In this pdf-note, we’ll start with the borders of the back:
Superior border passes through the external occipital protuberance and the superior nuchal line
Inferior border passes through the sacro-iliac joints, posterior segments of the ilium bones crests, coccyx
Lateral border passes through the posterior median line
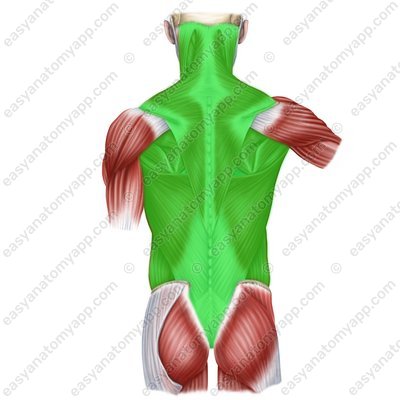
There are several anatomical regions within the back:
Vertebral region (regio vertebralis)
Scapular region (regio scapularis)
Infrascapular region (regio infrascapularis)
Lumbar region (regio lumbalis)
Sacral region (regio sacralis)
The muscles of the back are located within these regions. They are arranged in two layers: superficial and deep. In this pdf-note, we will learn about the superficial muscles of the back.
These include:
Trapezius muscle (m. trapezius)
Trapezius muscle (m. trapezius) 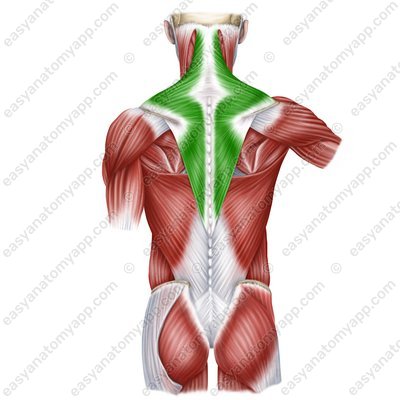
Trapezius muscle (m. trapezius) 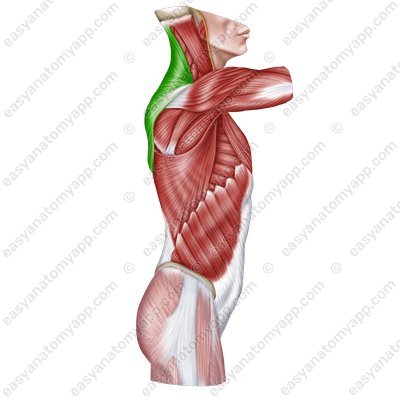
Trapezius muscle (m. trapezius) 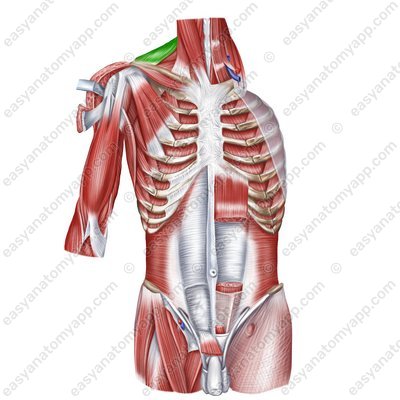
Trapezius muscle
(m. trapezius)Origin:
Descending part arises from the external occipital protuberance, superior nuchal line, spinous processes of vertebrae, nuchal ligament
Transverse part arises from the spinous processes of Th1-Th4 vertebrae
Ascending part arises from the spinous processes of Th5-Th12 vertebrae
Insertion:
Descending part inserts into the external third of the clavicle
Transverse part inserts into the acromion of the scapula, spine of the scapula
Ascending part inserts into the spine of the scapula
Function:
Descending part: brings the scapula closer to the spine (superiorly and medially), helps to extend the cervical spine, helps to turn the head to the contralateral side
Transverse part: pulls the scapula medially
Ascending part: pulls the scapula inferiorly and medially
Innervation:
Motor branches: accessory nerve
Sensory branches: cervical plexus (C3-C4)
Blood supply: transverse cervical artery, occipital, suprascapular, posterior intercostal arteries.
