There are the following borders of the neck region:
The superior border passes through the inferior border of the mandible, temporomandibular joint, mastoid process, superior nuchal line, and the external occipital protuberance
The inferior border passes through the jugular notch, clavicle, acromion of the scapula, and the spinous process of the C7 verteb
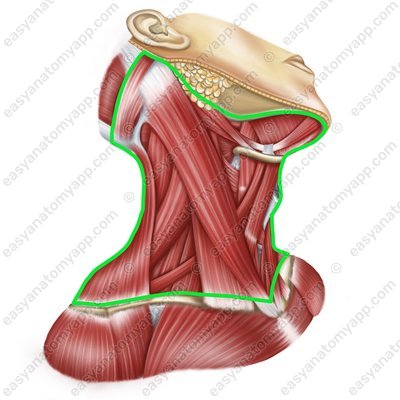
Borders of the neck region There are several anatomical regions within the neck:
Anterior cervical region (regio cervicalis anterior)
Lateral cervical region (regio cervicalis lateralis)
Posterior cervical region (regio cervicalis posterior)
Sternocleidomastoid region (regio sternocleidomastoidea)
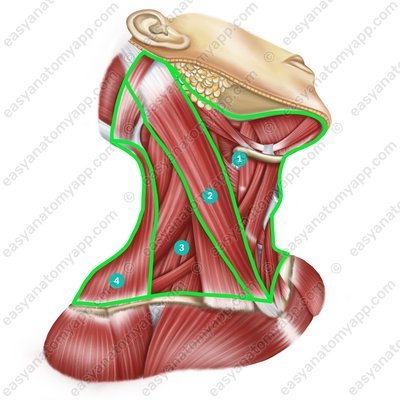
The muscles of the neck are located within these anatomical areas. They are divided into superficial and deep muscles.
There are two groups of the deep muscles:
Lateral group
Medial (prevertebral) group The lateral group includes:
Scalenus anterior muscle (m. scalenus anterior)
Scalenus anterior muscle (m. scalenus anterior) 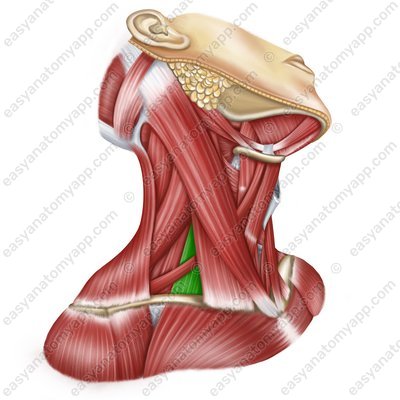
Scalenus anterior muscle (m. scalenus anterior) 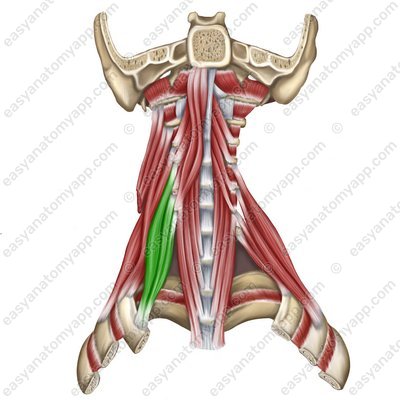
Scalenus anterior muscle (m. scalenus anterior) 
Scalenus anterior muscle (m. scalenus anterior) 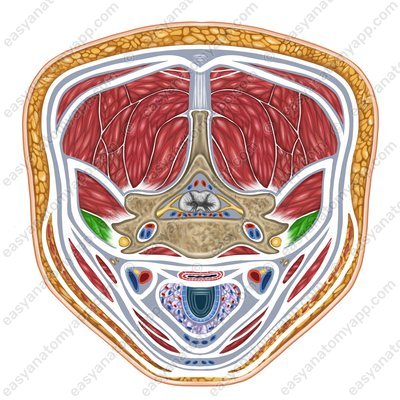
Scalenus anterior muscle
(m. scalenus anterior)Origin: anterior tubercles of transverse processes of the C2-C6 vertebrae
Insertion: tubercle of the scalenus anterior muscle on the 1st rib
Function: when the spine is fixed, it lifts the 1st and 2nd ribs, participating in the act of inhalation; when the ribs are fixed, it flexes the cervical spine, with unilateral contraction, it flexes it in its own direction
Innervation: cervical plexus (C5-C8)
Blood supply: ascending artery of the neck, inferior thyroid artery
Scalenus medius muscle (m. scalenus medius)
Scalenus medius muscle (m. scalenus medius) 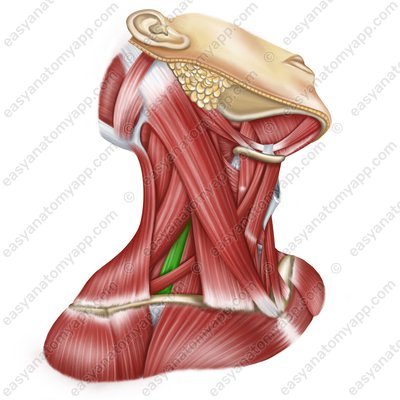
