In this pdf-note, we’ll start with the borders of the upper limb:
The anterior border is the deltopectoral groove
The posterior border is the posterior deltoid groove
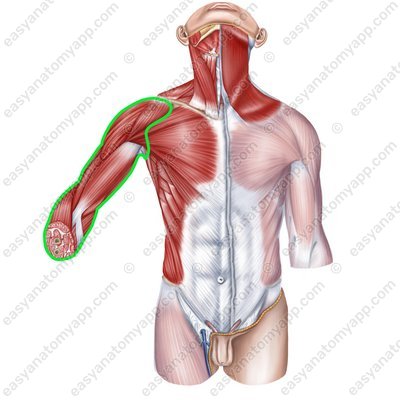
Borders of the upper limb 
Borders of the upper limb
Within the upper limb, there is a large number of regions:
Deltoid region (regio deltoidea)
Axillary region (regio axillaris)
Anterior region of the arm (regio brachialis anterior)
Posterior region of the arm (regio brachialis posterior)
Anterior region of the elbow (regio cubitalis anterior)
Posterior region of the elbow (regio cubitalis posterior)
Anterior region of the forearm (regio anterobrachialis anterior)
Posterior region of the forearm (regio anterobrachialis posterior)
Anterior region of the wrist (regio carpalis anterior)
Posterior region of the wrist (regio carpalis posterior)
Palmar region of the hand (regio palmaris manus)
Dorsal region of the hand (regio dorsalis manus)

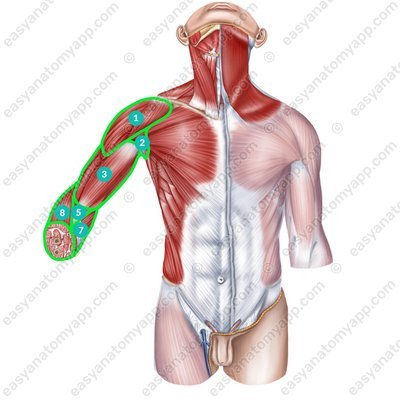
Within these areas, the muscles of the upper limb are located.
These include:
Pectoral girdle muscles
Muscles of the free part of the upper limb
The muscles of the free part of the upper limb are divided into:
Arm muscles
Forearm muscles
Hand muscles
There are two groups of forearm muscles: anterior and posterior.
The anterior group consists of the hand and finger flexor muscles. They are arranged in several layers.
Superficial layer:
Brachioradialis muscle (m. brachioradialis), which is sometimes described as part of a separate lateral group of forearm muscles, but this is of no principal significance
Brachioradialis muscle (m. brachioradialis) 
Brachioradialis muscle (m. brachioradialis) 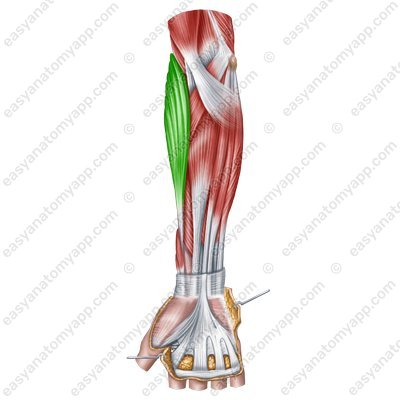
Brachioradialis muscle (m. brachioradialis) 
Brachioradialis muscle
(m. brachioradialis)Origin: medial supraepicondylar ridge of the humerus, lateral intermuscular septum of the arm
Insertion: above the styloid process of the radius
Function: flexes the upper limb at the elbow joint, supinates the hand. The hand pronates from the supination position.
