In addition to the obvious division into superficial and deep groups, muscles of the thorax are also classified depending on their embryological origin.
According to this classification, the following groups are distinguished among the superficial muscles:
Truncofugal muscles have migrated from the trunk to the shoulder girdle. They are innervated by branches of the brachial plexus.
Subclavius muscle (m. subclavius)
Subclavius muscle (m. subclavius) 
Serratus anterior muscle (m. serratus anterior)
Truncopetal muscles migrated from the limbs to the trunk. They are innervated by branches of the brachial plexus.
Pectoralis major muscle (m. pectoralis major)
Pectoralis major muscle (m. pectoralis major) 
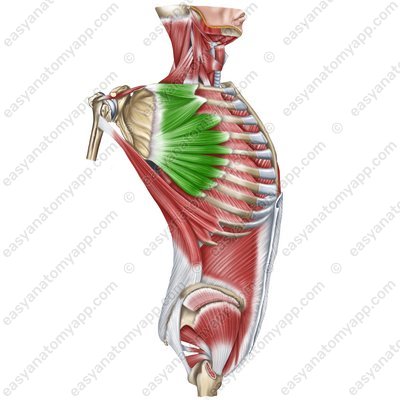
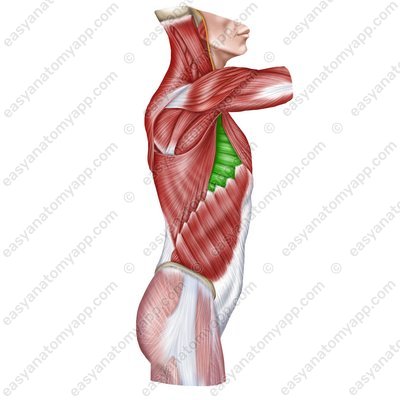
Pectoralis minor muscle (m. pectoralis minor)
Pectoralis minor muscle (m.pectoralis minor) 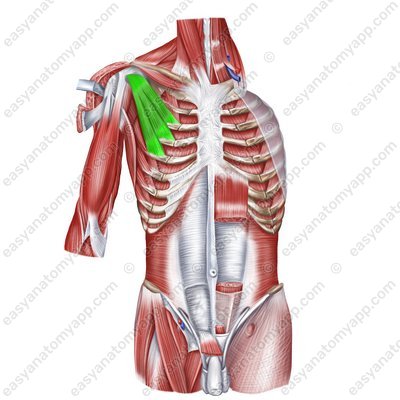
And the deep muscles of the front of the chest have an autochthonous origin. That means that during embryogenesis, they were laid in the region of the front of the chest, and remained there in the postnatal period. This group is innervated by the anterior branches of the spinal nerves, which are also called intercostal nerves. Autochthonous muscles include the following:
External intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales externi)
External intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales externi) 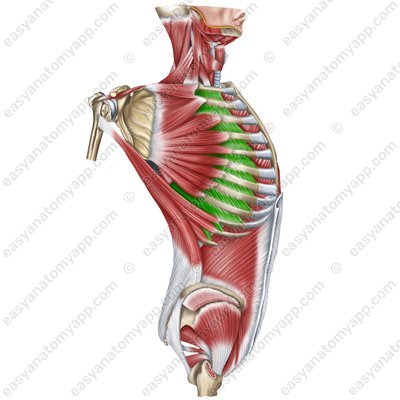
Internal intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales interni)
Internal intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales interni) 
Innermost intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales intimi)
Innermost intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales intimi) 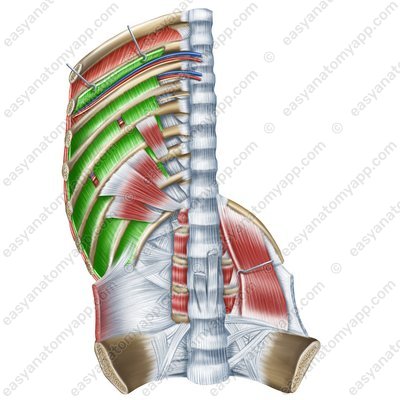
Subcostales muscles (mm. subcostales)
Subcostales muscles (mm. subcostales) 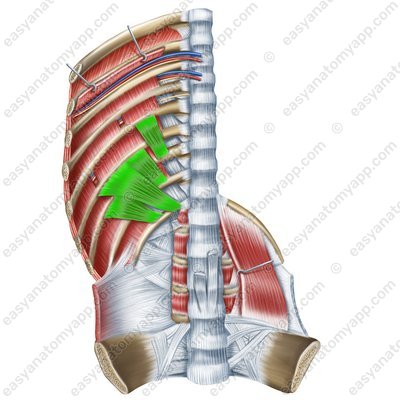
Transversus thoracis muscle (m. transversus thoracis)
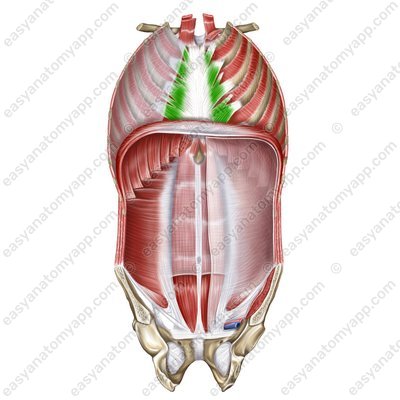
Thoracic muscles
- Pectoralis major muscle
- m. pectoralis major
- Pectoralis minor muscle
- m.pectoralis minor
- Subclavius muscle
- m. subclavius
- Serratus anterior muscle
- m. serratus anterior
- External intercostal muscles
- mm. intercostales externi
- Internal intercostal muscles
- mm. intercostales interni
- Innermost intercostal muscles
- mm. intercostales intimi
- Subcostales muscles
- mm. subcostales
- Transversus thoracis muscle
- m. transversus thoracis