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi)
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi) 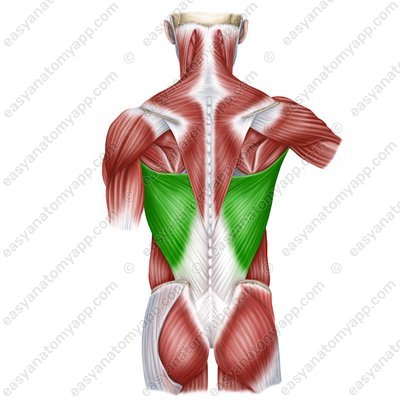
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi) 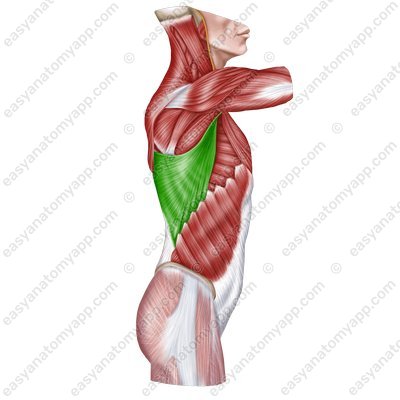
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi) 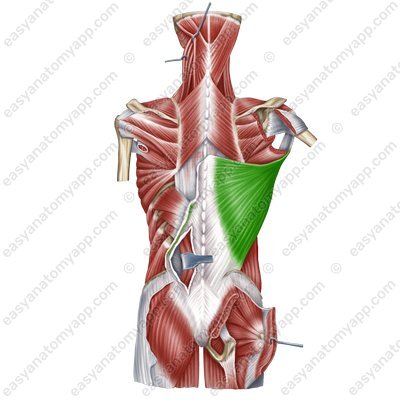
Latissimus dorsi muscle (m. latissimus dorsi) 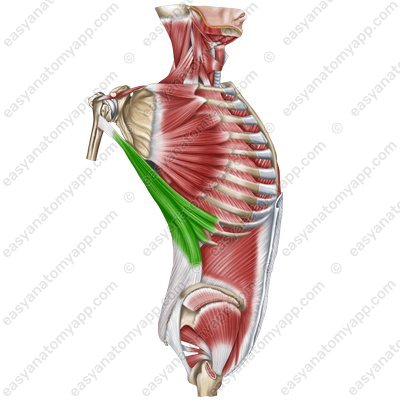
Latissimus dorsi muscle
(m. latissimus dorsi)Origin:
Vertebral part arises from the spinous processes of the Th7-Th12 vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia
Iliac part arises from the posterior third of the iliac crest
Rib part arises from the ribs 9-12
Scapular part arises from lower angle of the scapula
Insertion: crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus
Function: arm pronation, arm adduction, arm extension; also it slightly participates in the act of breathing.
Innervation: thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
Blood supply: thoracodorsal artery, posterior circumflex humeral artery, posterior intercostal arteries.
The following muscles are located slightly deeper than the previous ones.
Levator scapulae muscle (m. levator scapulae)
Levator scapulae muscle (m. levator scapulae) .jpg)
Levator scapulae muscle (m. levator scapulae) 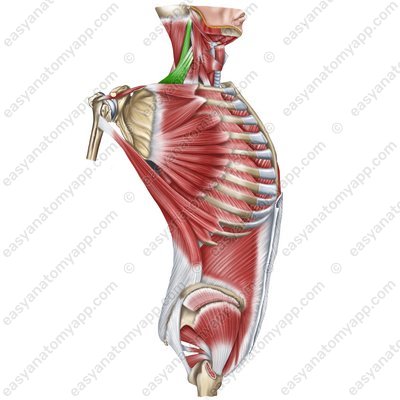
Levator scapulae muscle
(m. levator scapulae)Origin: transverse processes of the C1-C4 vertebrae
Insertion: medial margin of the scapula (between the superior angle and the spine)
Function: pulls the scapula superiorly and medially, shifts the articular cavity inferiorly, tilts the head ipsilaterally
Innervation: anterior branches of the spinal nerves (C3-C4), posterior scapular nerve (C5)
Blood supply: transverse cervical artery, ascending cervical artery
Rhomboid major muscle (m. rhomboideus major)
Rhomboid major muscle (m. rhomboideus major) 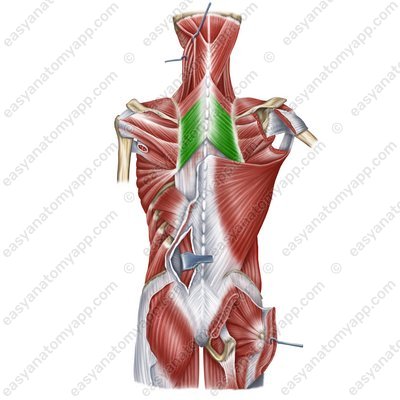
Rhomboid major muscle (m. rhomboideus major) 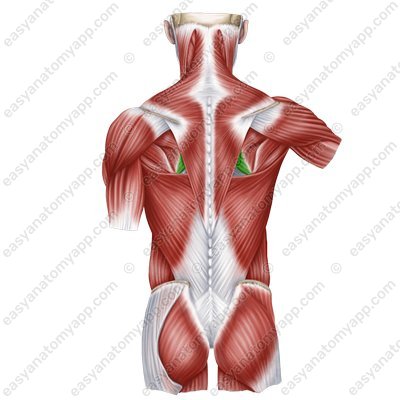
Rhomboid major muscle
(m. rhomboideus major)Origin: spinous processes of the Th2-Th5 vertebrae