Innervation: radial nerve (C5-C8)
Blood supply: collateral radial artery, recurrent radial artery, radial artery
Pronator teres muscle (m.pronator teres)
Pronator teres muscle (m. pronator teres) 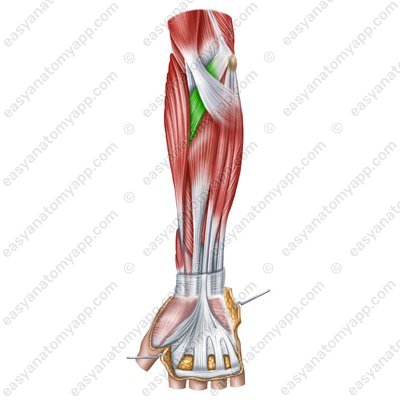
Pronator teres muscle(m. pronator teres) 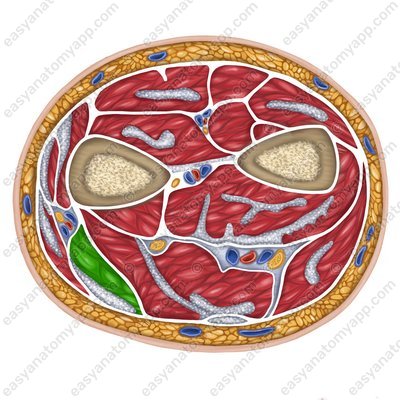
Pronator teres muscle
(m. pronator teres)Origin:
Humeral head (caput humerale) arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the medial intermuscular septum of the arm
Ulnar head (caput ulnare) arises from the tuberosity of the ulna, coronoid process of the ulna
Insertion: lateral surface of the body of the radius
Function: pronation of the forearm, flexion of the upper limb at the elbow joint
Innervation: median nerve (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: branches of the brachial, ulnar and radial arteries
Flexor carpi radialis muscle (m. flexor carpi radialis)
Flexor carpi radialis muscle (m. flexor carpi radialis) 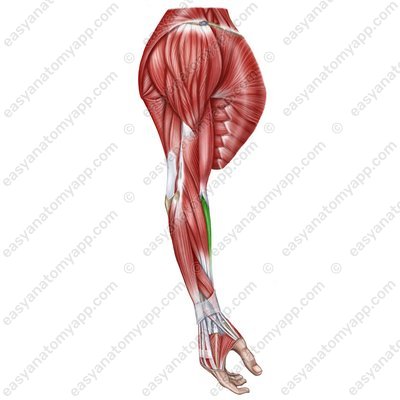
Flexor carpi radialis muscle (m. flexor carpi radialis) 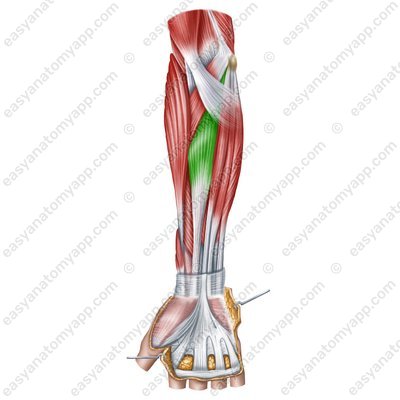
Flexor carpi radialis muscle (m. flexor carpi radialis) 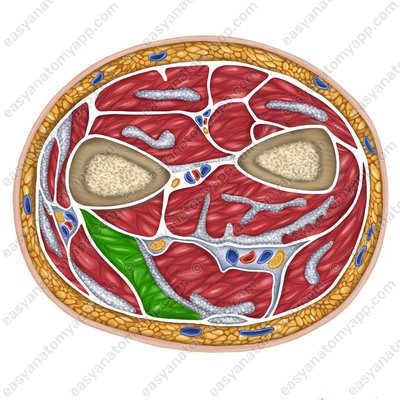
Flexor carpi radialis muscle
(m. flexor carpi radialis)Origin: medial epicondyle of the humerus, medial intermuscular septum of the arm
Insertion: palmar surfaces of the bases of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpals
Function: flexes and abducts the hand, flexes the forearm
Innervation: median nerve (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: branches of the brachial, ulnar and radial arteries
Palmaris longus muscle (m. palmaris longus)
Palmaris longus muscle (m. palmaris longus) 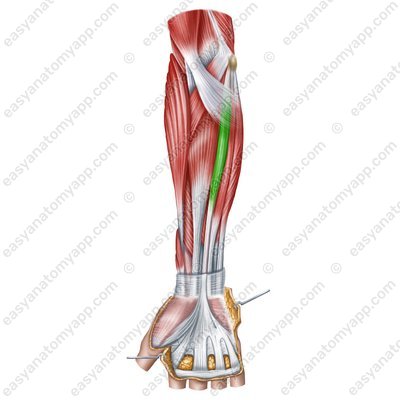
Palmaris longus muscle (m. palmaris longus) 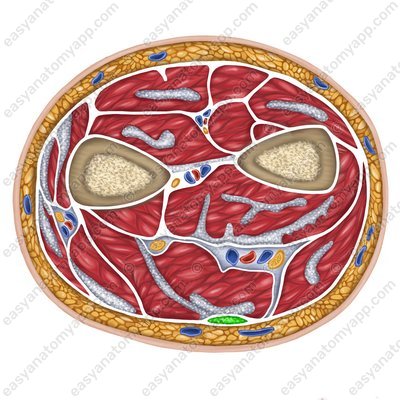
Palmaris longus muscle
(m. palmaris longus)Origin: medial epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: continues into the palmar aponeurosis, which attaches to the bases of the middle phalanges of the fingers 2-5 (4 tendons)
Function: stretches the palmar aponeurosis, flexes the hand and the forearm
Innervation: median nerve (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: radial artery
Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (m. flexor carpi ulnaris)
Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (m. flexor carpi ulnaris) 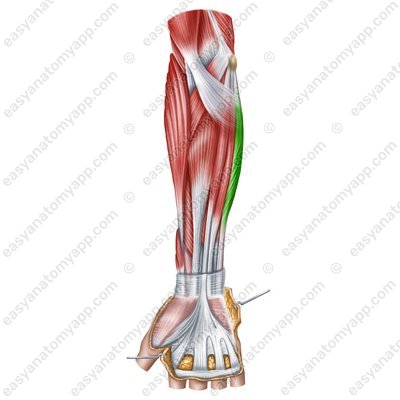
Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle (m. flexor carpi ulnaris) 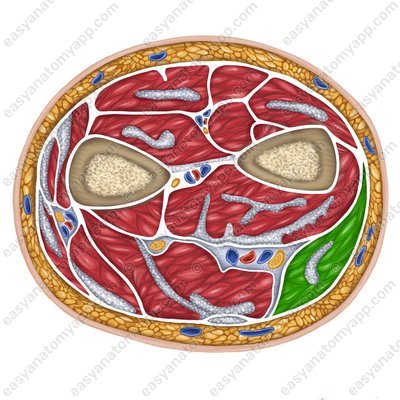
Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
(m. flexor carpi ulnaris)Origin:
Humeral head (caput humerale) arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the medial intermuscular septum of the arm
Ulnar head (caput ulnare) arises from the olecranon and the posterior border of the ulna
Insertion: pisiform bone, hamate bone, base of the 5th metacarpal
Function: flexes and adducts the hand
Innervation: ulnar nerve (C7-C8)
Blood supply: superior and inferior ulnar collateral arteries, ulnar artery
Second layer:
Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (m. flexor digitorum superficialis)
Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (m. flexor digitorum superficialis) 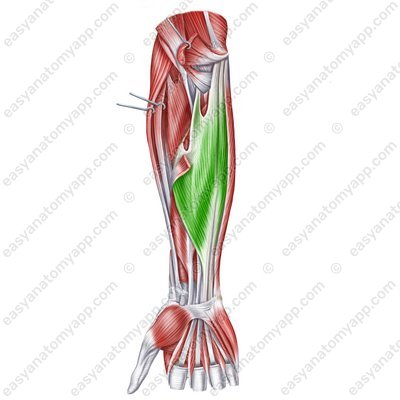
Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle (m. flexor digitorum superficialis) 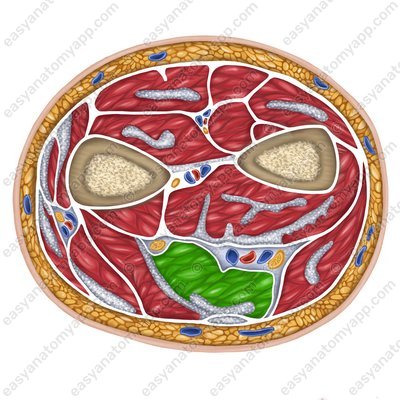
Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
(m. flexor digitorum superficialis)Origin:
Humero-ulnar head (caput humeroulnare) arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus, ulnar collateral ligament, and the coronoid process of the ulna
Radial head (caput radiale) arises from the anterior border of the radius
Insertion: divides into four tendons that reach the bases of the middle phalanges of the fingers 2-5 and bifurcate. The resulting cruses insert into the lateral surfaces of the bases of the middle phalanges
Function: flexes the middle phalanges of the fingers 2-5, flexes the hand, flexes the forearm
Innervation: median nerve (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: radial and ulnar arteries
Third layer:
Flexor digitorum profundus muscle (m. flexor digitorum profundus)
Flexor digitorum profundus muscle (m. flexor digitorum profundus) 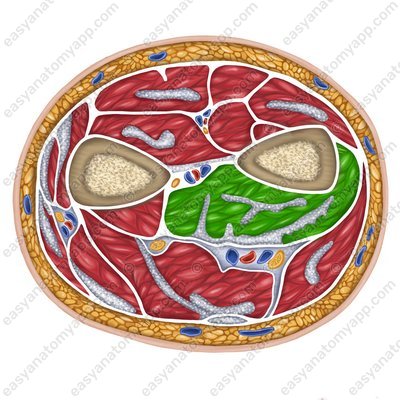
Flexor digitorum profundus muscle (m. flexor digitorum profundus) 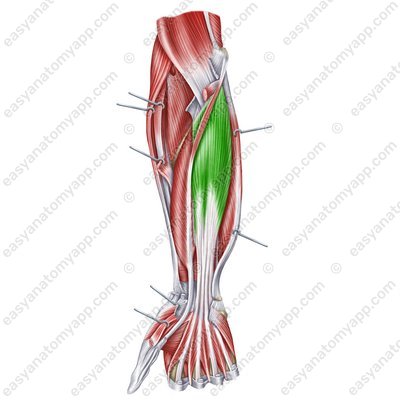
Flexor digitorum profundus muscle
(m. flexor digitorum profundus)Origin: anterior surface of the ulna, interosseous membrane of the forearm
Insertion: divides into four tendons, which insert into the bases of the distal phalanges of the fingers 2-5
Function: flexes the distal phalanges of the fingers 2-5