Scalenus medius muscle (m. scalenus medius) 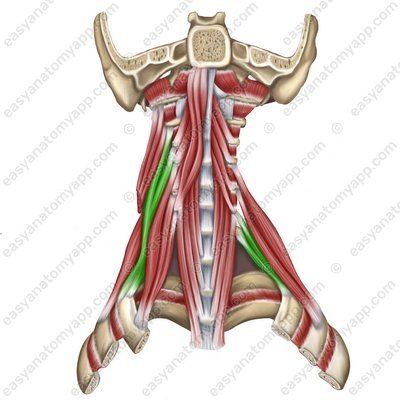
Scalenus medius muscle (m. scalenus medius) 
Scalenus medius muscle (m. scalenus medius) 
Scalenus medius muscle
(m. scalenus medius)Origin: anterior tubercles of transverse processes of the C2-C6 vertebrae
Insertion: tubercle of the scalenus medius muscle on the 1st rib
Function: when the spine is fixed, it lifts the 1st and 2nd ribs, participating in the act of inhalation; when the ribs are fixed, it flexes the cervical spine, with unilateral contraction, it flexes it in its own direction
Innervation: cervical plexus (C3-C8)
Blood supply: deep cervical artery, vertebral artery, transverse cervical artery
Scalenus posterior muscle (m. scalenus posterior)
Scalenus posterior muscle (m. scalenus posterior) 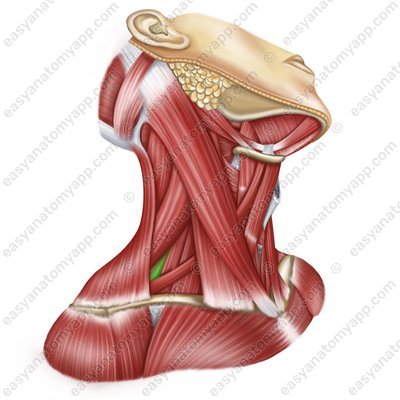
Scalenus posterior muscle (m. scalenus posterior) 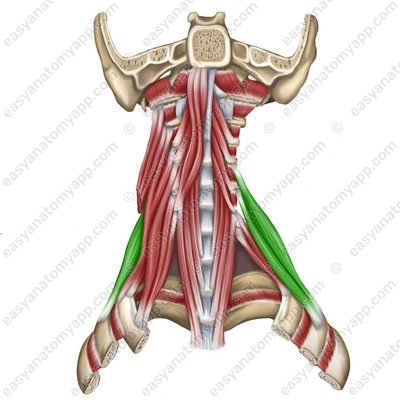
Scalenus posterior muscle (m. scalenus posterior) 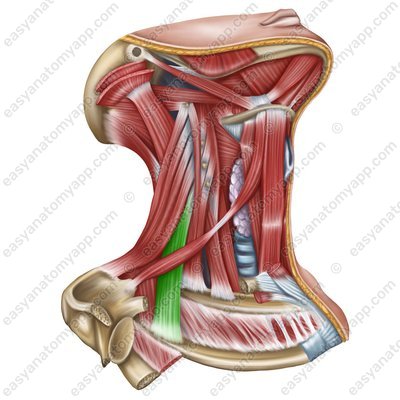
Scalenus posterior muscle (m. scalenus posterior) 
Scalenus posterior muscle
(m. scalenus posterior)Origin: anterior tubercles of transverse processes of the C4-C6 vertebrae
Insertion: tubercle of the scalenus posterior muscle on the 2nd rib
Function: when the spine is fixed, it lifts the 1st and 2nd ribs, participating in the act of inhalation; when the ribs are fixed, it flexes the cervical spine, with unilateral contraction, it flexes it in its own direction
Innervation: cervical plexus (C7-C8)
Blood supply: deep artery of the neck, transverse cervical artery, posterior intercostal artery
The medial (prevertebral) group includes:
Longus colli muscle (m. longus colli)
Longus colli muscle (m. longus colli) 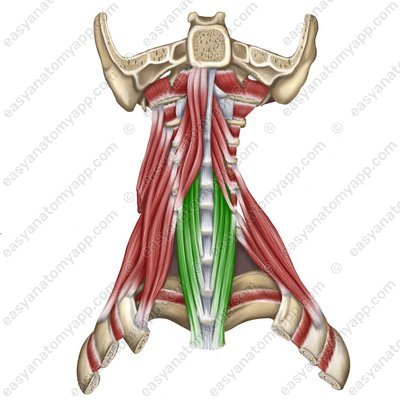
Longus colli muscle (m. longus colli) .jpg)
Longus colli muscle
(m. longus colli)Origin:
Vertical part arises from the bodies of the C2-C5, Th1-Th3 vertebrae
