In the previous pdf-note, we have learned about the superficial muscles of the chest. In this pdf-note, we will learn more about the deep muscles of the chest.
As discussed in the previous pdf-notes, the chest region has the following borders:
The superior border passes through the jugular notch of the sternum, superior border of the clavicle, and acromioclavicular joint
The inferior border passes through the xiphoid process of the sternum and the costal arch
The lateral border is the posterior median line

There are several anatomical regions within the chest:
Mammary region (regio mammaria)
Inframammary region (regio inframammaria)
Sternal region (regio sternalis)
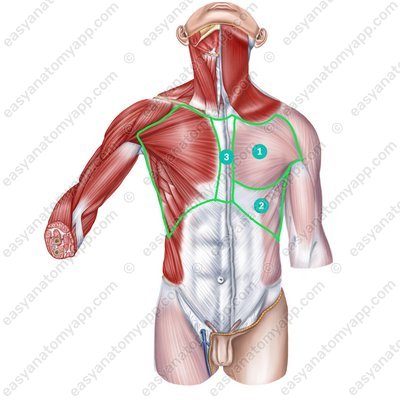
The muscles of the chest are located within these regions. The deep muscles of the chest include:
External intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales externi)
External intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales externi) 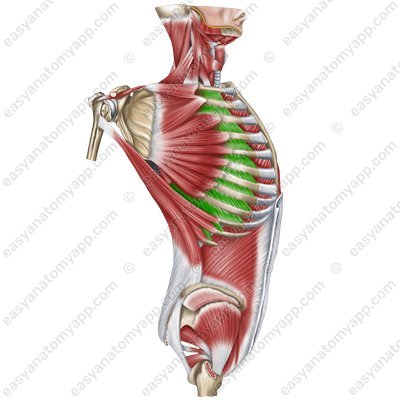
External intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales externi) 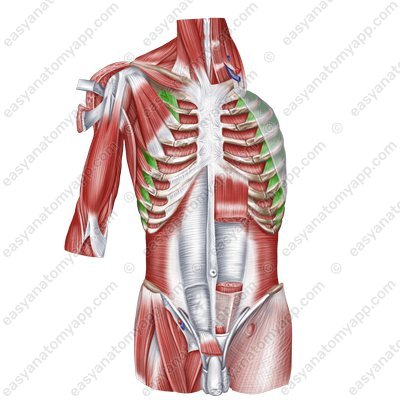
External intercostal muscles
(mm. intercostales externi)Origin: inferior margins of the superposed ribs
Insertion: superior margins of the underlying ribs
Function: lift the ribs during forced inhalation, support the intercostal spaces and thoracic cage
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th1-Th11)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, internal thoracic artery (anterior intercostal branches), musculophrenic artery
Internal intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales interni)
Internal intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales interni) 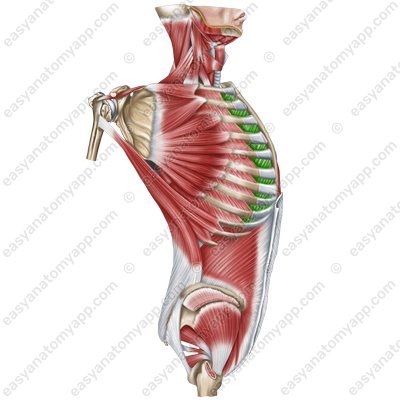
Internal intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales interni) 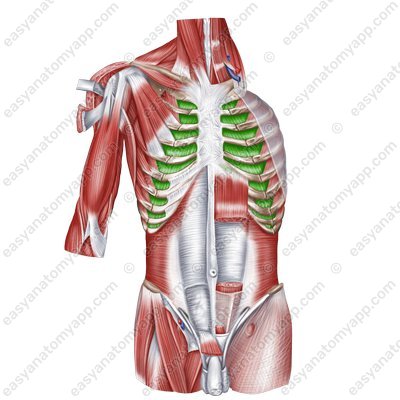
Internal intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales interni) 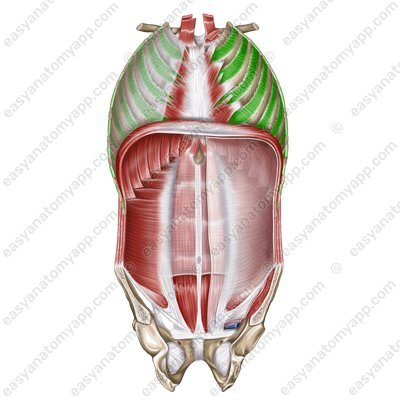
Internal intercostal muscles
(mm. intercostales interni)Origin: superior margins of the underlying ribs
Insertion: inferior margins of the superposed ribs
Function: lower the ribs during forced exhalation, support the intercostal spaces and thoracic cage
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th1-Th11)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, internal thoracic artery (anterior intercostal branches), musculophrenic artery
Innermost intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales intimi)
Innermost intercostal muscles (mm. intercostales intimi) 
Innermost intercostal muscles
(mm. intercostales intimi)Origin: superior margins of the underlying ribs
Insertion: inferior margins of the superposed ribs
Function: ower the ribs during forced exhalation, support the intercostal spaces and thoracic cage
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th1-Th11)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries, internal thoracic artery (anterior intercostal branches), musculophrenic artery
Subcostales muscles (mm. subcostales)
Subcostales muscles (mm. subcostales) 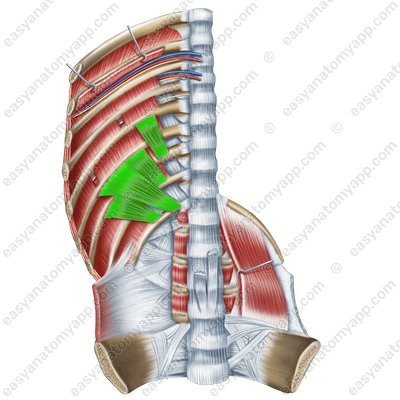
Subcostales muscles
(mm. subcostales)Origin: internal surface of the rib at the angle region
Insertion: internal surface of the superposed ribs (through 1-2-3)
Function: lower the ribs during forced exhalation, support the intercostal spaces and thoracic cage
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th1-Th11)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries
Transversus thoracis muscle (m. transversus thoracis)

(m. transversus thoracis)
Origin: posterior surface of the xiphoid process and the inferior part of the body of the sternum
Insertion: internal surface of the cartilages of the ribs 2-6
Function: lowers the ribs (participates in the act of inhalation)
Innervation: intercostal nerves (Th1-Th6)
Blood supply: internal thoracic artery
Sometimes the muscles of the chest also include the muscles that lift the ribs (mm. levatores costarum). Although according to the embryological classification they fit better into the group of the muscles of the back.
(mm. levatores costarum)
Origin: transverse processes of the C7-Th11 vertebrae
Insertion: superior margins of the underlying ribs
Function: lift the ribs, rotate the thoracic spine
Innervation: intercostal nerves (C3, Th1, Th2, Th6-Th10)
Blood supply: posterior intercostal arteries
Muscles of the thoracic wall
- Mammary region
- regio mammaria
- Inframammary region
- regio inframammaria
- Sternal region
- regio sternalis
- External intercostal muscles
- mm. intercostales externi
- Internal intercostal muscles
- mm. intercostales interni
- Innermost intercostal muscles
- mm. intercostales intimi
- Subcostales muscles
- mm. subcostales
- Transversus thoracis muscle
- m. transversus thoracis
- Levatores costarum muscles
- mm. levatores costarum


