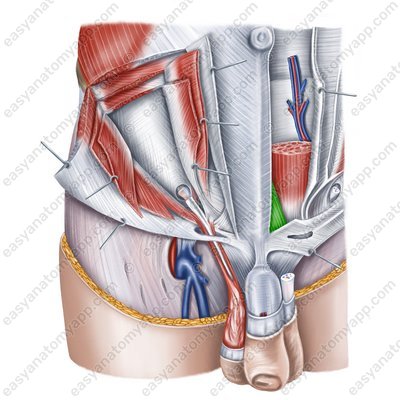
Pyramidalis muscle (m. pyramidalis) 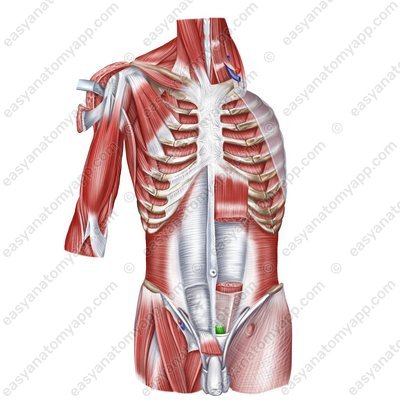
Pyramidalis muscle
(m. pyramidalis)Origin: pubic crest, pubic symphysis
Insertion: woven into the linea alba of the abdomen
Function: Stretches the linea alba of the abdomen
Innervation: subcostal nerve (Th12), iliohypogastric nerve (Th12-L1)
Blood supply: inferior epigastric artery, cremasteric artery
Posterior wall muscles
Quadratus lumborum muscle (m. quadratus lumborum)
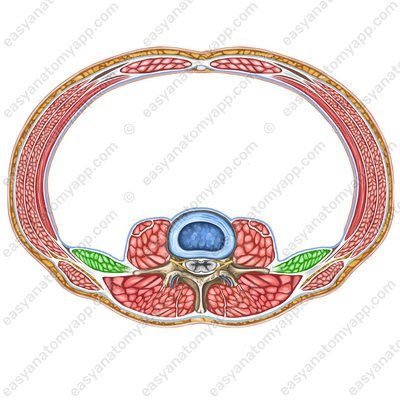
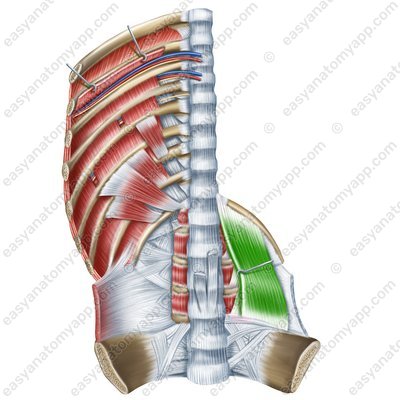

(m. quadratus lumborum)
Origin: iliac crest, iliolumbar ligament
Insertion: inferior border of the 12th rib, transverse processes of the L1-L4 vertebrae
Function: with bilateral contraction, it fixes the 12th rib during exhalation, and also participates in holding the trunk in an upright position; with unilateral contraction, it tilts the spine ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: subcostal nerve (Th12), anterior branches of the spinal nerves (L1-L4)
Blood supply: subcostal artery, lumbar arteries, iliolumbar artery
Abdominal Muscles
- Intercostal line
- linea bicostarum
- Interspinous line
- linea bispinarum
- Epigastric fossa
- epigastrium
- Mesogastrium
- mesogastrium
- Pubic region
- hypogastrium
- Epigastric region
- regio epigastrica
- Right hypochondrium
- regio hypochondrica dextra
- Left hypochondrium
- regio hypochondrica sinistra
- Umbilical region
- regio umbilicalis
- Right lateral abdominal region
- regio abdominalis lateralis dextra
- Left lateral abdominal region
- regio abdominalis lateralis sinistra
- Pubic region
- regio pubica
- Right inguinal region
- regio inguinalis dextra
- Left inguinal region
- regio inguinalis sinistra
- External oblique muscle
- m. obliquus externus abdominis
- Internal oblique muscle
- m. obliquus internus abdominis
- Transverse abdominal muscle
- m. transversus abdominis
- Rectus abdominis muscle
- m. rectus abdominis
- Pyramidalis muscle
- m. pyramidalis
- Quadratus lumborum muscle
- m. quadratus lumborum