Superior oblique part arises from the transverse processes of the C3-C5 vertebrae
Inferior oblique part arises from the bodies of the Th1-Th3 vertebrae
Insertion:
Vertical part inserts into the bodies of the C2-C4 vertebrae
Superior oblique part inserts into the anterior tubercle of the atlas and the bodies of the underlying cervical vertebrae
Inferior oblique part inserts into the anterior tubercles of the C5-C7 vertebrae
Function: with a bilateral contraction, it tilts the neck anteriorly, with a unilateral contraction, it tilts the neck laterally
Innervation: cervical plexus (C2-C6)
Blood supply: vertebral artery, ascending artery of the neck, deep cervical artery
Longus capitis muscle (m. longus capitis)
Longus capitis muscle (m. longus capitis) 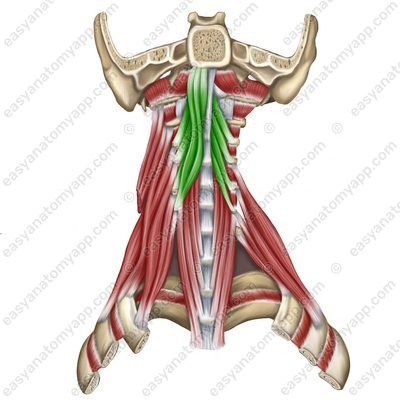
Longus capitis muscle (m. longus capitis) 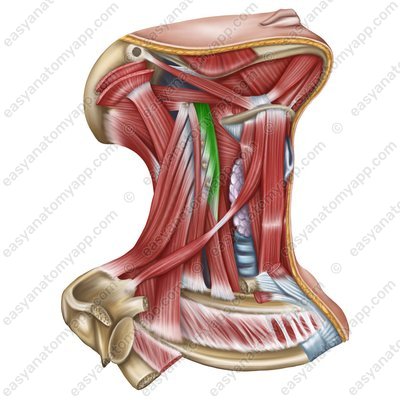
Longus capitis muscle
(m. longus capitis)Origin: anterior tubercles of transverse processes of the C3-C6 vertebrae
Insertion: basilar part of the occipital bone
Function: with a bilateral contraction, it tilts the head and neck anteriorly, with a unilateral contraction, it tilts the head and neck laterally
Innervation: Cervical plexus (C1-C4)
Blood supply: vertebral artery, ascending artery of the neck, deep cervical artery
Rectus capitis anterior muscle (m. rectus capitis anterior)
Rectus capitis anterior muscle (m. rectus capitis anterior) 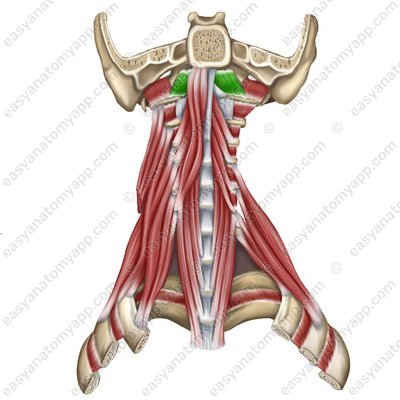
Rectus capitis anterior muscle
(m. rectus capitis anterior)Origin: lateral part of the anterior arch of the atlas
Insertion: basilar part of the occipital bone
Function: tilts the head in the anterior direction
Innervation: Cervical plexus (C1)
Blood supply: vertebral artery, ascending pharyngeal artery
Rectus capitis lateralis muscle (m. rectus capitis lateralis)
Rectus capitis lateralis muscle (m. rectus capitis lateralis) 