Insertion: medial margin of the scapula (between the inferior angle and the spine)
Function: pulls the scapula superiorly and medially, shifts the articular cavity inferiorly
Innervation: posterior nerve of the scapula (C5)
Blood supply: transverse cervical artery, suprascapular, posterior intercostal arteries
Rhomboid minor muscle (m. rhomboideus minor)
Rhomboid minor muscle (m. rhomboideus minor) 
Rhomboid minor muscle
(m. rhomboideus minor)Origin: nuchal ligament, spinous processes of the vertebrae C7-Th1
Insertion: medial margin of the the spine of the scapula and the scapula itself
Function: pulls the scapula superiorly and medially, shifts the articular cavity inferiorly
Innervation: posterior nerve of the scapula (C5)
Blood supply: transverse cervical artery, suprascapular, posterior intercostal arteries
Serratus posterior superior muscle (m. serratus posterior superior)
Serratus posterior superior muscle (m. serratus posterior superior) 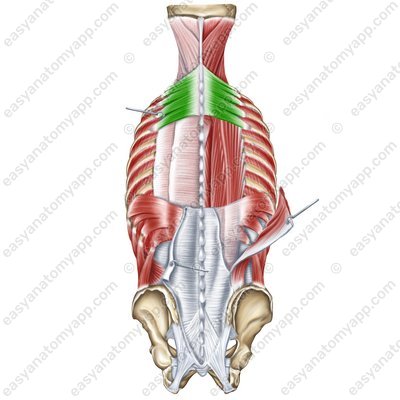
Serratus posterior superior muscle
(m. serratus posterior superior)Origin: spinous ligament, spinous processes of the vertebrae C7-Th3
Insertion: superior margins of the ribs 2-5
Function: lifts the ribs, participates in the act of inhalation
Innervation: 2nd-5th intercostal nerves
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, deep cervical artery
Serratus posterior inferior muscle (m. serratus posterior inferior)
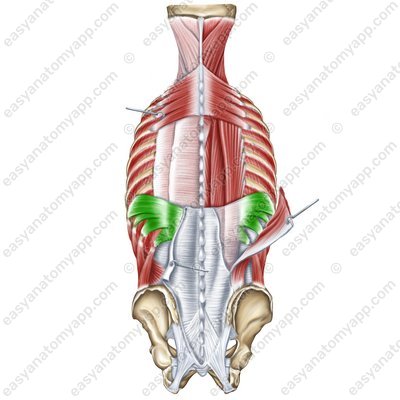
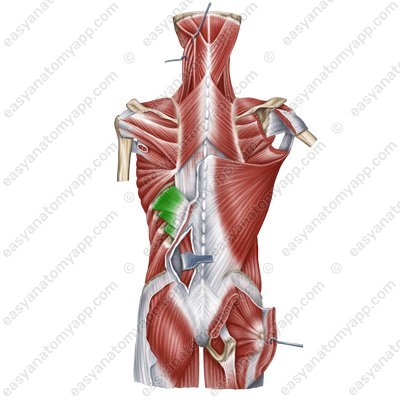
(m. serratus posterior inferior)
Origin: spinous processes of the Th11-L2 vertebrae
Insertion: inferior margins of the ribs 9-12
Function: lowers the ribs
Innervation: anterior branches of the spinal nerves 9-12 (they are also called the 9th-11th intercostal nerves)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries
Extrinsic back muscles
- Trapezius muscle
- m. trapezius
- Latissimus dorsi muscle
- m. latissimus dorsi
- Rhomboid major muscle
- m. rhomboideus major
- Rhomboid minor muscle
- m. rhomboideus minor
- Levator scapulae muscle
- m. levator scapulae
- Serratus posterior superior muscle
- m. serratus posterior superior
- Serratus posterior inferior muscle
- m. serratus posterior inferior