Innervation: ulnar and median nerves (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: radial artery, ulnar artery
Flexor pollicis longus muscle (m. flexor pollicis longus)
Flexor pollicis longus muscle (m. flexor pollicis longus) 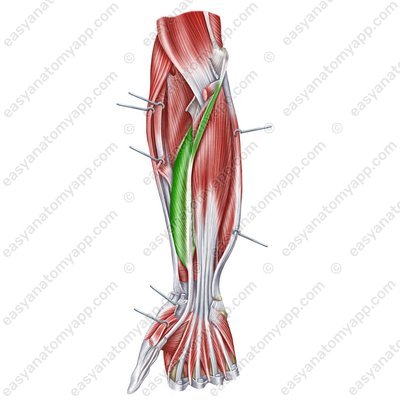
Flexor pollicis longus muscle (m. flexor pollicis longus) 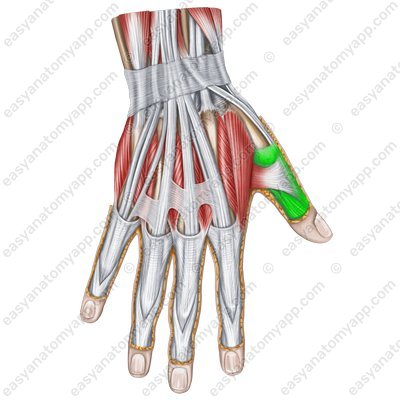
Flexor pollicis longus muscle
(m. flexor pollicis longus)Origin: anterior surface of the radius, interosseous membrane of the forearm, medial epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: base of the distal phalanx of the thumb
Function: flexes the distal phalanx of the thumb
Innervation: median nerve (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: radial artery, ulnar artery, anterior interosseous artery
Fourth layer:
Pronator quadratus muscle (m. pronator quadratus)
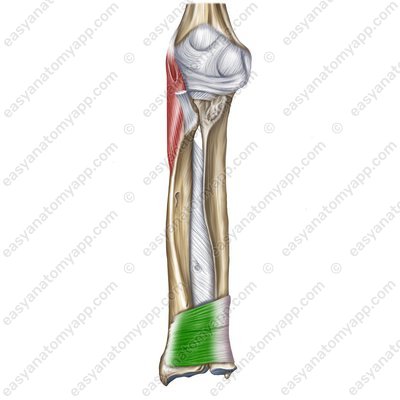
(m. pronator quadratus)
Origin: inferior third of the body of the ulna
Insertion: inferior third of the body of the radius
Function: pronates the forearm and the hand
Innervation: median nerve (C5-Th1)
Blood supply: anterior interosseous artery
Forearm muscles
- Deltoid region
- regio deltoidea
- Axillary region
- regio axillaris
- Anterior region of the arm
- regio brachialis anterior
- Posterior region of the arm
- regio brachialis posterior
- Anterior region of the elbow
- regio cubitalis anterior
- Posterior region of the elbow
- regio cubitalis posterior
- Anterior region of the forearm
- regio anterobrachialis anterior
- Posterior region of the forearm
- regio anterobrachialis posterior
- Anterior region of the wrist
- regio carpalis anterior
- Posterior region of the wrist
- regio carpalis posterior
- Palmar region of the hand
- regio palmaris manus
- Dorsal region of the hand
- regio dorsalis manus
- Brachioradialis muscle
- m. brachioradialis
- Pronator teres muscle
- m.pronator teres
- Flexor carpi radialis
- m. flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus muscle
- m. palmaris longus
- Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle
- m. flexor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
- m. flexor digitorum superficialis
- Flexor digitorum profundus muscle
- m. flexor digitorum profundus
- Flexor pollicis longus muscle
- m. flexor pollicis longus
- Pronator quadratus muscle
- m. pronator quadratus