Rectus capitis lateralis muscle (m. rectus capitis lateralis) 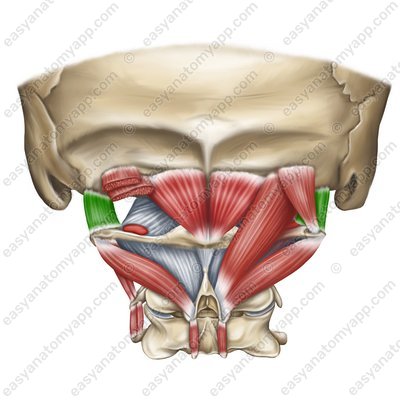
Rectus capitis lateralis muscle
(m. rectus capitis lateralis)Origin: transverse process of the atlas
Insertion: lateral part of the occipital bone
Function: tilts the head laterally
Innervation: Cervical plexus (C1)
Blood supply: occipital artery, vertebral artery
Also, the so-called suboccipital muscles (mm. suboccipitales), which are sometimes classified as muscles of the back, constitute a separate group:
Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle (m. rectus capitis posterior minor)
Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle (m. rectus capitis posterior minor) 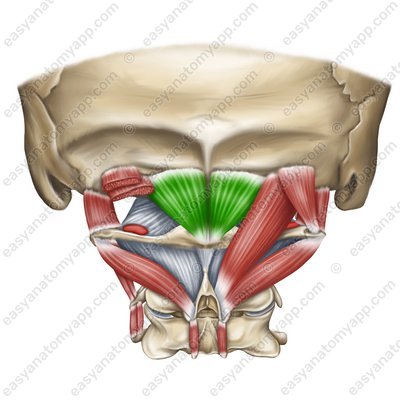
Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
(m. rectus capitis posterior minor)Origin: posterior tubercle of the atlas
Insertion: medial part of the inferior nuchal line
Function: with bilateral contraction, it extends the head, with unilateral contraction, it turns the head ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: occipital nerve, which is a posterior branch of the spinal nerve (C1)
Blood supply: deep cervical artery
Rectus capitis posterior major muscle (m. rectus capitis posterior major)
Rectus capitis posterior major muscle (m. rectus capitis posterior major) 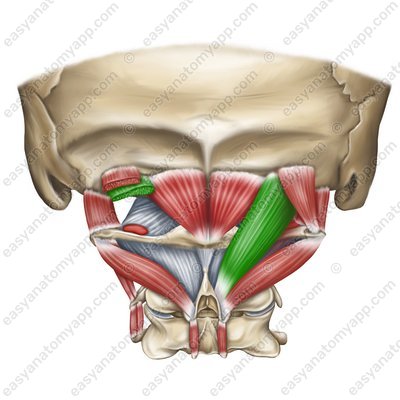
Rectus capitis posterior major muscle
(m. rectus capitis posterior major)Origin: spinous process of the C2 vertebra (axis)
Insertion: lateral part of the inferior nuchal line
Function: with bilateral contraction, it extends the head, with unilateral contraction, it turns the head ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: occipital nerve, which is a posterior branch of the spinal nerve (C1)
Blood supply: deep cervical artery
Obliquus capitis inferior muscle (m. obliquus capitis inferior)
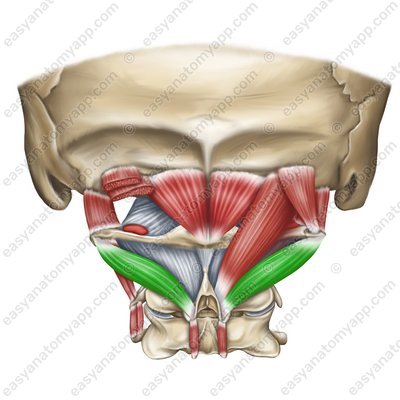
Obliquus capitis inferior muscle (m. obliquus capitis inferior) Obliquus capitis inferior muscle
