In addition to the obvious division into superficial and deep groups, muscles of the back are also classified depending on their embryological origin.
According to this classification, the following groups are distinguished among the deep muscles:
Autochthonous muscles formed in the back region during embryogenesis, where they remained in the postnatal period. This group is innervated by the posterior branches of the spinal nerves
Erector spinae muscle (m. erector spinae)

Transversospinalis muscle (m. transversospinalis)
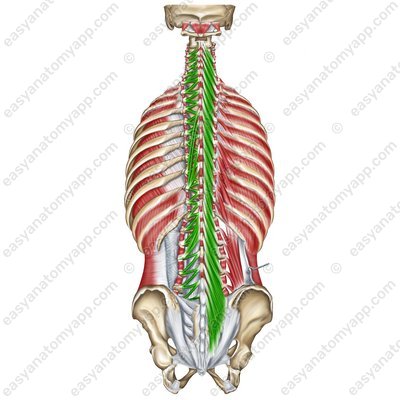
Interspinales muscles (mm. interspinales)
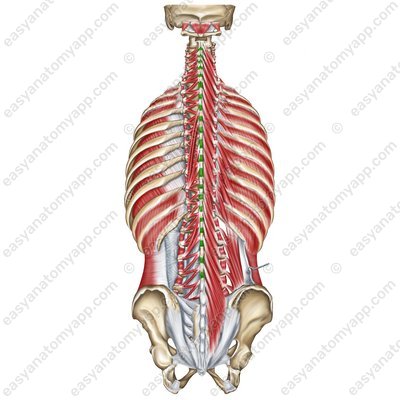
Intertransversarii muscles (mm. intertransversarii)

Ventral muscles formed in the ventral region during embryogenesis, and only then they migrated to the back. They are innervated by the anterior branches of the spinal nerves, which are called intercostal nerves
Levatores costarum muscles (mm. levatores costarum)
According to the embryological classification, the following groups are distinguished among the superficial muscles of the back:
Truncofugal muscles have migrated from the trunk to the shoulder girdle. They are innervated by branches of the brachial plexus
Rhomboid major muscle (m. rhomboideus major)
Rhomboid major muscle (m. rhomboideus major) 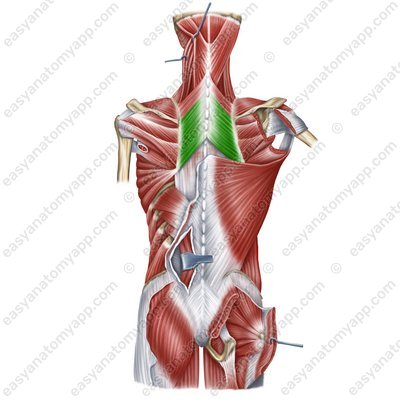
Rhomboid minor muscle (m. rhomboideus minor)
Rhomboid minor muscle (m. rhomboideus minor) 
Levator scapulae muscle (m. levator scapulae)
Levator scapulae muscle (m. levator scapulae) .jpg)
Truncopetal muscles migrated from the limbs to the trunk. They are innervated by branches of the brachial plexus.
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi)
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi) 
Muscles of ventral origin have migrated from the chest region to the back region. They are innervated by the anterior branches of the spinal nerves.
Serratus posterior superior muscle (m. serratus posterior superior)
Serratus posterior superior muscle (m. serratus posterior superior) 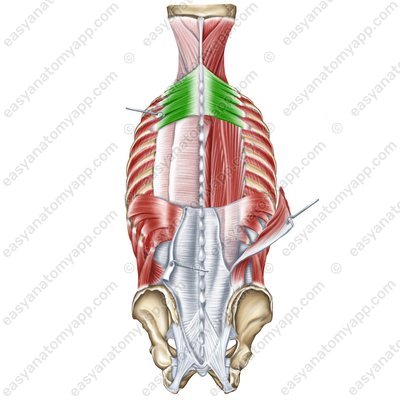
Serratus posterior inferior muscle (m. serratus posterior inferior)
Serratus posterior inferior muscle (m. serratus posterior inferior) 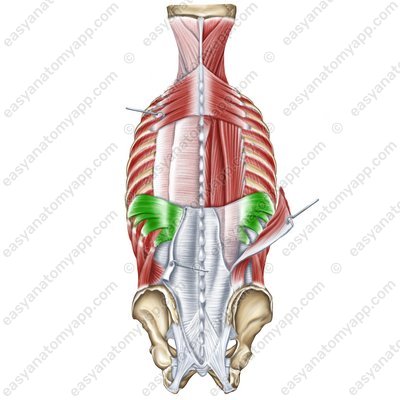
Muscles of cranial origin have migrated from the head region to the back region. They are innervated by the accessory nerve.
Trapezius muscle (m. trapezius)
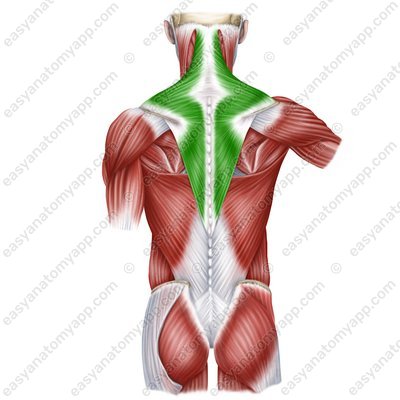
Back muscles: Development
- Trapezius muscle
- m. trapezius
- Latissimus dorsi muscle
- m. latissimus dorsi
- Rhomboid major muscle
- m. rhomboideus major
- Rhomboid minor muscle
- m. rhomboideus minor
- Levator scapulae muscle
- m. levator scapulae
- Serratus posterior superior muscle
- m. serratus posterior superior
- Serratus posterior inferior muscle
- m. serratus posterior inferior
- Erector spinae muscle
- m. erector spinae
- Transversospinalis muscle
- m. transversospinalis
- Interspinales muscles
- mm. interspinales
- Intertransversarii muscles
- mm. intertransversarii


