The inguinal canal (canalis inguinalis) is an important topographic structure located in the inferior part of the inguinal region. It is a gap 4-6 cm long, which connects the superficial and deep inguinal rings.
The deep inguinal ring (anulus inguinalis profundus) is located above the middle of the inguinal ligament and corresponds to the location of the lateral inguinal fossa on the internal surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is the site of the formation of oblique inguinal hernias
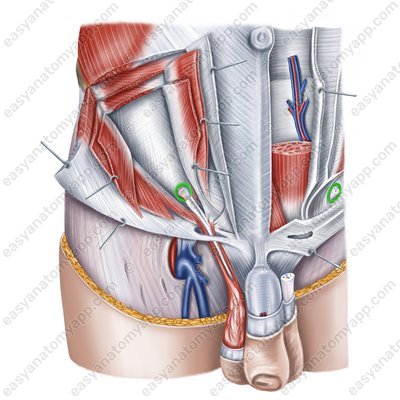
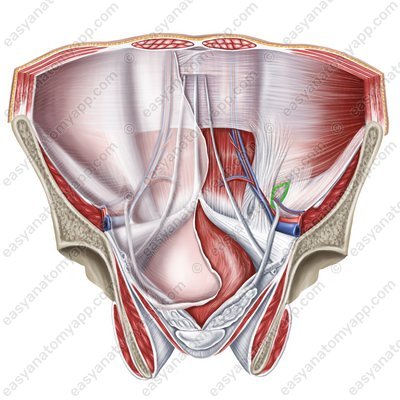
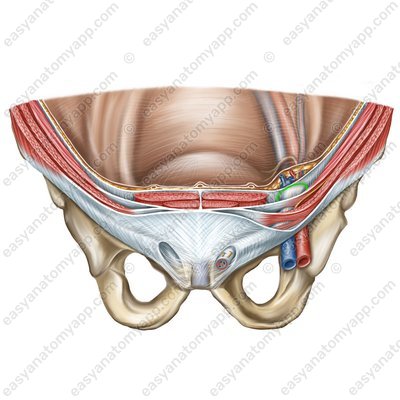
The superficial inguinal ring (anulus inguinalis supeficialis) is located between the lateral and the medial cruses of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. It corresponds to the location of the medial inguinal fossa on the internal surface of the anterior abdominal wall. It is the site of the formation of direct inguinal hernias.
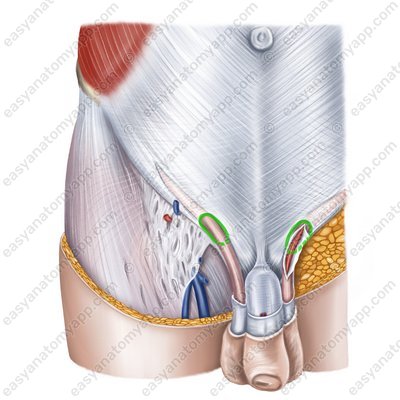
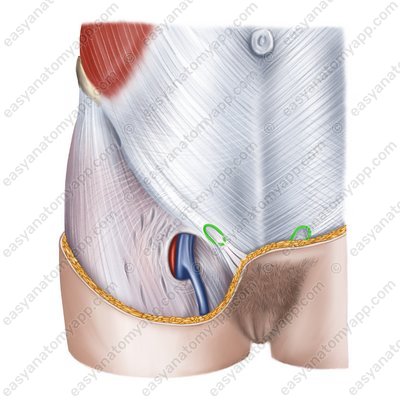
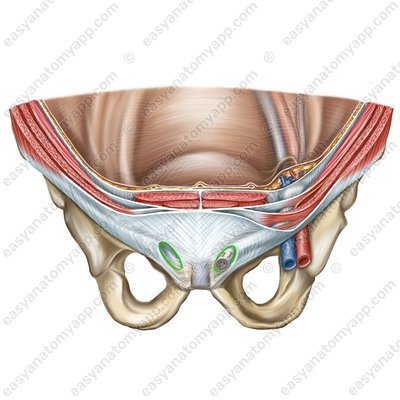
The spermatic cord (in men) and the round ligament of the uterus pass through the inguinal canal. It also contains the ilio-inguinal nerve and the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve.
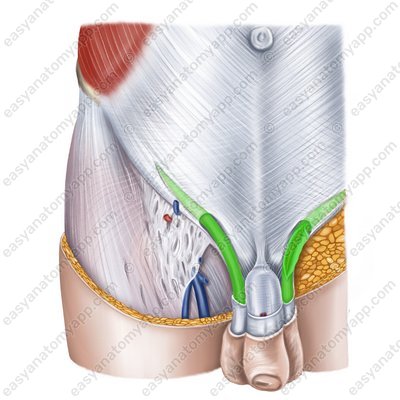
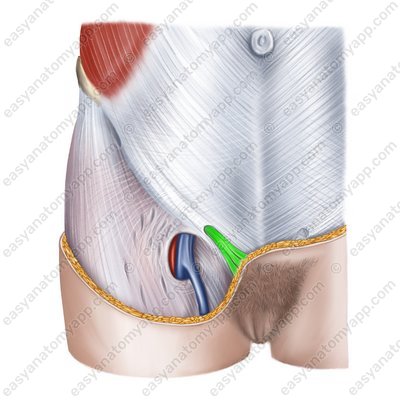
The inguinal canal has 4 walls:
The anterior wall is the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
The posterior wall consists of the transversalis fascia and the parietal peritoneum
The superior wall consists of the inferior fibres of the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles
The inferior wall is the inguinal ligament

Inguinal canal
- Inguinal canal
- canalis inguinalis
- Deep inguinal ring
- anulus inguinalis profundus
- Superficial inguinal ring
- anulus inguinalis supeficialis