(m. obliquus capitis inferior)Origin: spinous process of the C2 vertebra (axis)
Insertion: transverse process of the C1 vertebra (atlas)
Function: with bilateral contraction, it extends the head, with unilateral contraction, it turns the head ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: occipital nerve, which is a posterior branch of the spinal nerve (C1)
Blood supply: deep cervical artery
Obliquus capitis superior muscle (m. obliquus capitis superior)
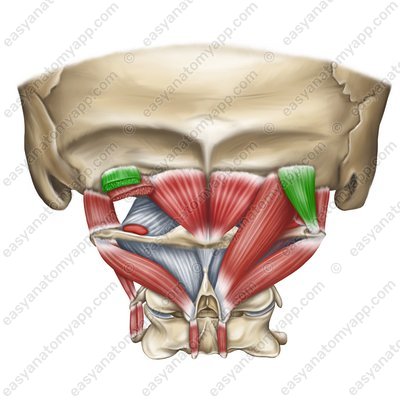
(m. obliquus capitis superior)
Origin: transverse process of the C1 vertebra (atlas)
Insertion: occipital bone between the superior and inferior nuchal lines
Function: with bilateral contraction, it extends the head, with unilateral contraction, it turns and tilts the head ipsilaterally (in its own direction)
Innervation: occipital nerve, which is a posterior branch of the spinal nerve (C1)
Blood supply: deep cervical artery
Deep muscles of the neck
- Anterior cervical region
- regio cervicalis anterior
- Lateral cervical region
- regio cervicalis lateralis
- Posterior cervical region
- regio cervicalis posterior
- Sternocleidomastoid region
- regio sternocleidomastoidea
- Scalenus anterior muscle
- m. scalenus anterior
- Scalenus medius muscle
- m. scalenus medius
- Scalenus posterior muscle
- m. scalenus posterior
- Longus colli muscle
- m. longus colli
- Longus capitis muscle
- m. longus capitis
- Rectus capitis anterior muscle
- m. rectus capitis anterior
- Rectus capitis lateralis muscle
- m. rectus capitis lateralis
- Suboccipital muscles
- mm. suboccipitales
- Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- m. rectus capitis posterior minor
- Rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- m. rectus capitis posterior major
- Obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- m. obliquus capitis inferior
- Obliquus capitis superior muscle
- m. obliquus capitis superior


